아주대학교 김상훈 교수님의 운영체제 강의와 강의 자료를 바탕으로 작성된 글입니다.
Scheduling Criteria
Scheduling Algorithms들을 평가할 때는 어떤 게 어떤 것보다 더 낫다 이 정도로는 부족하다. 어떤 AL이 어떤 AL보다 어떤 방면에서 더 낫다 이런 식으로 평가할 줄 알아야 한다.
- CPU utilization (want to maximize)
- Throughput (want to maximize)
- num of processes that complete their execution per time unit
- Turnaround time (want to minimize)
- Amount of time to finish executing a particular process
- ready queue에 있던 시간 + 처리된 시간
- Waiting time (want to minimize)
- Amount of time a process has been waiting in the ready queue
- ready queue에 있던 시간
- Average Waiting time: (process가 ready queue에 있던 시간) / 총 process 수
- Response time (want to minimize)
- From when a job is arrived to when it starts to serve the job
- ready된 시점부터 최초로 schedule 될 때까지의 시간
Preemptive Scheduling
- Non-preemptive scheduling
- The scheduler waits for the running job to volutarily yield the CPU
- Preemptive scheduling
- The sheduler can interrupt a job and force a context switch
Starvation
- A situation where a job is prevented from making progress because another jobs keep holding a resource it requires
- process는 이미 ready 상태이지만 계속 schedule 될 시간이 확정되지 않는 상태이다.
FCFS(First-Come, First-Served)/FIFO
- Jobs are scheduled in order that they arrive
- Typically, non-preemptive
- No starvation
- Problems: Convoy effect
- processing time이 오래 걸리는 process를 먼저 처리하면서 전반적인 turnaround/waiting time도 증가하는 현상이다.
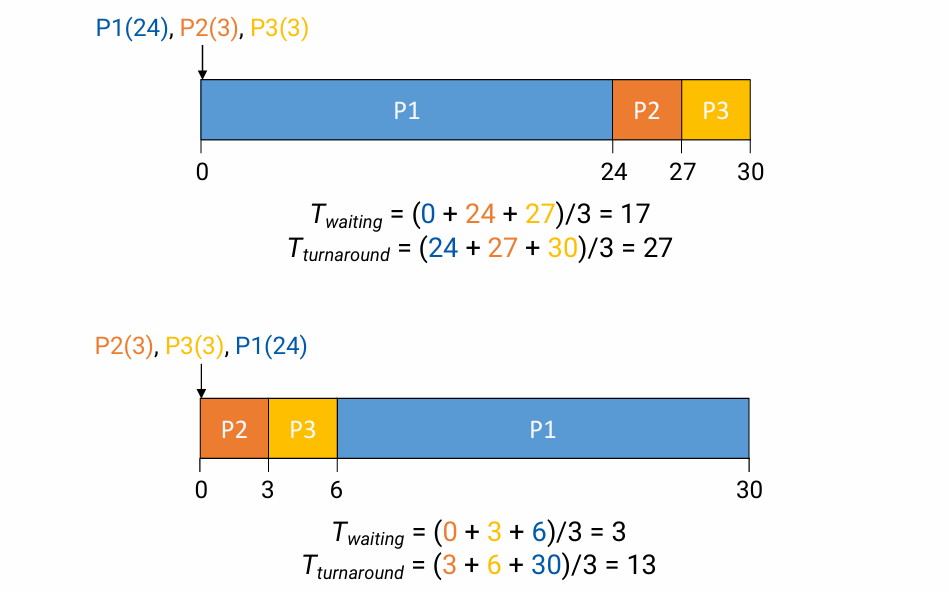
processing time이 짧은 process를 먼저 처리했을 때, waiting time과 turnaround time도 짧아지는 것을 알 수 있다.
SJF(Shortest Job First)
- Choose the job with the smallest expected CPU burst
- Gurantee the minimum average waiting time
- Non-preemptive
- potentially starve
- Priority Scheduling
- priority = the inverse of predicted next CPU burst time
- Problems: Impossible to know the size of future CPU burst
- 현재 시점에서는 미래 정보인 process의 processing time을 정확히 알 수 있는 방법이 없음
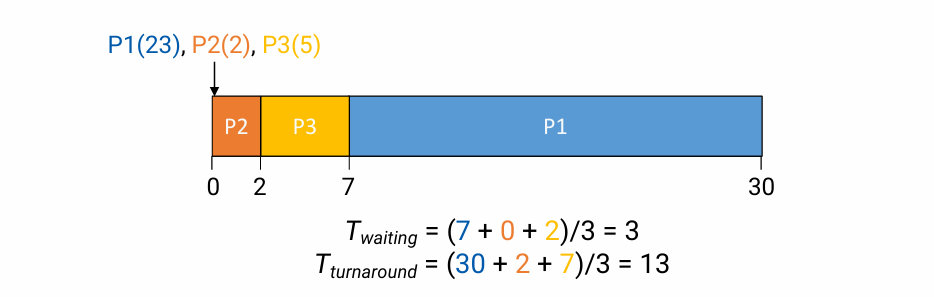
SJF 배울 때 헷갈렸던 게, 제일 빨리 끝나는 process를 먼저 처리하는 것 맞지만, 그 비교군에 현재 실행 중인 process는 포함되지 않는다는 것이다. 지금 실행 중인 애는 끝날 때까지 CPU를 사용할 수 있게 보장해 준다.
STCF(Shortest Time-to-Completion First)
- A preemptive version of SJF
- 현재 처리하고 있는 process를 포함한 기존에 있던 process와 새로 들어온 process 중 run time이 가장 짧은 process를 먼저 처리하는 방식이다.
- preemptive
- starvation
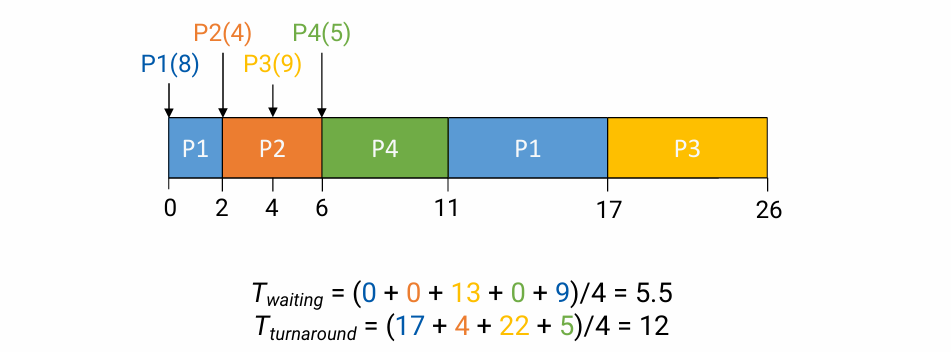
RR(Roud Robin)
- Each job is given a time slice(variable) ( or shceduling quantum(constant) )
- Run a job for a time slice and then switches to the next job in the run queue
- Multiple of the time-interrupt period or the timer tick
- Too SHORT -> higher context switch overhead
- Too LONG -> less responsive
- RR은 빠른 response time(내 response time = quantum * 앞에 있는 process)이 보장된 AL인데, 이 장점이 사라져 버린다.
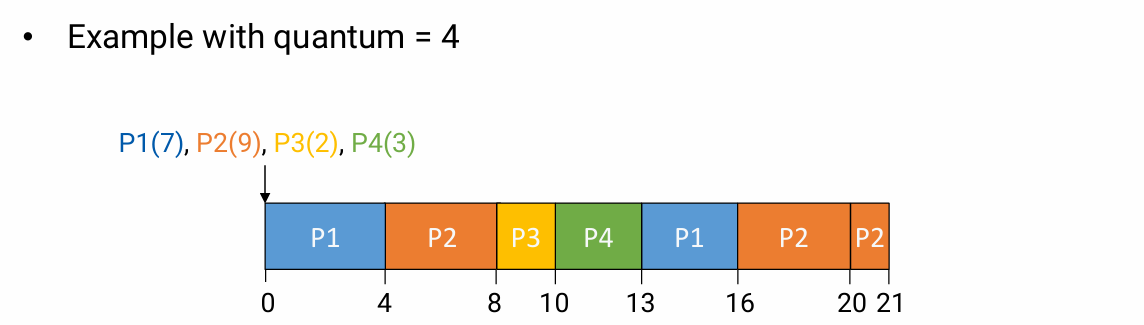
- Preemptive
- No starvation
- Problem: Waiting time
- 위 예시에서, P1이 처음 scheduling 되고 그 뒤에 30개의 process가 있다고 해 보자. 이 경우, P1의 연산이 제일 먼저 실행됐지만, 끝나기까지 굉장히 오랜 시간이 걸릴 수 있다.
Priority Scheduling
-
Each job has a priority
-
CPU is allocated to the job with the highest priority
(priority를 숫자로 부여할 경우, 높은 숫자가 priority가 높은 건지, 낮은 숫자가 priority가 높은 건지 정의해야 함, 아래 예시에서는 숫자가 낮을수록 priority가 높은 거임.) -
can be preemptive(e.g., STCF) or non-preemptive(e.g., SJF)
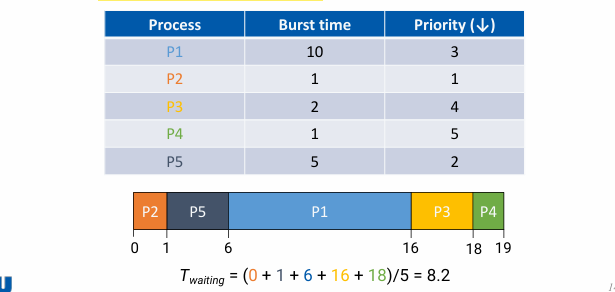
-
Problem: Starvation
- low priority processes may never execute if there is an endless supply of high priority jobs
- Solution: Aging or priority boosting
- Aging: ready 상태의 process을 기다리는 시간을 고려하여 priority를 높여 주는 방식
- Priority boosting: 임의의 process의 priority를 높여 주는 방식
-
Problem: Priority Inversion
- 가정: Priority schedule + non-sharable resource + preemptive schedule + more than 3 processes
- a low-priority task holds the unsharable resource
- a high-priority task needs that resource as well
- blocked until the low-priority task releases the required resource
- an intermediate-priority task becomes ready to run
- Effectivey, the intermediate-priority task indirectly preempts the high-priority task
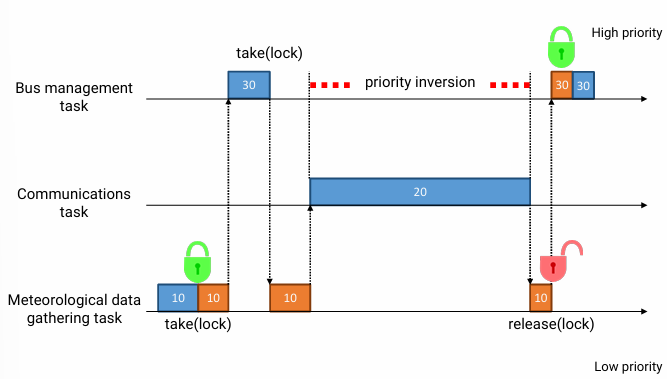 위 사진에서 Priority schedule + non-sharable resource + preemptive schedule + more than 3 processes를 가정했을 때,
위 사진에서 Priority schedule + non-sharable resource + preemptive schedule + more than 3 processes를 가정했을 때,
- 1. priority 10인 M(Meteorological data gathering task)이 unsharable resource에 lock을 검
- 2. M보단 늦게 들어온 priority 30인 B(Bus management task)가 unsharable resource를 쓰려고 함. 그러나 해당 resource는 lock 걸린 상태라 사용 X
- 3. 따라서 M이 resource를 계속 쓰고 있다가 priority가 20인 C(Communications task)가 들어옴
- 4. C는 M보다 priority가 높아 CPU를 preempt 함. C가 계속 CPU를 쓸 동안 C보다 priority가 높은 B도 실행되지 않음. (M이 resource에 대한 lock를 풀지 않았기 때문)
- 5. 즉, low priority가 잡고 있는 non sharable resource 때문에 high-priority task가 indirectly delayed 되는 상황을 priority inversion이라고 한다.
Solution for Priority Inversion
resource contending : resource 1개를 여러 process가 이용하려고 하는 상황
resource contention
In computing, 'resource contention' refers to a conflict over a shared resource between several components.
https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/resource-contention
- Priority inheritance protocol (PIP)
- The higher-priority job donates its priority to the lower-priority job holding the resource it requires
- Should be set to the original priority once it releases the resource
- resource가 필요할 때 자신의 priority를 donate 하므로 코드가 복잡해질 수 있으나, contending 자체가 많이 안 일어나므로 그 코드는 많이 안 불릴 것임. 따라서 효율이 좋다.
- Priority ceiling protocol (PCP)
- The priority of the low-priority thread is raised immediately when it gets the resource
- The priority ceiling value must be predetermined
- 구현은 쉽다. 그러나 resource contending이 자주 발생하는 현상이 아님에도, 항상 resource를 잡은 process의 priority를 boosting 해 주는 것은 computing power를 낭비하는 것임. 또 resource가 여러 개일 때도 문제가 됨.
추가 내용
priority inversion의 정의를 찾아보면 medium-priority process의 언급 없이 정의된 경우가 많아 헷갈렸다.
아래 내용은 다음 사이트의 글을 읽고 정리한 글이다.
https://www.digikey.com/en/maker/projects/introduction-to-rtos-solution-to-part-11-priority-inversion/abf4b8f7cd4a4c70bece35678d178321
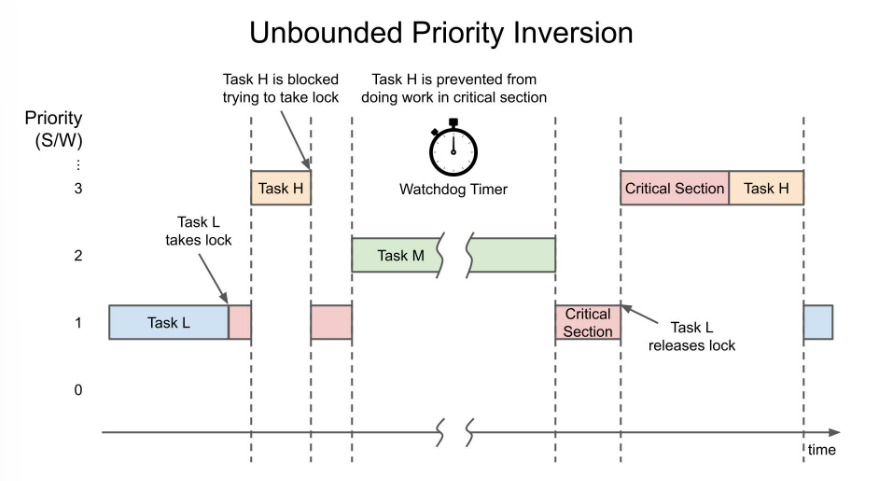
priority inversion에도 bounded priority inversion이 있고 unbounded priority inversion이 있다고 한다.
- bounded priority inversion
- a bug that occurs when a high priority task is indirectly preempted by a low priority task.
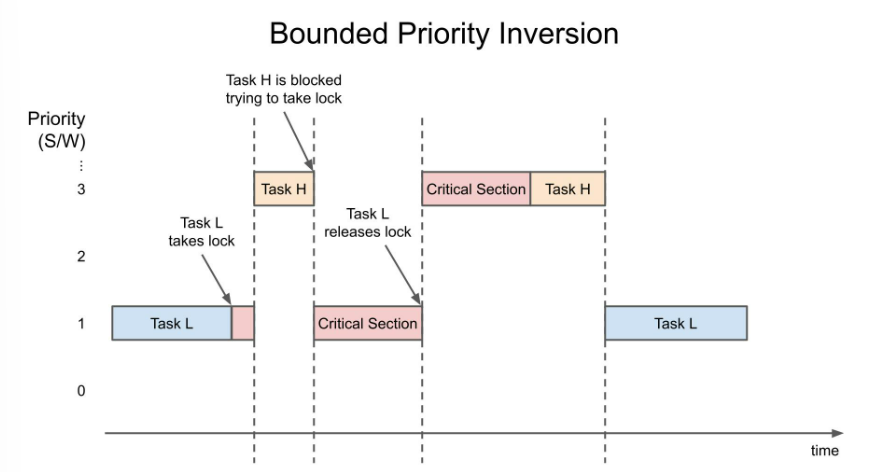
- low priority task가 lock을 갖고 있는 시간 만큼 inversion이 발생하기 때문에 bounded 라고 한다.
- a bug that occurs when a high priority task is indirectly preempted by a low priority task.
- unbounded priority inversion
- occurs when a medium priority task interrupts low priority task while it holds the lock
- low가 lock를 갖고 있는 한, medium priority는 high priority task를 사실상 얼마든지 block할 수 있기 때문에 unbounded 라고 표현한다.