아주대학교 김상훈 교수님의 운영체제 강의와 강의 자료를 바탕으로 작성된 글입니다.
What is Process Scheduling?
-
Runnig multiple processes on multiple processors
-
What if we have only one processors?
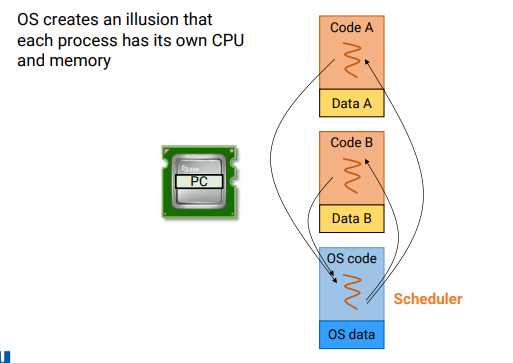
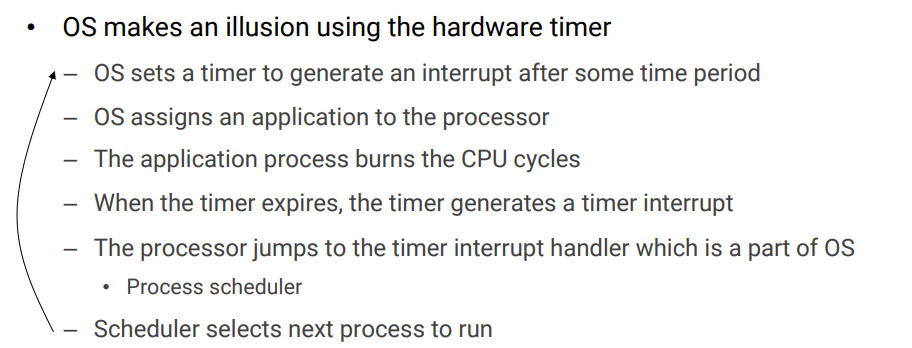
-> OS creates an illusion that each process has its own CPU and memory
-> 즉, A가 돌다가 timer interrupt 터지면 timer handler로 jump함. handler code 실행하다 보면 scheduler 코드로 와서 다른 process 돌릴 수 있게 됨
Process Scheduling
- Goal: Quickly switch processes onto CPU
- 실행 중인 process가 I/O를 기다릴 때 CPU는 idle한 상태가 됨
- CPU의 idle 상태를 방지하고자 여러 process를 바꾸며 실행시키는 게 process scheduling임
- Process scheduler selects a process among available processes for next execution on CPU
- Learning process scheduling means to learn;
- How to switch between processes
- How to find/manage available processes for scheduling
- ready process를 어떻게 찾을까
- 어떤 process를 복원할지
- 복원할 process는 어디서부터 실행해야 하는지
- How to select next process to run
- ready 상태의 process 중 어떤 process를 뽑는 게 최선일까?
Parallelism vs Concurrency
CPU가 2개 있어서 여러 process가 동시에 실행되는 경우가 있을 것이고, CPU 1개에서 여러 process가 번갈아 실행되는 경우가 있을 것이다. 거시적으로 봤을 때는 여러 process가 동시에 실행되는 것처럼 보이지만, 이걸 좀 더 세부적으로 구별할 필요가 있다.
- Parallelism
- Imply a system that can perform more than one task simultaneously
- 여러 명이 각자의 삽을 들고 각자의 구덩이를 파는 것
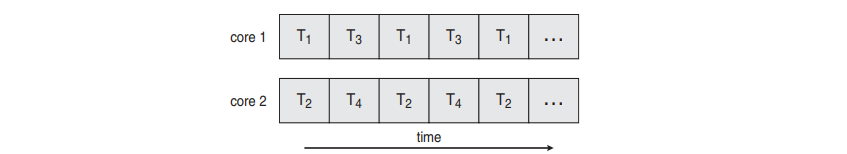
- Concurrency
- Support more than one task making progress
- 여러 명이 한 개의 삽을 돌아가며 쓰면서 각자의 구덩이를 파는 것
- Concurrency는 parallelism 없이 제공이 가능하다.
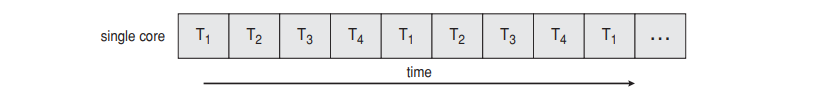
Time Sharing in Modern OSes
Mechanism vs. Policy
-
Mechanism
- How to do something?
- process간 전환을 어떻게 할 것인가?
- It refers to the process, methods, or tools used to achieve a particular task
- How to do something?
-
Policy
- What should be done?
- What is the next process to run?
- system은 중요 작업을 비중요 작업보다 우선해야 한다.
- It defines the rules, objectives, or guidelines that describe what actions or outcomes are desired.
- What should be done?
Policy는 바뀔 수 있지만 Mechanism은 좀 general하게 되어 있다. 따라서 잘 만들어진 Mechanism은 policy가 바뀌어도 잘 바뀌지 않는다.
Context Switch
-
When CPU switches to another process, the system must save the state of the current process and load the state of the next process
-
Context of a process is represented in the PCB
- PCB: Process Control Block
- Each PCB represents a process
-
Context-switch time is overhead
- The system does no useful work while switching
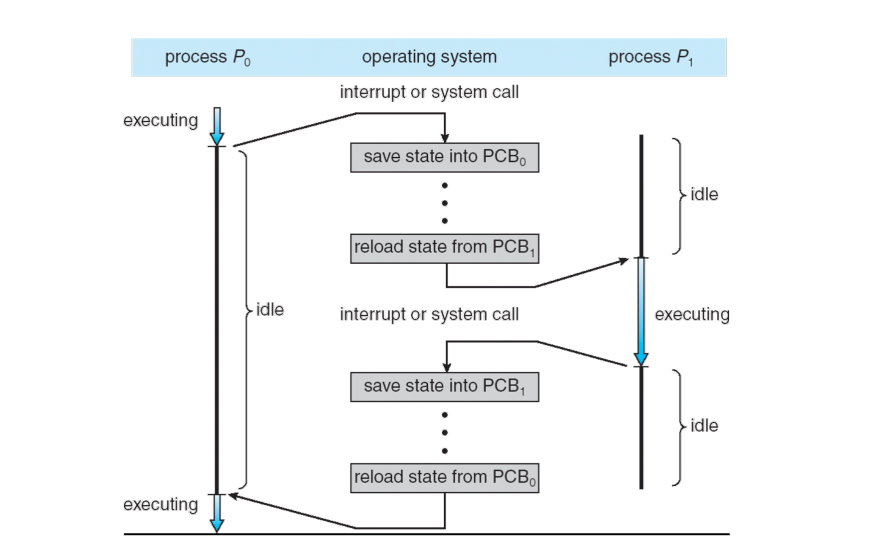
1. P0가 실행되다가 context out 되어 PCB0에 저장된다.
2. PCB1로부터 P1의 상태를 복원한다. P1은 context in 된다.
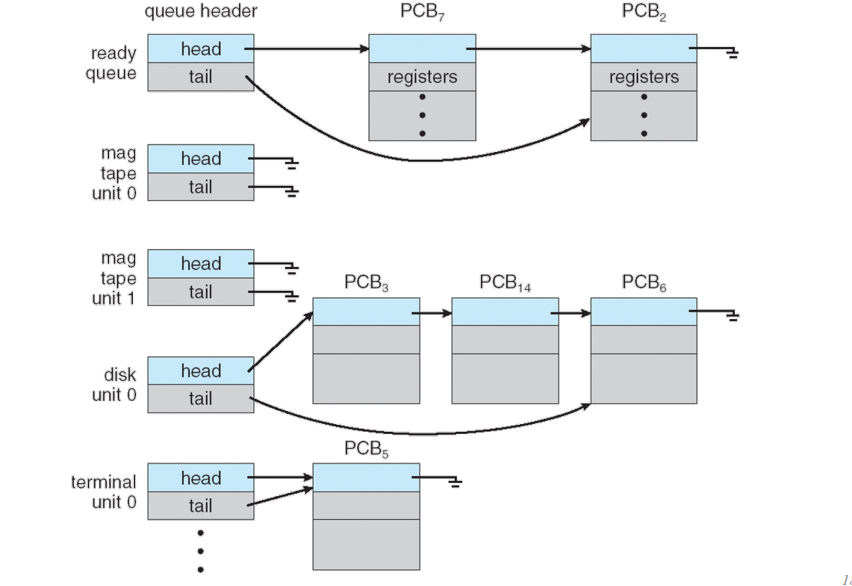
Scheduling Queues
-
A를 wait 하는 process B는 A의 wait list에 추가된다.
- 보통 wait 할 수 있는 대상에는 wait list가 각각 있다.
(각자 wait하는 대상이 다른 processes을 하나의 linked list로 관리하면 특정 process를 찾는 과정이 번거롭기 때문이다.)
- 보통 wait 할 수 있는 대상에는 wait list가 각각 있다.
-
예시
- 디스크를 기다리는 process는 디스크의 wait list에 추가된다.
-> interrupt가 터지면 그 process는 ready list에 추가된다. - A process가 B process에 대해 waitpid를 걸면 B process의 wait list에 A가 추가된다.
-> B가 terminate 되면 OS가 작업을 수행하고 B의 wait list를 살펴본다.
-> OS는 A process의 존재를 확인하고, B의 종료값과 종료 상태를 전달한 다음, A를 ready list에 추가한다.
- 디스크를 기다리는 process는 디스크의 wait list에 추가된다.