Day6. String Methods - Calculate Special Bonus
Problem
Table: Employees
| Column Name | Type |
|---|---|
| employee_id | int |
| name | varchar |
| salary | int |
employee_id is the primary key (column with unique values) for this table.
Each row of this table indicates the employee ID, employee name, and salary.
Write a solution to calculate the bonus of each employee. The bonus of an employee is 100% of their salary if the ID of the employee is an odd number and the employee's name does not start with the character 'M'. The bonus of an employee is 0 otherwise.
Return the result table ordered by employee_id.
The result format is in the following example.
Example 1:
Input:
Employees table:
| employee_id | name | salary |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Meir | 3000 |
| 3 | Michael | 3800 |
| 7 | Addilyn | 7400 |
| 8 | Juan | 6100 |
| 9 | Kannon | 7700 |
Output:
| employee_id | bonus |
|---|---|
| 2 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 |
| 7 | 7400 |
| 8 | 0 |
| 9 | 7700 |
Explanation:
The employees with IDs 2 and 8 get 0 bonus because they have an even employee_id.
The employee with ID 3 gets 0 bonus because their name starts with 'M'.
The rest of the employees get a 100% bonus.
Solution
# my solution
import pandas as pd
def calculate_special_bonus(employees: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
employees['salary'][(employees['employee_id'] % 2 == 0) | (employees['name'].str[0]=='M')] = 0
employees = employees.rename(columns={'salary': 'bonus'})
employees = employees.sort_values(by=['employee_id'])
return employees[['employee_id', 'bonus']]# check result
data = [[2, 'Meir', 3000], [3, 'Michael', 3800], [7, 'Addilyn', 7400], [8, 'Juan', 6100], [9, 'Kannon', 7700]]
Employees = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['employee_id', 'name', 'salary']).astype({'employee_id':'int64', 'name':'object', 'salary':'int64'})
calculate_special_bonus(Employees)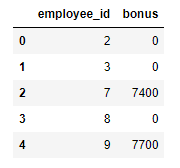
Learn new method
When I checked popular solution, It was a little different from my solution. Today I learn about sort_values method through Pandas API reference.[1] Because I had never used sort_values method, before I solved this problem.
pandas.DataFrame.sort_values
DataFrame.sort_values(by, *, axis=0, ascending=True, inplace=False, kind='quicksort', na_position='last', ignore_index=False, key=None) sort by the values along either axis. To use this method, You have to set parameter by as str or list of str to sort by certain axis. Let's look into some example.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame({
'col1': ['A', 'A', 'B', np.nan, 'D', 'C'],
'col2': [2, 1, 9, 8, 7, 4],
'col3': [0, 1, 9, 4, 2, 3],
'col4': ['a', 'B', 'c', 'D', 'e', 'F']
})
df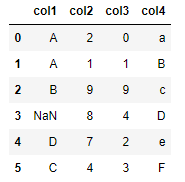
df.sort_values(by=['col1'])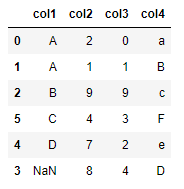
df.sort_values(by='col1', ascending=False, na_position='first')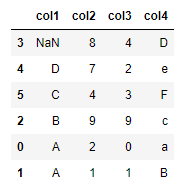 If you check above result, You could know that parameter
If you check above result, You could know that parameter by need to sort by certain axis. In addition, If you use the other parameters, You could set sort option such as sort inverse, etc...
df.sort_values(by=['col1', 'col2'])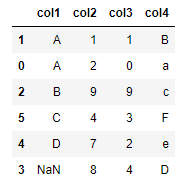 Also, You could sort by many axis.
Also, You could sort by many axis.
reference
Problem
leetcode - 30 Days of Pandas / Calculate Special Bonus [0]
Pandas API reference
pandas.DataFrame.sort_values — pandas 2.0.3 documentation [1]
