Mybatis
MyBatis는 앞서 설명한 JdbcTemplate보다 더 많은 기능을 제공하는 SQL Mapper 이다.
기본적으로 JdbcTemplate이 제공하는 대부분의 기능을 제공한다.
JdbcTemplate과 비교해서 MyBatis의 가장 매력적인 점은 SQL을 XML에 편리하게 작성할 수 있고 또 동적 쿼리를 매우 편리하게 작성할 수 있다는 점이다.
먼저 SQL이 여러줄에 걸쳐 있을 때 둘을 비교해보자.
여러줄 일 때
JdbcTemplate - SQL 여러줄
String sql = "update item " +
"set item_name=:itemName, price=:price, quantity=:quantity " +
"where id=:id"; 그리고 여기서 중요한 것은 항상 문장 끝에 " " 공백문자가 들어있어야 한다는 것이다.
그렇지 않으면 붙어버리기 때문이다.
MyBatis - SQL 여러줄
<update id="update">
update item
set item_name=#{itemName},
price=#{price},
quantity=#{quantity}
where id = #{id}
</update>동적 쿼리
JdbcTemplate - 동적 쿼리
String sql = "select id, item_name, price, quantity from item";
//동적 쿼리
if (StringUtils.hasText(itemName) || maxPrice != null) {
sql += " where";
}
boolean andFlag = false;
if (StringUtils.hasText(itemName)) {
sql += " item_name like concat('%',:itemName,'%')";
andFlag = true;
}
if (maxPrice != null) {
if (andFlag) {
sql += " and";
}
sql += " price <= :maxPrice";
}
log.info("sql={}", sql);
return template.query(sql, param, itemRowMapper()); MyBatis - 동적 쿼리
<select id="findAll" resultType="Item">
select id, item_name, price, quantity
from item
<where>
<if test="itemName != null and itemName != ''">
and item_name like concat('%',#{itemName},'%')
</if>
<if test="maxPrice != null">
and price <= #{maxPrice}
</if>
</where>
</select>JdbcTemplate은 자바 코드로 직접 동적 쿼리를 작성해야 한다. 반면에 MyBatis는 동적 쿼리를 매우 편리하게 작성할 수 있는 다양한 기능들을 제공해준다.
설정의 장단점
JdbcTemplate은 스프링에 내장된 기능이고, 별도의 설정없이 사용할 수 있다는 장점이 있다. 반면에 MyBatis는 약간의 설정이 필요하다.
정리
프로젝트에서 동적 쿼리와 복잡한 쿼리가 많다면 MyBatis를 사용하고, 단순한 쿼리들이 많으면 JdbcTemplate을 선택해서 사용하면 된다. 물론 둘을 함께 사용해도 된다. 하지만 MyBatis를 선택했다면 그것으로 충분할 것이다.
MyBatis Configuration
내가 잘 못 알고 있는 상식이 하나 있었다. 바로 스프링 부트가 모든 의존성을 자동으로 버전관리 해준다는 것이었다.
하지만 이는 스프링이 공식적으로 지원해주는 라이브러리에 한한것이고 나머지는 버전을 명시해줘야한다.
build.gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
//JdbcTemplate 추가
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jdbc'
//MyBatis 스프링 부트 3.0 추가
implementation 'org.mybatis.spring.boot:mybatis-spring-boot-starter:3.0.1'
//H2 데이터베이스 추가
runtimeOnly 'com.h2database:h2'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
//테스트에서 lombok 사용
testCompileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testAnnotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
}application.properties
spring.profiles.active=local
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost/~/test
spring.datasource.username=sa
logging.level.org.springframework.jdbc=debug
#MyBatis
mybatis.type-aliases-package=hello.itemservice.domain
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
logging.level.hello.itemservice.repository.mybatis=tracemybatis.type-aliases-package
마이바티스에서 타입 정보를 사용할 때는 패키지 이름을 적어주어야 하는데, 여기에 명시하면 패키지 이름을 생략할 수 있다.
지정한 패키지와 그 하위 패키지가 자동으로 인식된다.
여러 위치를 지정하려면 , , ; 로 구분하면 된다.
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case
JdbcTemplate의 BeanPropertyRowMapper 에서 처럼 snake_case를 carmelCase로 자동 변경해주는 기능을 활성화 한다.
바로 다음에 설명하는 관례의 불일치 내용을 참고하자.
logging.level.hello.itemservice.repository.mybatis=trace
MyBatis에서 실행되는 쿼리 로그를 확인할 수 있다
MyBatis 작성
xxxMapper interface 작성
@Mapper
public interface ItemMapper {
void save(Item item);
void update(@Param("id") Long id, @Param("updateParam") ItemUpdateDto updateParam);
List<Item> findAll(ItemSearchCond itemSearch);
Optional<Item> findById(Long id);
}마이바티스 매핑 XML을 호출해주는 매퍼 인터페이스이다.
이 인터페이스에는 @Mapper 애노테이션을 붙여주어야 한다. 그래야 MyBatis에서 인식할 수 있다.
이 인터페이스의 메서드를 호출하면 다음에 보이는 xml 의 해당 SQL을 실행하고 결과를 돌려준다.
위 예제 코드의 update() 함수에서 파라미터가 Long id , ItemUpdateDto updateParam 으로 2개이다. 파라미터가 1개만 있으면 @Param 을 지정하지 않아도 되지만, 파라미터가 2개 이상이면 @Param 으로 이름을 지정해서 파라미터를 구분
해야 한다.
자바 코드에서 반환 객체가 하나이면 Item , Optional<Item> 과 같이 사용하면 되고, 반환 객체가 하나 이상
이면 컬렉션을 사용하면 된다. 주로 List 를 사용한다.
xxxMapper.xml 작성
위치에 실행할 SQL이 있는 XML 매핑 파일작성
참고로 자바 코드가 아니기 때문에 src/main/resources 하위에 만들되, 패키지 위치는 맞추어 주어야 한다.
ItemMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="hello.itemservice.repository.mybatis.ItemMapper">
<insert id="save" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into item (item_name, price, quantity)
values (#{itemName}, #{price}, #{quantity})
</insert>
<update id="update">
update item
set item_name=#{updateParam.itemName},
price=#{updateParam.price},
quantity=#{updateParam.quantity}
where id = #{id}
</update>
<select id="findById" resultType="Item">
select id, item_name, price, quantity
from item
where id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="findAll" resultType="Item">
select id, item_name, price, quantity
from item
<where>
<if test="itemName != null and itemName != ''">
and item_name like concat('%',#{itemName},'%')
</if>
<if test="maxPrice != null">
and price <= #{maxPrice}
</if>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>namespace : 앞서 만든 매퍼 인터페이스를 지정하면 된다. 이때 경로와 파일 이름에 주의하면 된다.
-
각 sql 문법 별로 태그를 사용하면 되고 해당 태그의 id 에는 매퍼 인터페이스에 설정한 메서드 이름을 지정하면 된다.
-
파라미터는
#{}문법을 사용하면 된다. 그리고 매퍼에서 넘긴 객체의 프로퍼티 이름을 적어주면 된다. -
#{}문법을 사용하면 PreparedStatement 를 사용한다. JDBC의 sql문 내부의 "?" 를 치환한다 생각하면 된다. -
useGeneratedKeys 는 데이터베이스가 키를 생성해 주는 IDENTITY 전략일 때 사용한다. keyProperty는 생성되는 키의 속성 이름을 지정한다. Insert가 끝나면 item 객체의 id 속성에 생성된 값이 입력된다.
-
resultType 은 반환 타입을 명시하면 된다. 여기서는 결과를 Item 객체에 매핑한다.
-
application.properties 에 mybatis.type-aliasespackage=hello.itemservice.domain 속성을 지정한 덕분에 모든 패키지 명을 다 적지는 않아도된다. 그렇지 않으면 모든 패키지 명을 다 적어야 한다.
JdbcTemplate의 BeanPropertyRowMapper 처럼 SELECT SQL의 결과를 편리하게 객체로 바로 변환해준다. -
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true속성을 지정한 덕분에 언더스코어를 카멜 표기법으로 자동으로 처리해준다. ( item_name itemName ) -
Mybatis는 <where> , <if> 같은 동적 쿼리 문법을 통해 편리한 동적 쿼리를 지원한다.
<if> 는 해당 조건이 만족하면 구문을 추가한다.
<where> 은 적절하게 where 문장을 만들어준다.
예제에서 <if> 가 모두 실패하게 되면 SQL where 를 만들지 않는다.
예제에서 <if> 가 하나라도 성공하면 처음 나타나는 and 를 where 로 변환하여 쿼리상 이상이 없도록 해준다 -
XML 특수문자
<=를 사용하지 않고<=를 사용한 것을 확인할 수 있다. 그 이유는 XML에서는 데이터 영역에<,>같은 특수 문자를 사용할 수 없기 때문이다. 이유는 간단한데, XML에서 TAG가 시작하거나 종료할 때<,>와 같은 특수문자를 사용하기 때문이다.
< : <
> : >
& : &다른 해결 방안으로는 XML에서 지원하는 CDATA 구문 문법을 사용하는 것이다. 이 구문 안에서는 특수문자를 사용할 수 있다. 대신 이 구문 안에서는 XML TAG가 단순 문자로 인식되기 때문에 <if> , <where> 등이 적용되지 않는다
- 참고 - XML 파일 경로 수정하기
XML 파일을 원하는 위치에 두고 싶으면 application.properties 에 다음과 같이 설정하면 된다.
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/**/*.xml
이렇게 하면 resources/mapper 를 포함한 그 하위 폴더에 있는 XML을 XML 매핑 파일로 인식한다. 이 경우
파일 이름은 자유롭게 설정해도 된다.
참고로 테스트의 application.properties 파일도 함께 수정해야 테스트를 실행할 때 인식할 수 있다.
xxxMapper Interface의 구현체 작성
보면 인터페이스를 의존관계로 주입받았는데 이는 아서 Mapper에 @Mapper 어노테이션을 등록을 해두었기 때문에 스프링모듈이 자동으로 인식하여 어떠한 구현체를 만들어내고 이 구현체의 역할은 메서드 이름을 바탕으로 xml을 호출해주는 것이다.
무튼 그 구현체를 스프링 빈으로 등록해주기 때문에 의존성을 주입받을 수 있다.
@Repository
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MyBatisItemRepository implements ItemRepository {
private final ItemMapper itemMapper;
@Override
public Item save(Item item) {
itemMapper.save(item);
return item;
}
@Override
public void update(Long itemId, ItemUpdateDto updateParam) {
itemMapper.update(itemId, updateParam);
}
@Override
public Optional<Item> findById(Long id) {
return itemMapper.findById(id);
}
@Override
public List<Item> findAll(ItemSearchCond cond) {
return itemMapper.findAll(cond);
}
}xxxMapper Config
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MyBatisConfig {
private final ItemMapper itemMapper;
@Bean
public ItemService itemService() {
return new ItemServiceV1(itemRepository());
}
@Bean
public ItemRepository itemRepository() {
return new MyBatisItemRepository(itemMapper);
}
}보면 dataSource를 받는게 아니라 그냥 itemMapper 인터페이스를 받았는데 이는 MyBatis 모듈이 DataSource나 TransactionManager같은 것들을 다 읽어서 해당 @Mapper와 다 연결시켜준다. 그래서 괜찮다.
MyBatis 동작 원리
ItemMapper 매퍼 인터페이스의 구현체가 없는데 어떻게 동작한 것일까?
ItemMapper 인터페이스
@Mapper
public interface ItemMapper {
void save(Item item);
void update(@Param("id") Long id, @Param("updateParam") ItemUpdateDto updateParam);
List<Item> findAll(ItemSearchCond itemSearch);
Optional<Item> findById(Long id);
}이 부분은 MyBatis 스프링 연동 모듈에서 자동으로 처리해주는데 다음과 같다
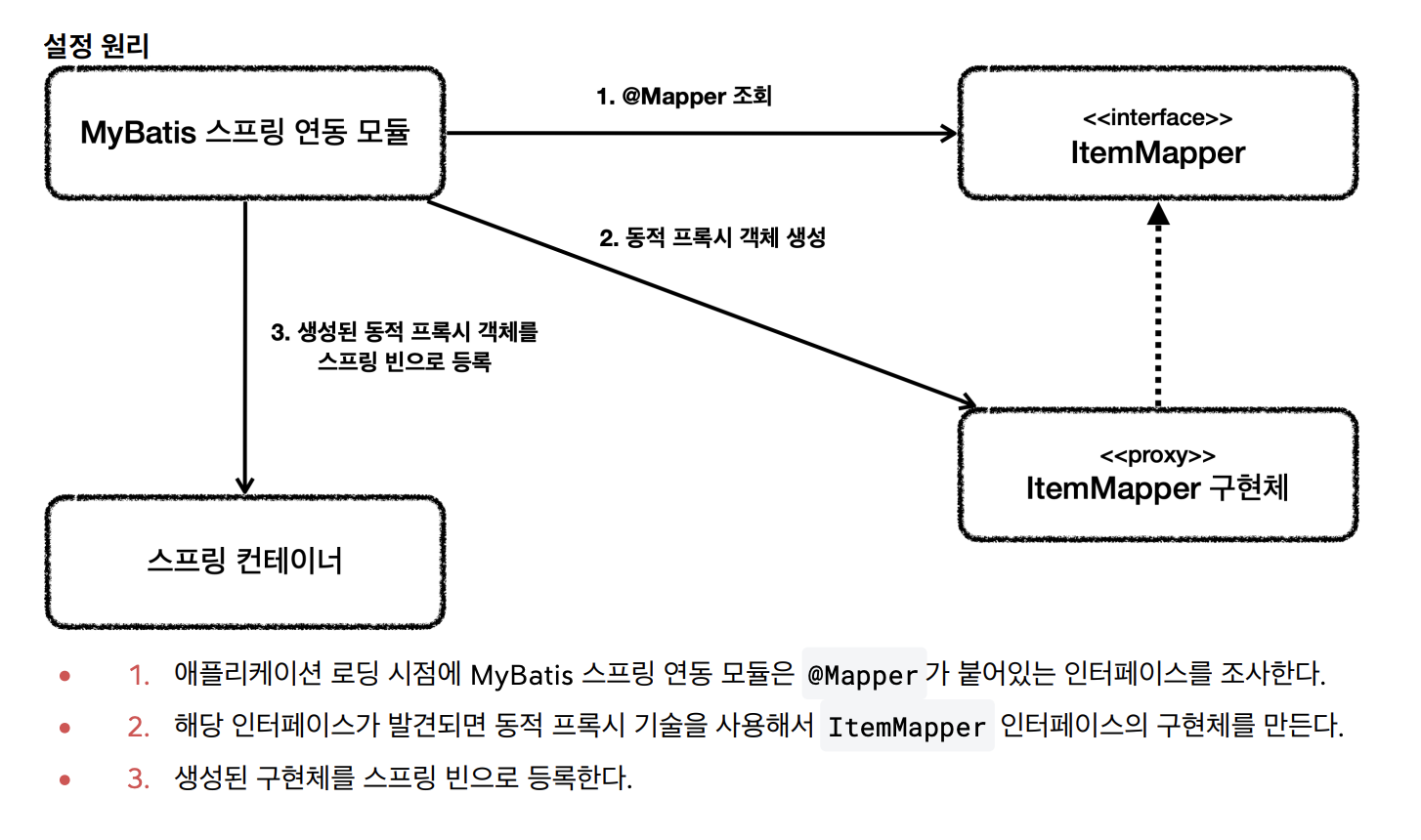
그래서 해당 레포지토리 코드에 로그를 찍어보면  아래와 같이 con.sun.proxy.$Proxy66이 찍히는 걸 볼 수 있다.
아래와 같이 con.sun.proxy.$Proxy66이 찍히는 걸 볼 수 있다.

매퍼 구현체
마이바티스 스프링 연동 모듈이 만들어주는 "ItemMapper 구현체" 덕분에 인터페이스 만으로 편리하게 XML의 데이터를 찾아서 호출할 수 있다.
원래 마이바티스를 사용하려면 더 번잡한 코드를 거쳐야 하는데, 이런 부분을 인터페이스 하나로 매우 깔끔하고 편리하게 사용할 수 있다.
매퍼 구현체는 예외 변환까지 처리해준다. MyBatis에서 발생한 예외를 스프링 예외 추상화인 DataAccessException 에 맞게 변환해서 반환해준다. JdbcTemplate이 제공하는 예외 변환 기능을 여기서도 제공한다고 이해하면 된다.
- 정리
눈에는 보이지 않는 "매퍼 구현체" 덕분에 마이바티스를 스프링에 편리하게 통합해서 사용할 수 있다.
"매퍼 구현체"를 사용하면 스프링 예외 추상화도 함께 적용된다.
마이바티스 스프링 연동 모듈이 많은 부분을 자동으로 설정해주는데, 데이터베이스 커넥션, 트랜잭션과 관련된 기능도 마이바티스와 함께 연동하고, 동기화해준다.
추가로 마이바티스 스프링 연동 모듈이 자동으로 등록해주는 부분은 MybatisAutoConfiguration 클래스 검색하여 한 번 보면 된다.
동적 쿼리
MyBatis 공식 메뉴얼
MyBatis 스프링 공식 메뉴얼
동적 SQL
마이바티스가 제공하는 최고의 기능이자 마이바티스를 사용하는 이유는 바로 동적 SQL 기능 때문이다.
동적 쿼리를 위해 제공되는 기능은 다음과 같다.
if
choose (when, otherwise)
trim (where, set)
foreachif
<select id="findActiveBlogWithTitleLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<if test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</if>
</select> 해당 조건에 따라 값을 추가할지 말지 판단한다.
내부의 문법은 OGNL을 사용한다.
choose, when, otherwise
<select id="findActiveBlogLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND featured = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select> 자바의 switch 구문과 유사한 구문도 사용할 수 있다.
trim, where, set
where
<select id="findActiveBlogLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
<where>
<if test="state != null">
state = #{state}
</if>
<if test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
</if>
</where>
</select>trim
<where> 와 같은 기능을 수행한다.
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR ">
...
</trim>foreach
<select id="selectPostIn" resultType="domain.blog.Post">
SELECT *
FROM POST P
<where>
<foreach item="item" index="index" collection="list"
open="ID in (" separator="," close=")" nullable="true">
#{item}
</foreach>
</where>
</select> 컬렉션을 반복 처리할 때 사용한다. where in (1,2,3,4,5,6) 와 같은 문장을 쉽게 완성할 수 있다.
파라미터로 List 를 전달하면 된다.
참고
동적 쿼리에 대한 자세한 내용은 다음을 참고하자.
https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/ko/dynamic-sql.html
기타 기능
1. 재사용 가능한 SQL 조각
<sql> 을 사용하면 SQL 코드를 재사용 할 수 있다.
 만약 위 사진과 같이 중복되는 부분이 있다면
만약 위 사진과 같이 중복되는 부분이 있다면
<sql id="userColumns"> ${alias}.id,${alias}.username,${alias}.password </sql> 이렇게 따로 떼서
<select id="selectUsers" resultType="map">
select
<include refid="userColumns"><property name="alias" value="t1"/></include>,
<include refid="userColumns"><property name="alias" value="t2"/></include>
from some_table t1
cross join some_table t2
</select> <include> 를 통해서 <sql> 조각을 찾아서 사용할 수 있다.
<sql id="sometable">
${prefix}Table
</sql>
<sql id="someinclude">
from
<include refid="${include_target}"/>
</sql>
<select id="select" resultType="map">
select
field1, field2, field3
<include refid="someinclude">
<property name="prefix" value="Some"/>
<property name="include_target" value="sometable"/>
</include>
</select> 프로퍼티 값을 전달할 수 있고, 해당 값은 내부에서 사용할 수 있다.
2. Result Maps
결과를 매핑할 때 테이블은 user_id 이지만 객체는 id 이다.
이 경우 컬럼명과 객체의 프로퍼티 명이 다르다. 그러면 다음과 같이 별칭( as )을 사용하면 된다.
<select id="selectUsers" resultType="User">
select
user_id as "id",
user_name as "userName",
hashed_password as "hashedPassword"
from some_table
where id = #{id}
</select>별칭을 사용하지 않고도 문제를 해결할 수 있는데, 다음과 같이 resultMap 을 선언해서 사용하면 된다.
<resultMap id="userResultMap" type="User">
<id property="id" column="user_id" />
<result property="username" column="user_name"/>
<result property="password" column="hashed_password"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUsers" resultMap="userResultMap">
select user_id, user_name, hashed_password
from some_table
where id = #{id}
</select> 복잡한 결과매핑
MyBatis도 매우 복잡한 결과에 객체 연관관계를 고려해서 데이터를 조회하는 것이 가능하다.
이때는 <association> , <collection> 등을 사용한다. 이 부분은 성능과 실효성에서 측면에서 많은 고민이 필요하다.
JPA는 객체와 관계형 데이터베이스를 ORM 개념으로 매핑하기 때문에 이런 부분이 자연스럽지만, MyBatis에서는 들어가는 공수도 많고, 성능을 최적화하기도 어렵다. 따라서 해당기능을 사용할 때는 신중하게 사용해야 한다.
해당 기능에 대한 자세한 내용은 공식 메뉴얼을 참고하자.
