lombok 설치
sudo java -jar lombok.jarbin 폴더 보이게 하기
... > filters and customizations
decompiler 설치
help > eclipse user storage > open marketplace
Java 삭제
https://namocom.tistory.com/705
sudo rm -rf openjdk-20.0.2Java 환경변수 재설정
https://jsikim1.tistory.com/23
https://hymndev.tistory.com/5
이클립스 빌드하기
프로젝트 우클릭 > properties > libraries > classpath > add external jars > lombok.jar 파일 선택 > apply and close
롬복 오류 해결완료 ㅠㅜㅜㅜㅠㅜㅠㅜ
환경변수는 자바 20버전이고 롬복은 18버전이라 호환이 맞지 않아 발생한 오류였다...
시스템 재부팅을 하면 자꾸 환경변수가 20버전으로 되돌아가서 아예 20버전을 삭제하고 자바 환경변수를 17버전으로 바꿔주니 해결됐다.
3장. 연산자
- 산술연산
- 관계연산
- 논리연산
- 10진수
- 2진수
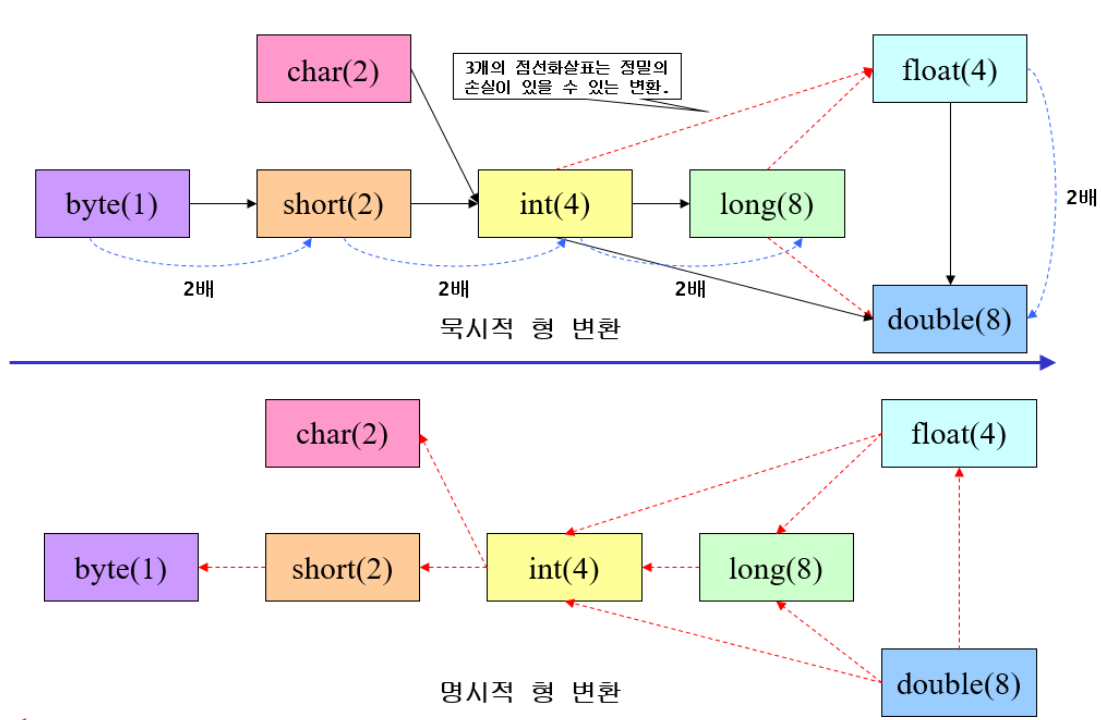
형 변환
묵시적 형 변환: 넓은쪽 -> 좁은쪽 (float -> int)
명시적 형 변환: 좁은쪽 -> 넓은쪽 (int -> float)
OpTest1.java
package basic;
public class OpTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=7, b=4;
System.out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + (a + b));
System.out.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + (a - b));
System.out.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + (a * b));
System.out.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + (a / b));
System.out.println(a + "%" + b + "=" + (a % b));
}
}
OpTest2.java
package basic;
public class OpTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 7, b = 4;
System.out.println();
}
}
OpTest3.java
package basic;
public class OpTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(true && true);
System.out.println(true && false);
System.out.println(false && false);
System.out.println(true || true);
System.out.println(true || false);
System.out.println(false || false);
}
}
OpTest4.java
package basic;
public class OpTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10; //
int b = 4;
System.out.print(a & b);
}
}
OpTest5.java
package basic;
public class OpTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 5;
i++;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
OpTest6.java
package basic;
public class OpTest6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double seed_money = 1_000_000;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
seed_money = seed_money + (seed_money/2 * 0.4);
seed_money = seed_money - (seed_money/2 * 0.3);
System.out.println(seed_money);
}
}
}
OpTest7.java
package basic;
public class OpTest7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 7;
int t = 4;
t += a + 3; // t += (a + 3)
// t = t + (a + 3);
System.out.println(a + "," + t);
}
}
OpTest10.java
package basic;
public class OpTest10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
a += 2; // a = a + 2;
System.out.println(a);
a -= 2; // a = a - 2;
System.out.println(a);
a *= 2; // a = a * 2;
System.out.println(a);
a /= 2; // a = a / 2;
System.out.println(a);
a %= 2; // a = a % 2;
System.out.println(a);
}
}
OpTest12.java
package basic;
public class OpTest12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 2;
System.out.print(n == 1 ? "남자" :
n == 2 ? "여자" :
n == 3 ? "남자" :
n == 4 ? "여자" :
"에러");
}
}
OpTest13.java
package basic;
public class OpTest13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 23;
// n이 양수인지 음수인지 판별
System.out.print(n > 0 ? "양수" : n < 0 ? "음수" : "양수도 음수도 아님");
System.out.print(n % 2 == 1 ? "홀수" : "짝수");
}
}
OpTest14.java
package basic;
public class OpTest14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double n = 10; // 묵시적 형변환 (자동 형변환)
System.out.println(n);
int p = (int) 3.14; //명시적 형변환 (강제 형변)
}
}
OpTest15.java
package basic;
public class OpTest15 {
public static void man(String[] args) {
// Math.random = 0~0.9999999999999
// 1~6 사이의 난수 발생
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*6)+1);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*6)+1);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*6)+1);
// Q. 4~15사이의 정수 난수 발생
// 4 5 6 7 8 9
// 10 11 12 13 14 15
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*12)+4);
// Q. 반드시 아래 숫자로만 난수 발생
// 600 700 800 900 1000
// 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500
// 1600 1700 1800 1900 2000
// 2100 2200 2300
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*18+6)*100);
}
}
PrimitiveTypeTest.java
package basic;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class PrimitiveTypeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b = true;
System.out.println(b);
byte b2 = 127; // 127을 넘 숫자는 byte에서 사용할 수 없다.
System.out.println(b2);
char c = '뷁';
System.out.println(c);
char 뷁 = '헐';
System.out.println(뷁);
short s = 32767;
System.out.println(s);
int i = 2147483647 + 1;
System.out.println(i);
long l1 = 2147483648L;
System.out.println(l1);
double p = 3.1415926535;
System.out.println(p);
float p2 = 3.1415926535f;
System.out.println(p2);
System.out.println(2 - 1.1);
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal("2");
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("1.1");
System.out.println(bd1.subtract(bd2));
// double p1 =
}
}
4장. 제어문과 제어 키워드
제어문
조건문
- if, switch
IfTest1.java
package control;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int score = 90;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("0~100사이의 점수를 입력 > ");
int score = sc.nextInt();
if (90 <= score && score <= 100) System.out.println("A");
else if (80 <= score && score < 90) System.out.println("B");
else if (70 <= score && score < 80) System.out.println("C");
else if (60 <= score && score < 70) System.out.println("D");
else System.out.println("F");
System.out.println(String.valueOf("hi"));
}
}
SwitchTest1.java
package control;
public class SwitchTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 2;
switch (n) {
case 1:
System.out.println("남");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("여");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("남");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("여");
break;
default:
System.out.print("에러");
break;
}
}
}
SwitchTest2.java
package control;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("0~100사이의 점수를 입력 > ");
int score = sc.nextInt();
switch (score / 10) {
// case 10:
// System.out.println("A");
// break;
case 10, 9:
System.out.println("A");
break;
case 8:
System.out.println("B");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("C");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("D");
break;
default:
System.out.print("F");
break;
}
}
}
반복문
- for, while
- do~while
- 조건식이 참이면 다시 do 구문을 실행하고, 거짓이면 제어문을 탈출한다.
ForTest1.java
package control;
public class ForTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i=1; i<=3 ; i++ ) {
System.out.println(i + ":황수연");
}
System.out.println("종료");
for (int i=10; i<=30 ; i+=10 ) {
System.out.println(i + ":김기훈");
}
System.out.println("종료");
}
}ForTest2.java
package control;
public class ForTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1부터 1000까지 3의 배수의 정수의 합계
int a = 0;
for (int i=1; i<=1000 ; i++ ) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
a += i;
}
a += i;
}
System.out.println(a);
for (int i=3; i<=1000 ; i+=3 ) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
a += i;
}
a += i;
}
System.out.println(a);
}
}
ForTest3.java
package control;
public class ForTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=2; i<=9; i+=4) {
for(int j=1; j<=9; j++) {
for (int k=0; k<=3; k++) {
System.out.print((i+k)+"*"+j+"="+((i+k)*j)+"\t");
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
}
}WhileTest1.java
package control;
public class WhileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0;
while (a<=3) {
System.out.println(a + ":황수연");
a++;
}
System.out.println("종료");
int b = 0;
while (b<=30){
System.out.println(b + ":김기훈");
b+=10;
}
System.out.println("종료");
}
}
WhileTest2.java
package control;
public class WhileTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1부터 1000까지 3의 배수의 정수의 합계
int a = 0;
int sum = 0;
while(a<=1000) {
if (a % 3 == 0) {
sum += a;
}
sum += a;
a++;
}
System.out.println(sum);
int b = 0;
sum = 0;
while(b<=1000) {
if (b % 3 == 0) {
sum += b;
}
sum += b;
b+=3;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
WhileTest3.java
package control;
public class WhileTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 2;
while(a <= 9) {
int b = 1;
while(b <= 9) {
int c = 0;
while(c <= 3) {
System.out.print((a+c)+"*"+b+"="+((a+c)*b)+"\t");
c++;
}
System.out.println("\n");
b++;
}
System.out.println("\n");
a += 4;
}
}
}
DoWhiletest1.java
package control;
public class DoWhiletest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
do {
System.out.println(i * 10 + ":황수연");
i++;
} while (i<=3);
System.out.println();
}
}
DoWhiletest2.java
package control;
public class DoWhiletest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int dice1, dice2;
dice1 = (int)(Math.random() * 6)+1;
do {
dice2 = (int)(Math.random() * 6)+1;
} while (dice1 == dice2);
System.out.println(dice1 + "," + dice2);
}
}
NumberGame.java
package control;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NumberGame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int s, b, count = 0;
int c1, c2, c3;
int h1, h2, h3;
c1 = (int)(Math.random()*10);
do {
c2 = (int)(Math.random()*10);
} while (c2 == c1);
do {
c3 = (int)(Math.random()*10);
} while(c3 == c2 || c3 == c1);
do {
System.out.print("0~9사이의 중복되지 않은 숫자 3개 입력 (ex.1 2 3) > ");
s = b = 0;
h1 = sc.nextInt();
h2 = sc.nextInt();
h3 = sc.nextInt();
if(h1 == c1) s++;
else if(h1 == c2 || h1 == c3) b++;
if (h2 == c2) s++;
else if(h2 == c1 || h2 == c3) b++;
if (h3 == c3) s++;
else if(h3 == c1 || h3 == c2) b++;
System.out.println("[" + s + "S " + b + "B]");
count++;
} while(s != 3);
System.out.println("축하합니다." + count + "번 만에 맞추셨습니다.");
}
}
기타제어문
- continue, break, return
