Materials
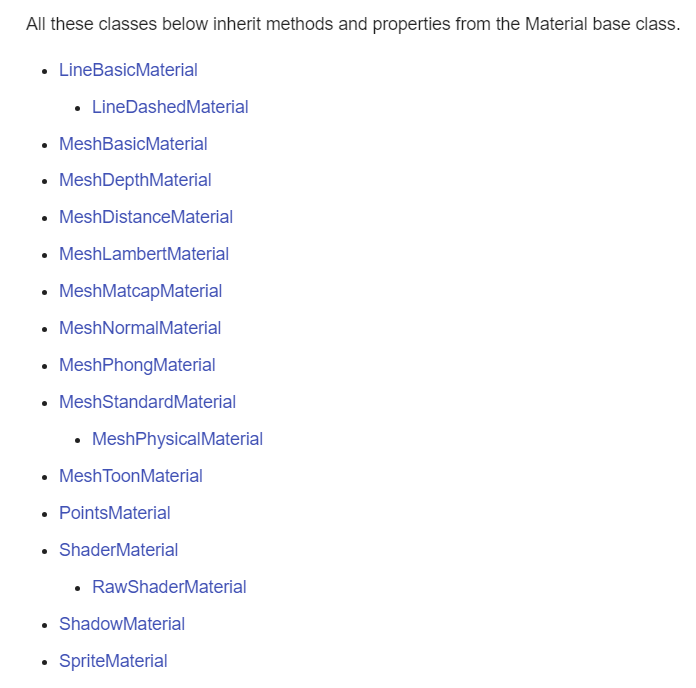
메테리얼의 종류는 굉장히 많다. 그리고 앞서 포스팅한 것과 같이 Material은 Geometry 객채를 만들 때 여러번 재사용이 가능하다고 했었다.
그리고 해당 Material 에 변화를 주면 모든 Geometry 도 함께 변한다고 했었다.
우선 main.ts 는 다음과 같다.
import './style.css'
import * as THREE from 'three'
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js'
import Stats from 'three/addons/libs/stats.module.js'
import { GUI } from 'dat.gui'
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
scene.environment = new THREE.CubeTextureLoader().setPath('https://sbcode.net/img/').load(['px.png', 'nx.png', 'py.png', 'ny.png', 'pz.png', 'nz.png'])
// 엑시즈 헬퍼
const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(5)
scene.add(axesHelper)
// 그리드 헬퍼
const gridHelper = new THREE.GridHelper()
gridHelper.position.y = -1
scene.add(gridHelper)
// 카메라
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000)
camera.position.set(0, 2, 7)
// 렌더러
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true })
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
})
// 컨트롤
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement)
// 카메라에 관성을 부여하여 부드러운 욺직임 추가
controls.enableDamping = true
// 각 지오메트리 생성
const boxGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry()
const sphereGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry()
const icosahedronGeometry = new THREE.IcosahedronGeometry()
const planeGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry()
const torusKnotGeometry = new THREE.TorusKnotGeometry()
// 메테리얼 생성
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial()
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(boxGeometry, material)
cube.position.set(5, 0, 0)
scene.add(cube)
const sphere = new THREE.Mesh(sphereGeometry, material)
sphere.position.set(3, 0, 0)
scene.add(sphere)
const icosahedron = new THREE.Mesh(icosahedronGeometry, material)
icosahedron.position.set(0, 0, 0)
scene.add(icosahedron)
const plane = new THREE.Mesh(planeGeometry, material)
plane.position.set(-2, 0, 0)
scene.add(plane)
const torusKnot = new THREE.Mesh(torusKnotGeometry, material)
torusKnot.position.set(-5, 0, 0)
scene.add(torusKnot)
const stats = new Stats()
document.body.appendChild(stats.dom)
const options = {
side: {
FrontSide: THREE.FrontSide,
BackSide: THREE.BackSide,
DoubleSide: THREE.DoubleSide,
},
}
const gui = new GUI()
const materialFolder = gui.addFolder('THREE.Material')
materialFolder.add(material, 'transparent').onChange(() => (material.needsUpdate = true))
materialFolder.add(material, 'opacity', 0, 1, 0.01)
materialFolder.add(material, 'alphaTest', 0, 1, 0.01).onChange(() => updateMaterial())
materialFolder.add(material, 'visible')
materialFolder.add(material, 'side', options.side).onChange(() => updateMaterial())
materialFolder.open()
function updateMaterial() {
material.side = Number(material.side) as THREE.Side
material.needsUpdate = true
}
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
controls.update()
renderer.render(scene, camera)
stats.update()
}
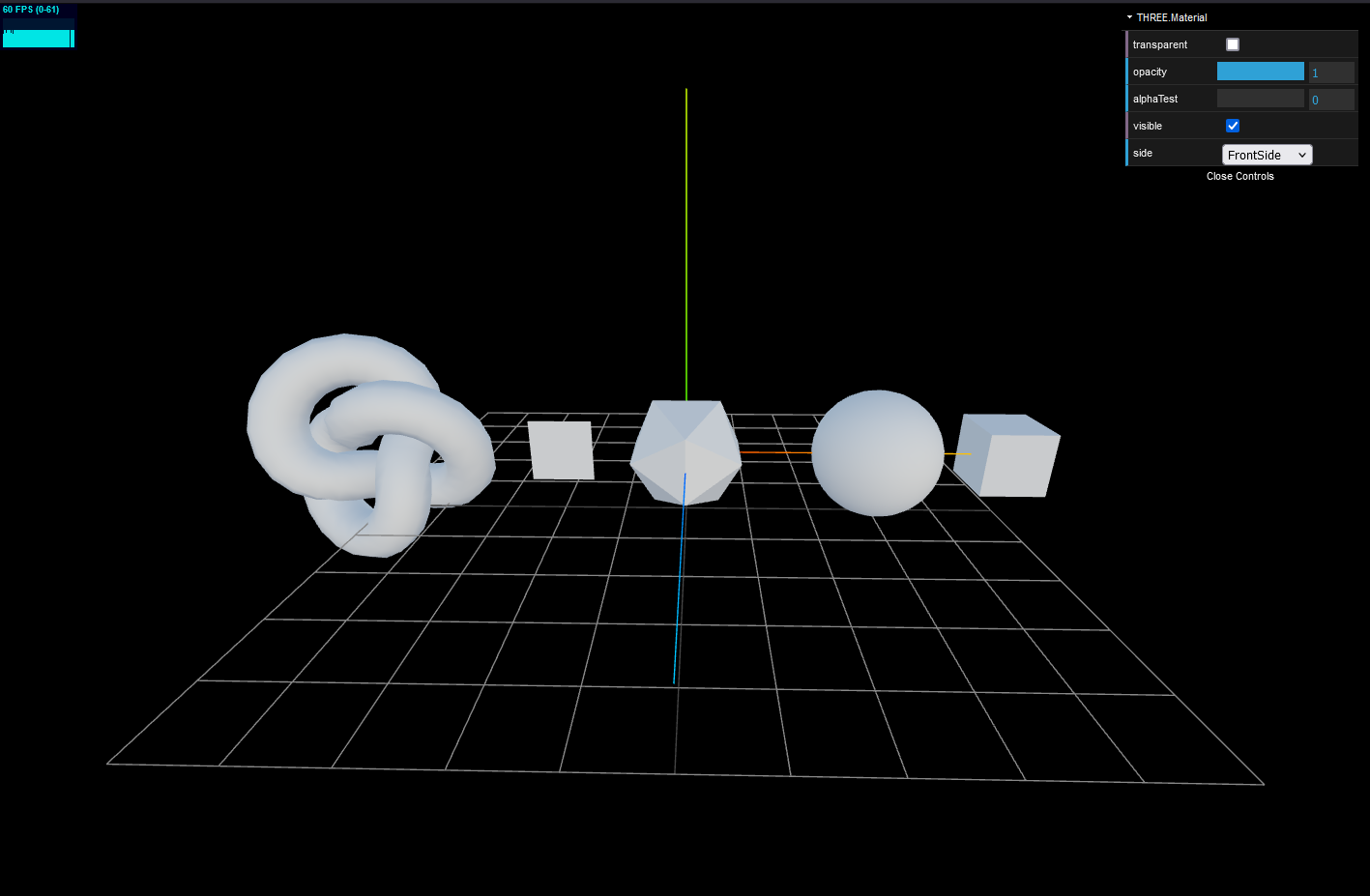
animate()참고로 위 코드에서는 MeshStandardMaterial 를 사용했는데 그냥 Material 는 아무것도 안 보이니 Material 를 구현한 클래스를 사용하도록 하자.
이제 대표적인 Material 몇가지에 대해 알아보자.
MeshStandardMaterial
materialFolder.add(material, 'transparent').onChange(() => (material.needsUpdate = true))
materialFolder.add(material, 'opacity', 0, 1, 0.01)
materialFolder.add(material, 'alphaTest', 0, 1, 0.01).onChange(() => updateMaterial())
materialFolder.add(material, 'visible')
materialFolder.add(material, 'side', options.side).onChange(() => updateMaterial())transparent 는 투명도 설정 여부를 표시한다.
opacity 는 투명도의 강도를 설정하고
alphaTest 값은 해당 값보다 작으면 visible 을 false 로 한다.
visible 은 표출 여부이고
side 는 앞면, 뒷면, 혹은 어느 이중 측면을 표출한다.
function updateMaterial() {
material.side = Number(material.side) as THREE.Side
material.needsUpdate = true
}그리고 반드시 메테리얼에 변경사항이 생겼다면 .needsUpdate() 함수로 업데이트를 해줘야한다.
다만, visibility 나 opacity 는 예외 (안 해줘도 됨.)
Mesh Basic Material
new THREE.Mesh(geometry, new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: data.color })),
const meshBasicMaterialFolder = gui.addFolder('MeshBasicMaterial')
meshBasicMaterialFolder.addColor(data, 'color').onChange(() => {
;(meshes[0].material as THREE.MeshBasicMaterial).color.set(data.color)
})
meshBasicMaterialFolder.add(meshes[0].material, 'wireframe')
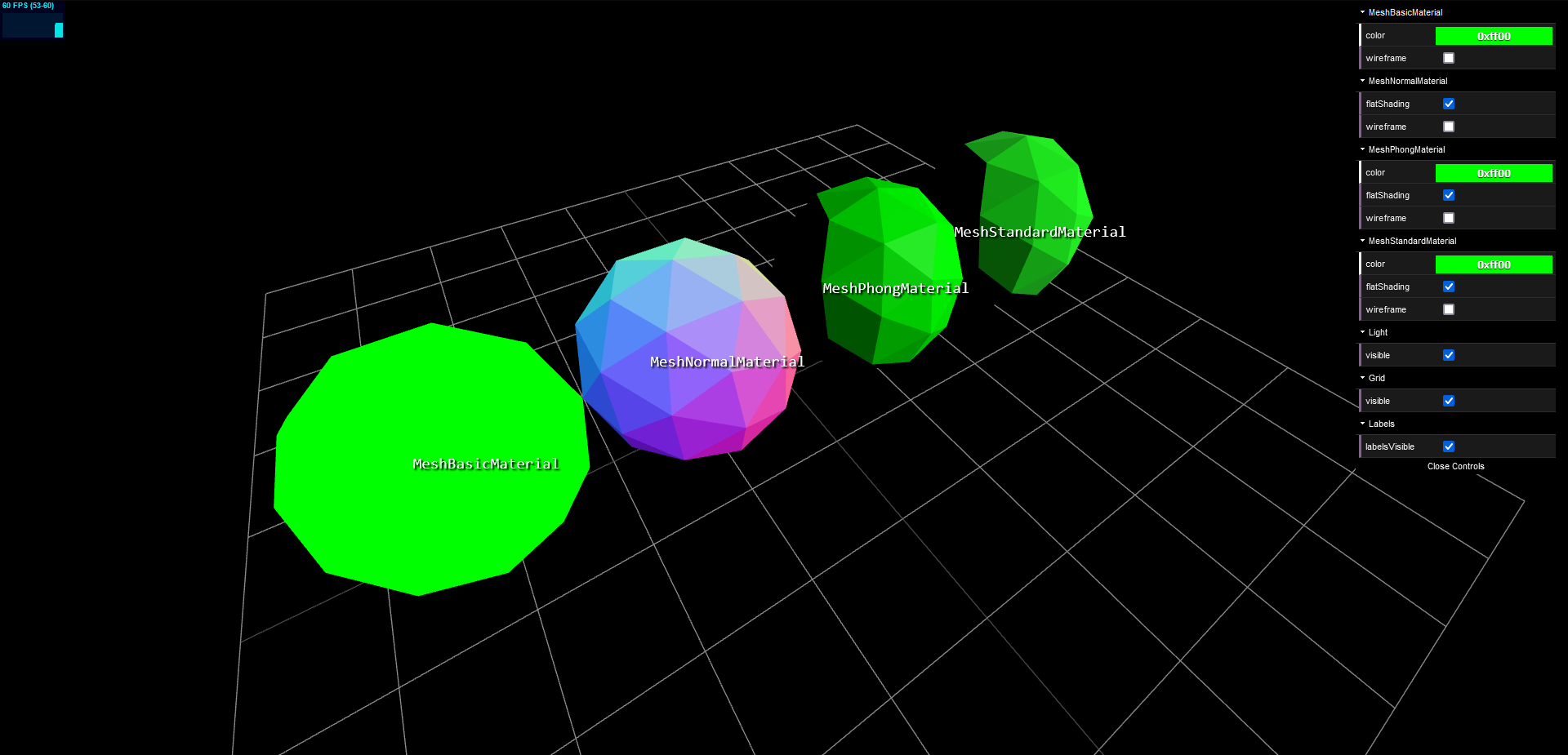
meshBasicMaterialFolder.open()MashBasicMaterial 은 보다싶이 단색이다. 빛의 영향을 받지 않고 무조건 단색으로 표출된다.
Mesh Normal Material
new THREE.Mesh(geometry, new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({ flatShading: true }))
const meshNormalMaterialFolder = gui.addFolder('MeshNormalMaterial')
meshNormalMaterialFolder.add(meshes[1].material as THREE.MeshNormalMaterial, 'flatShading').onChange(() => {
meshes[1].material.needsUpdate = true
})
meshNormalMaterialFolder.add(meshes[1].material, 'wireframe')
meshNormalMaterialFolder.open()MeshNoarmalMaterial 은 light 에 reflection 하지만 카메라 방향에 따라 다르다. 이때, 카메라 상단은 연한 파랑 카메라 하단은 항상 보라색으로 표현된다.
그러면 우리는 카메라 위치를 기준으로 어떤 음영을 넣을지 결정할 수 있다.
이는 소재나 조명을 결정하지 않았을 때 아주 유용한 도구가 될 수 있다.
Mesh Phong Material
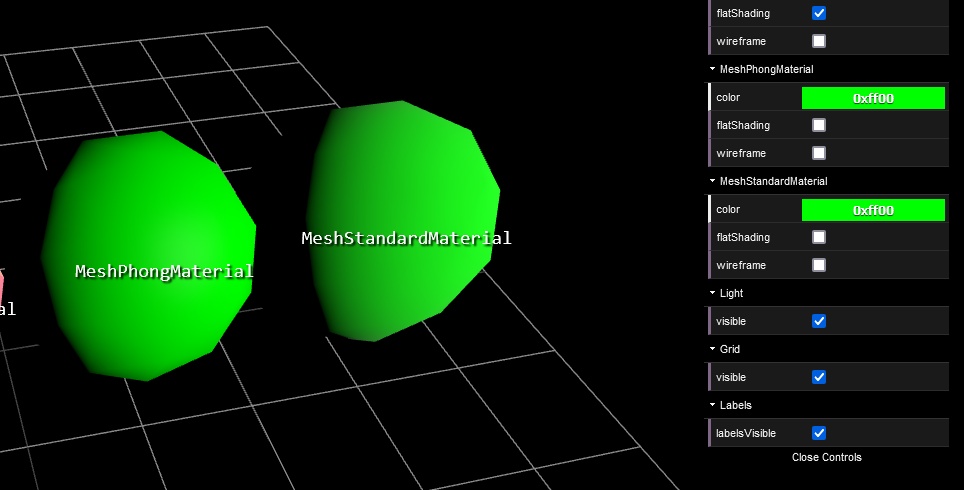
퐁과 스탠다드는 굉장히 비슷하게 생겼다. 사실 동일하다고 봐도 되지만 차이점은 분명 존재한다.
MeshPhongMaterial 은 MeshStandardMaterial 보다 더 render 에 빠른 Material 이다.
하지만 더 Mordern 하고 더 많이 사용되는 것은 MeshStandardMaterial 이다.
Mesh Standard Material
최근 PBR 이 JS 표준이 되면서 결과적으로 MeshStandardMaterial 을 더 많이 사용하게 되었다.
빛이 표면과 상호작용을 하는 방식이 비슷하게 한다는 점에서 Phong 과는 다르다.
그리하여 결과적으로는 Phong 에 비해 더 정확하고 사실적인 결과가 나온다.
대신 Computationally 하게 더 비싸다.
그리고 결과적으로 차이점은 Phong 은 light 가 있어야 visible 하지만 Standard 는 배경이 있어도 보인다.
아래 사진은 Map 을 추가하여 light 를 껐을 때의 결과이다.
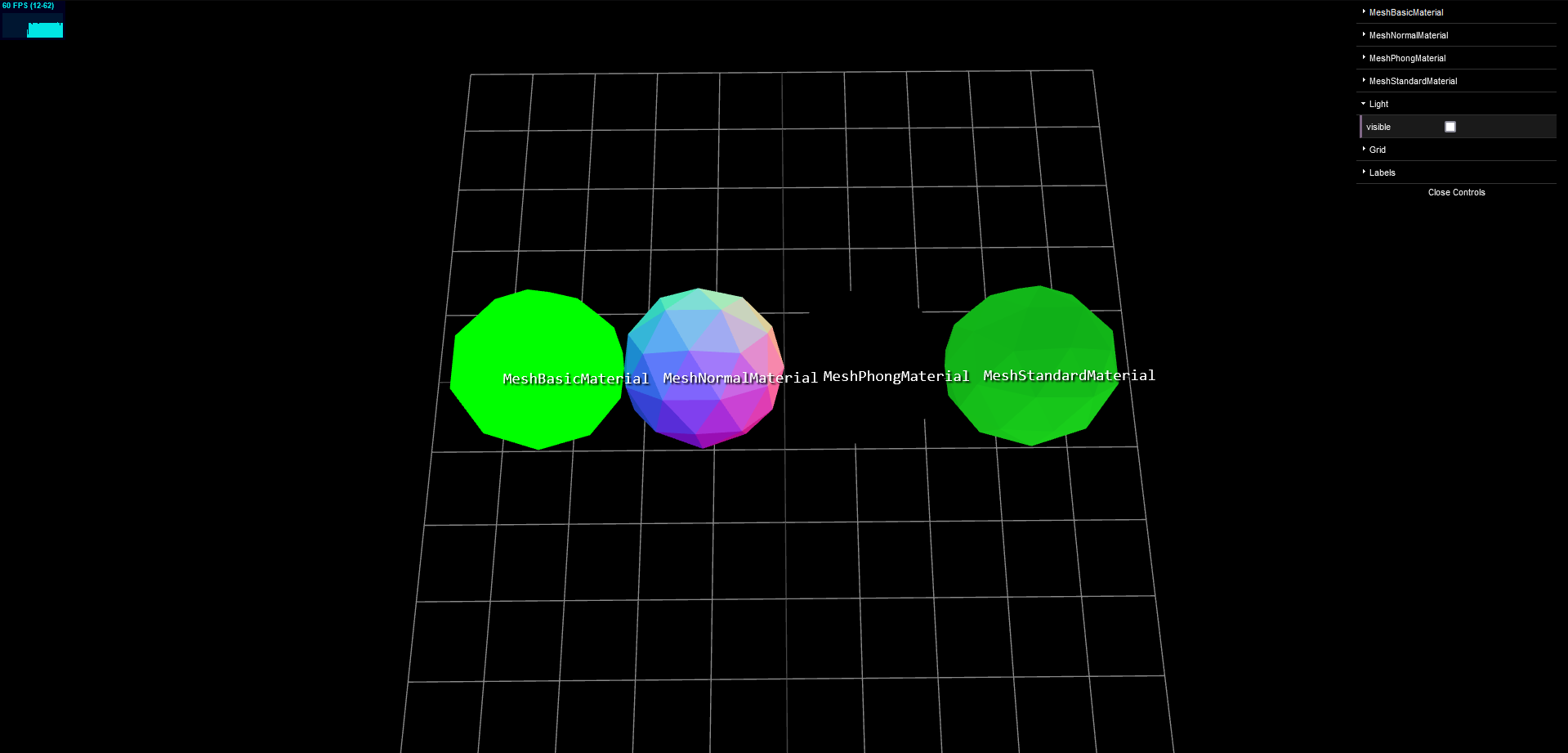
따라서 좋은 environment Map 이 있다면 MeshStandardMaterial 가 훨씬 더 좋은 결과를 낼 것이다.
Material 코드
import './style.css'
import * as THREE from 'three'
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js'
import Stats from 'three/addons/libs/stats.module.js'
import { GUI } from 'dat.gui'
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
scene.environment = new THREE.CubeTextureLoader().setPath('https://sbcode.net/img/').load(['px.png', 'nx.png', 'py.png', 'ny.png', 'pz.png', 'nz.png'])
const gridHelper = new THREE.GridHelper()
scene.add(gridHelper)
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 100)
camera.position.set(-1, 4, 2.5)
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true })
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
})
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement)
controls.enableDamping = true
// 각 Material 의 차이점을 알아보기 위한 조명 추가.
const light = new THREE.DirectionalLight(undefined, Math.PI)
light.position.set(1, 1, 1)
scene.add(light)
const data = { color: 0x00ff00, labelsVisible: true }
const plane = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.PlaneGeometry(10, 10), new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 }))
plane.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2
plane.visible = false
scene.add(plane)
const geometry = new THREE.IcosahedronGeometry(1, 1)
const meshes = [
new THREE.Mesh(geometry, new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: data.color })),
new THREE.Mesh(geometry, new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({ flatShading: true })),
new THREE.Mesh(geometry, new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({ color: data.color, flatShading: true })),
new THREE.Mesh(geometry, new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: data.color, flatShading: true })),
]
meshes[0].position.set(-3, 1, 0)
meshes[1].position.set(-1, 1, 0)
meshes[2].position.set(1, 1, 0)
meshes[3].position.set(3, 1, 0)
scene.add(...meshes)
const stats = new Stats()
document.body.appendChild(stats.dom)
const gui = new GUI()
const meshBasicMaterialFolder = gui.addFolder('MeshBasicMaterial')
meshBasicMaterialFolder.addColor(data, 'color').onChange(() => {
;(meshes[0].material as THREE.MeshBasicMaterial).color.set(data.color)
})
meshBasicMaterialFolder.add(meshes[0].material, 'wireframe')
meshBasicMaterialFolder.open()
const meshNormalMaterialFolder = gui.addFolder('MeshNormalMaterial')
meshNormalMaterialFolder.add(meshes[1].material as THREE.MeshNormalMaterial, 'flatShading').onChange(() => {
meshes[1].material.needsUpdate = true
})
meshNormalMaterialFolder.add(meshes[1].material, 'wireframe')
meshNormalMaterialFolder.open()
const meshPhongMaterialFolder = gui.addFolder('MeshPhongMaterial')
meshPhongMaterialFolder.addColor(data, 'color').onChange(() => {
;(meshes[2].material as THREE.MeshPhongMaterial).color.set(data.color)
})
meshPhongMaterialFolder.add(meshes[2].material as THREE.MeshPhongMaterial, 'flatShading').onChange(() => {
meshes[2].material.needsUpdate = true
})
meshPhongMaterialFolder.add(meshes[2].material, 'wireframe')
meshPhongMaterialFolder.open()
const meshStandardMaterialFolder = gui.addFolder('MeshStandardMaterial')
meshStandardMaterialFolder.addColor(data, 'color').onChange(() => {
;(meshes[3].material as THREE.MeshStandardMaterial).color.set(data.color)
})
meshStandardMaterialFolder.add(meshes[3].material as THREE.MeshStandardMaterial, 'flatShading').onChange(() => {
meshes[3].material.needsUpdate = true
})
meshStandardMaterialFolder.add(meshes[3].material, 'wireframe')
meshStandardMaterialFolder.open()
const lightFolder = gui.addFolder('Light')
lightFolder.add(light, 'visible')
lightFolder.open()
const gridFolder = gui.addFolder('Grid')
gridFolder.add(gridHelper, 'visible')
gridFolder.open()
const labelsFolder = gui.addFolder('Labels')
labelsFolder.add(data, 'labelsVisible')
labelsFolder.open()
const labels = document.querySelectorAll<HTMLDivElement>('.label')
let x, y
const v = new THREE.Vector3()
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
controls.update()
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
v.copy(meshes[i].position)
v.project(camera)
x = ((1 + v.x) / 2) * innerWidth - 50
y = ((1 - v.y) / 2) * innerHeight
labels[i].style.left = x + 'px'
labels[i].style.top = y + 'px'
labels[i].style.display = data.labelsVisible ? 'block' : 'none'
}
renderer.render(scene, camera)
stats.update()
}
animate()