Software - a "softer" medium.
Machine Language or Machine Code = Binary Code
In early days of computing, people had to write entire programs in machine code.
- Write in English (pseudo code).
- Pseudo-Code : an informal, high-level description of a program.
- Translate into machine code by hand, using things like opcode tables.
Assembly Language (1940s and 1950s)
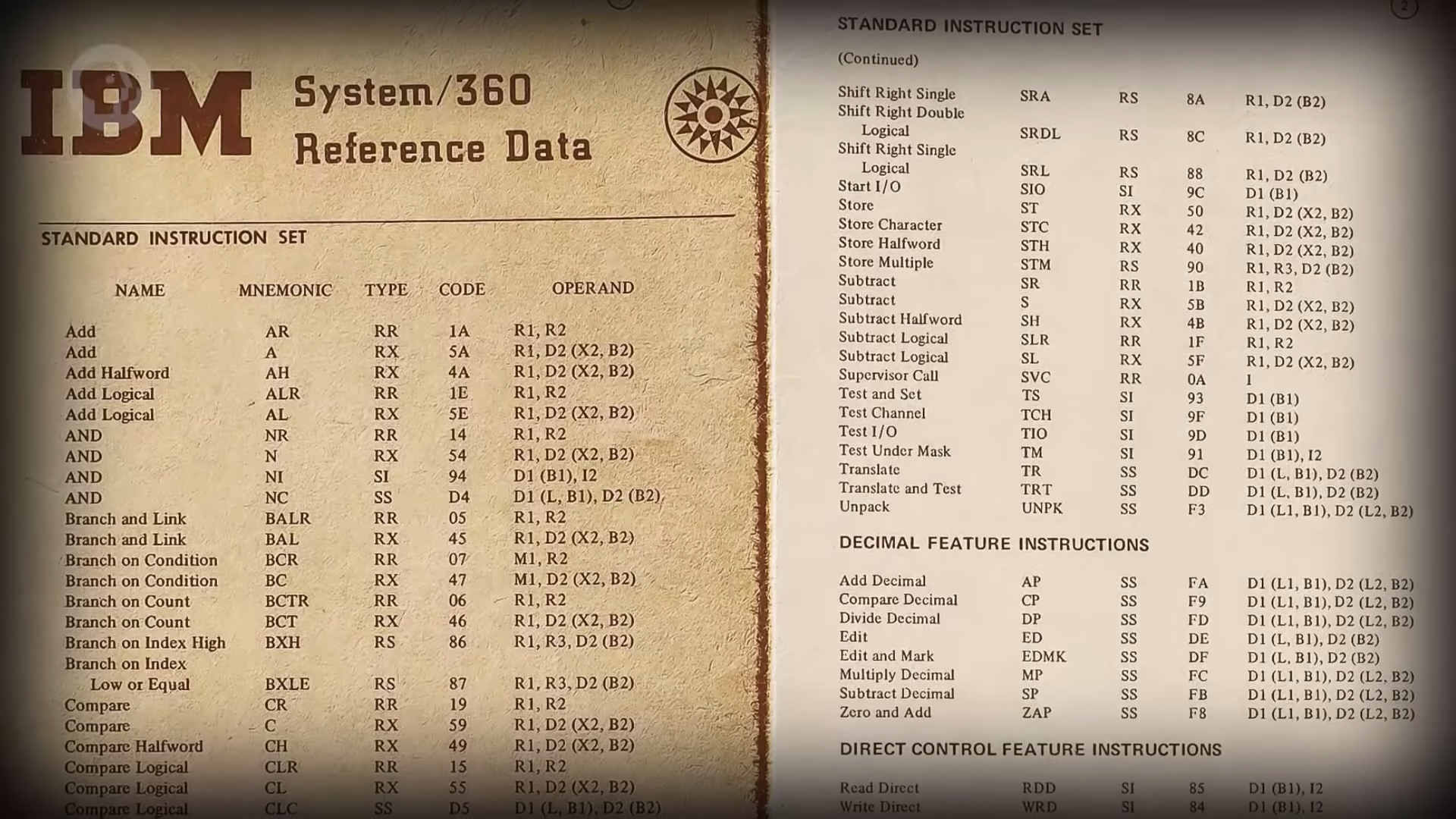
Opcodes were given simple names called mnemonics, followed by operands to form instructions.
- mnemonics : 연상 기호
- operands : a quantity or function upon which a mathematical or logical operation is performed
An Assembler
** assemble : 모으다, 조립하다.
-
Programmers created reusable helper programs, in binary, that read in text-based instructions (assembly code) and assemble them into the correspoding binary instructions (machine code) automatically.
-
Programmers could focus more on programming.
However, assembly languages are a thin veneer over machine code.
- Each assembly language instruction converts directly to a correspoding machine instruction - a one-to-one mapping - so it's inherently tied to the underlying hardware.
- Assembler still forces programmers to think about which registers and memory locations they will use.
Dr. Grace Hopper (1906 ~ 1992)
As a naval officer, she was one of the first programmers on the Havard Mark 1 Computer.

- She designed a high-level programming language called "Arithmetic Language Version 0" (A-0).
- Single line of high-level programming language result in dozens of instruction being executed by the CPU.
A Compiler (1952)
- Hopper built the first compiler in 1952.
- A specialized program that transforms source code written in a programming language into a low-level language (assembly or binary machine code which CPU can directly process).
"I had a running compiler and nobody would touch it... they carefully told me, computers could only do arithmetic; they could not do programs." - Grace Hopper
- Programming languages abstract low-level and unnecessary complexity (registers, memory locations...)
- Programmer creates abstractions for needed memory locations (variables) and give them names.
FORTRAN (1957)
- A-0 and its later variants weren't widely used.
- FORTRAN, short for formula translation, was released by IBM in 1957 and dominated early computer programming.
" Much of my work has come from being lazy. I didn't like writing programs, and so... I started work on a programming system to make it easier to write programs." - John Backus, the FORTRAN project director
- On average, programs written in FORTRAN were 20 times shorter than equivalent handwritten assembly code.
- The community was skeptical that the performance would decrease, but was an economical choice for saving time.
- FORTRAN could only be compiled and run on IBM computers, as they were on the business of selling computers.
COBOL (1959)
- Most programming languages and compilers of the 1950s could only run on a single type of computer.
- To fix this problem, computer experts from industry, academia and government formed a consortium, the Committee on Data Systems Languages (1959).
- Advised by Grace Hopper, it worked on developing a common programming language that could be used acrross different machines.
- The result was COBOL, Common Business-Oriented Language.
- Each computers needed its own COBOL compiler to deal with different underlying hardware, but could all accept the same COBOL source code - "write once, run anywhere".
High level programming language reduced computing's barrier to entry.
- From a realm exclusive to computer experts, who had the job as a profession, to different professions incorporating computation into their work.
- The abstraction allowed computer experts to become professional programmers.
1960's - ALGOL, LISP, BASIC
1970's - Pascal, C, Smalltalk
1980's - C++, Objective-C, Perl
1990's - Python, Ruby, Java
2000's - Swift, C#, Go
- Internet brower is writtein in C++ or Objective-C (safari).
- Each new language attempts to leverage new and clever abstractions, or take advantage of emerging technologies and platforms to make some aspect of programming easier or more powerful.
Vocabulary
- cumbersome - large and heavy / complicated and inefficient (system or process)
- infelxible - antonym of flexible.
- versatile - 다재다능한, (기계 등이) 다용도로 사용가능한
- painstakingly - (조사, 연구를) 힘들여, 공들여
- pseudo - 허위의, 모조의
- do away with - discard, abolish
- veneer - a thin layer of wood or plastic which is used to improve the appearance of something.
- inherently - 본질적으로, 타고난
- forefront - 선두, 최전선
- skeptical - having doubts about it.
- underway
- is underway : it already started
- gets underway : it gets started
- consortium (컨소시엄) - a group of people or firms who have agreed to co-operate with each other.
- notion - an idea or belief about something
- esoteric - known, understood, or appreciated by only a small number of people.
Thoughts
- 내가 모르는 영어단어가 이렇게 많이 나올줄은 몰랐다. 그냥 조금 애매하다 싶은 것도 다 적었더니 엄청 많이 나왔네.
- CPU 가 쓰는 binary 코드는 어떤 식으로 이루어져 있는지, 그리고 어셈블리어는 도대체 뭔지 막연했는데(vague) 이번 에피소드에서 그 내용이 명확해졌다. 너무 좋다. 마치 머리에 낀 먹구름이 사라진 느낌이랄까.
- C는 이제 50년이 되었는데도 아직도 사용하고 있다는 점이 놀랍다. C++ 도 40년은 되었는데 아직도 활발히 사용되고 있다.
