앙상블 기법
- 여러 개의 모델을 조합하여, 하나의 모델보다 더 좋은 예측 성능을 내는 방법
특징
- 서로 다른 관점(모델)을 결합함으로써 오류를 줄일 수 있음
- 개별 모델의 편향(Bias)과 분산(Variance) 상호 보완
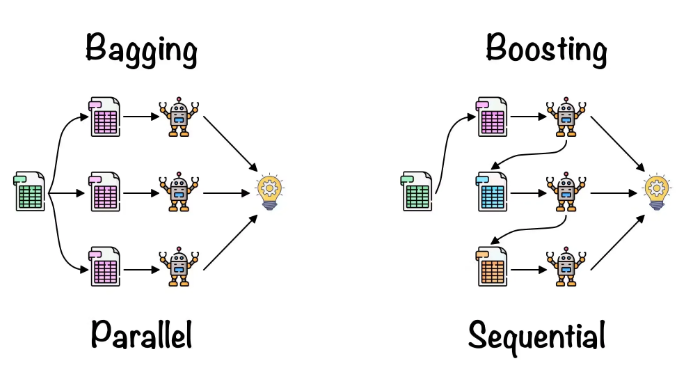
배깅(Bagging, Bootstrap Aggregating)
원리
- 학습 데이터를 무작위로 여러 부분 샘플(부트스트랩)로 나누어 각각 독립적으로 모델을 학습
- 예측 시에는 여러 모델의 결과를 평균(회귀) 혹은 다수결(분류)로 결정
예시
-
랜덤 포레스트 -> 분류, 회귀 모두 가능
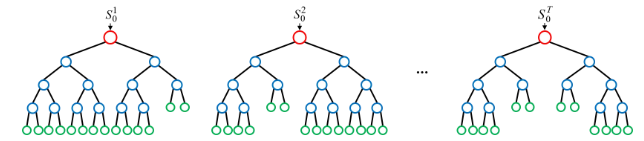
-
결정 트리 여러 개를 만들 때, 각 트리에 사용하는 피처와 데이터 샘플을 무작위로 선택
(피처 샘플링 + 데이터 샘플링)
장점
- 각 모델이 독립적으로 학습하므로 병렬 처리 가능(학습 속도가 상대적으로 빠름)
- 모델 간 상호 간섭이 적어 안정적
- 과적합을 줄여주는 효과 (예측의 분산 감소)
단점
- 많은 수의 모델을 학습해야 하므로 메모리 사용량이 많아질 수 있음
- 해석이 어려움
랜덤포레스트 코드 예시
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
# 1. 데이터 로드
data = load_breast_cancer()
X = data.data
y = data.target
# 2. 학습/테스트 분할
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=42,
stratify=y
)
# 3. 랜덤 포레스트 모델 생성
# n_estimators는 사용할 트리의 개수, max_depth는 각 트리의 최대 깊이를 의미하며
# 위 2개의 값을 높일 수록 시간과 연산량은 늘어나지만 더욱 복잡한 특징을 잡을 수 있음
rf_model = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=100,
max_depth=None,
random_state=42
)
# 4. 모델 학습
rf_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 5. 예측
y_pred = rf_model.predict(X_test)
# 6. 성능 평가
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {acc:.4f}")
print("Confusion Matrix:\n", cm)
print("Classification Report:\n", report)부스팅(Boosting)
- 순차적으로 모델을 학습하면서 이전 모델이 만든 오류를 보정하도록 설계
- 각각의 모델은 이전 모델이 틀린 부분에 가중치를 더 둬서 학습
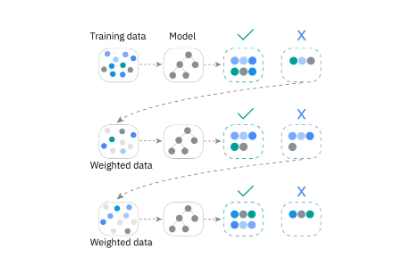
대표적인 알고리즘 - 분류, 회귀 모두 가능
- XGBoost(Extreme Gradient Boosting)
- LightGBM
- CatBoost
장점
- 높은 정확도 달성 가능
- 각 단계에서의 오류를 보정하기 때문에, 복잡한 데이터 패턴을 잘 포착
단점
- 순차적으로 학습하므로 병렬화가 쉽지 않음
- 하이퍼파라미터가 많고 튜닝이 까다로움

촙촙촙 츄파춥스하고갑니다