Lombok(롬북)은 기존에 VO, DTO, Entity 등의 객체를 생성하고 getter/setter와 toSring 메서드를 따로 만들어주어야만 했던 것을 어노테이션을 기반으로 관련 작업을 쉽게 할 수 있게 해주는 라이브러리 이다.
Lombok(롬북)을 사용하면 어노테이션 기반으로 자동으로 코드를 자동 생성하므로 생산성이 높아지고, 가독성이 좋아지며, 유지보수에 용이하다.
프로젝트에 따라 Lombok을 사용하기도, 사용하지 않기도 한다. 자동 생성으로 인해서 개발자의 의도대로 정확하게 구현하지 못하기도 하기 때문이다.
Lombok 사용하기
Lombok 의존성 추가
먼저, Lombok을 사용하기 위해서는 의존성을 추가해야 한다.
build.gradle(maven인 경우에는 pom.xml)에 Lombok 의존성을 추가한다.
configurations {
compileOnly {
extendsFrom annotationProcessor
}
}
dependencies {
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
}'Lombok' plugin 설치
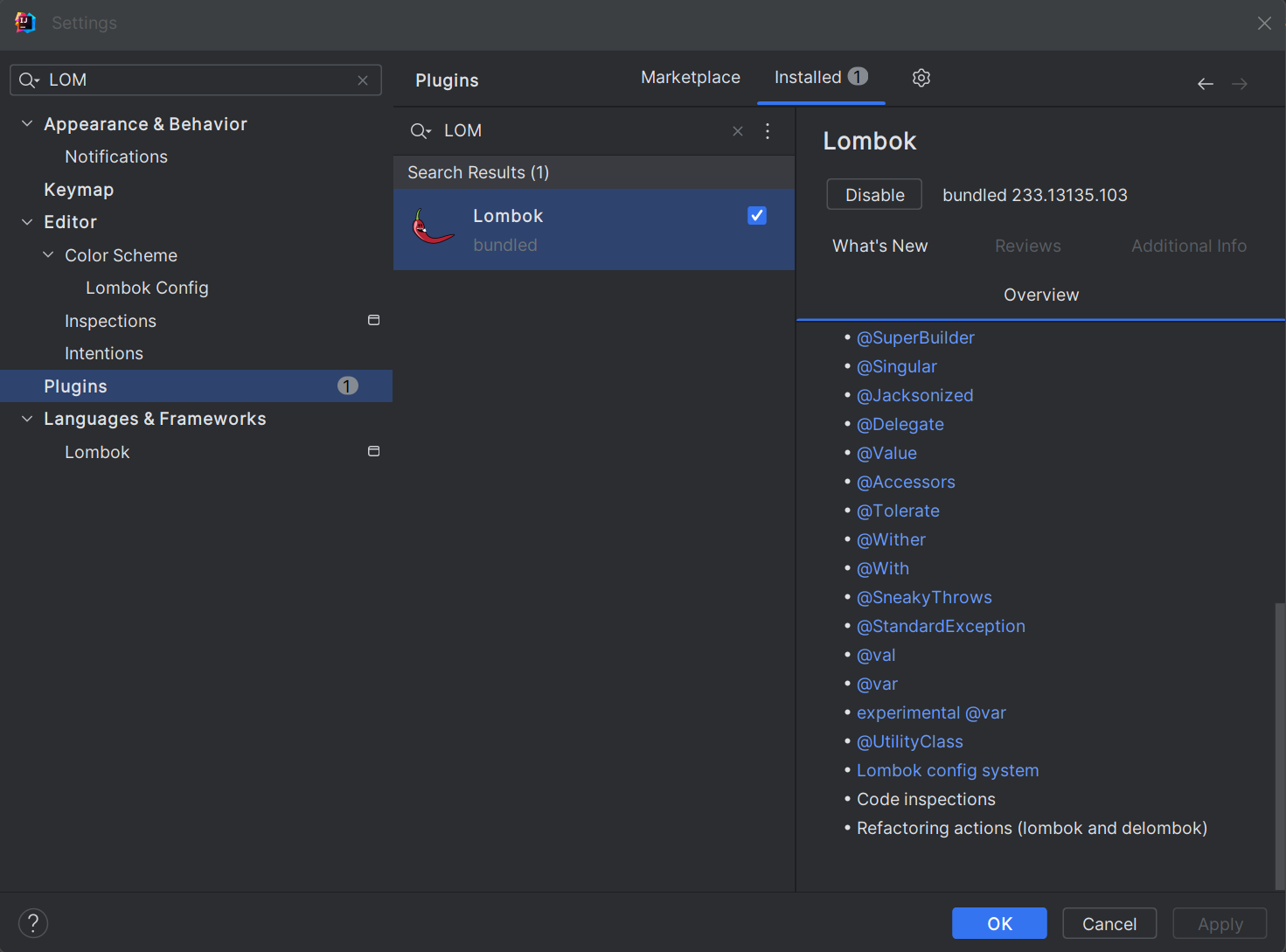
Lombok이 설치된 것을 확인하였다면,
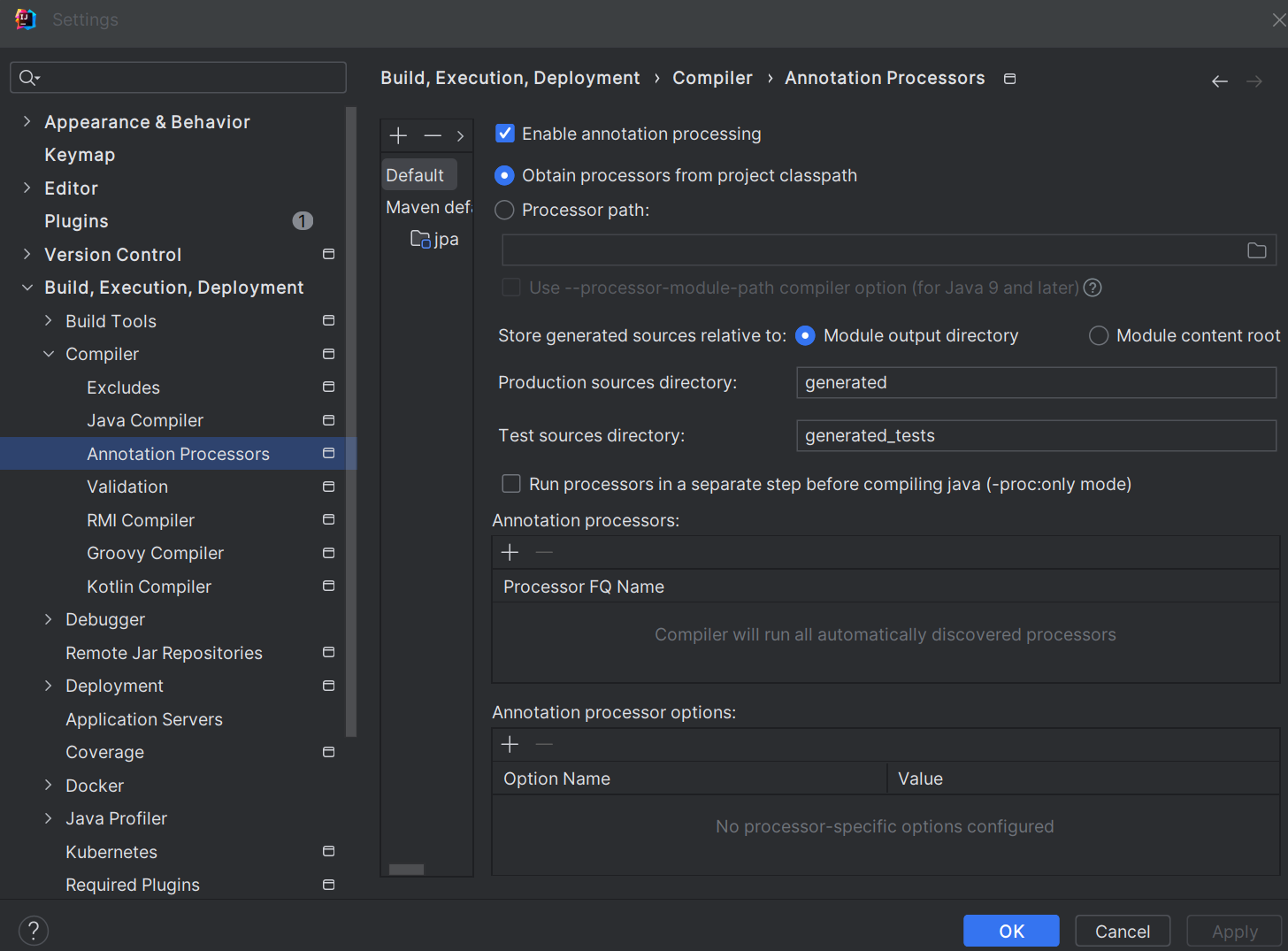
해당 화면에서 Enable annotation processing이 체크되어있는지 확인한 후 마친다.
@Getter/@Setter
@Getter 사용 전
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long number;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false)
private Integer price;
@Column(nullable = false)
private Integer stock;
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
private LocalDateTime updatedAt;
public Long getNumber() {
return this.number;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Integer getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
public Integer getStock() {
return this.stock;
}
public LocalDateTime getCreatedAt() {
return this.createdAt;
}
public LocalDateTime getUpdatedAt() {
return this.updatedAt;
}
}@Getter 사용 후
@Getter
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long number;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false)
private Integer price;
@Column(nullable = false)
private Integer stock;
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
private LocalDateTime updatedAt;
}
Product 클래스를 우클릭 한 후 Refactor에서 Delombok을 클릭하면 실제 코드로 리팩토링 된다.
Delombok을 하지 않고, 화면 좌측의 Structure를 클릭하면 클래스에 정의 된 메서드 목록을 모두 볼 수 있다.
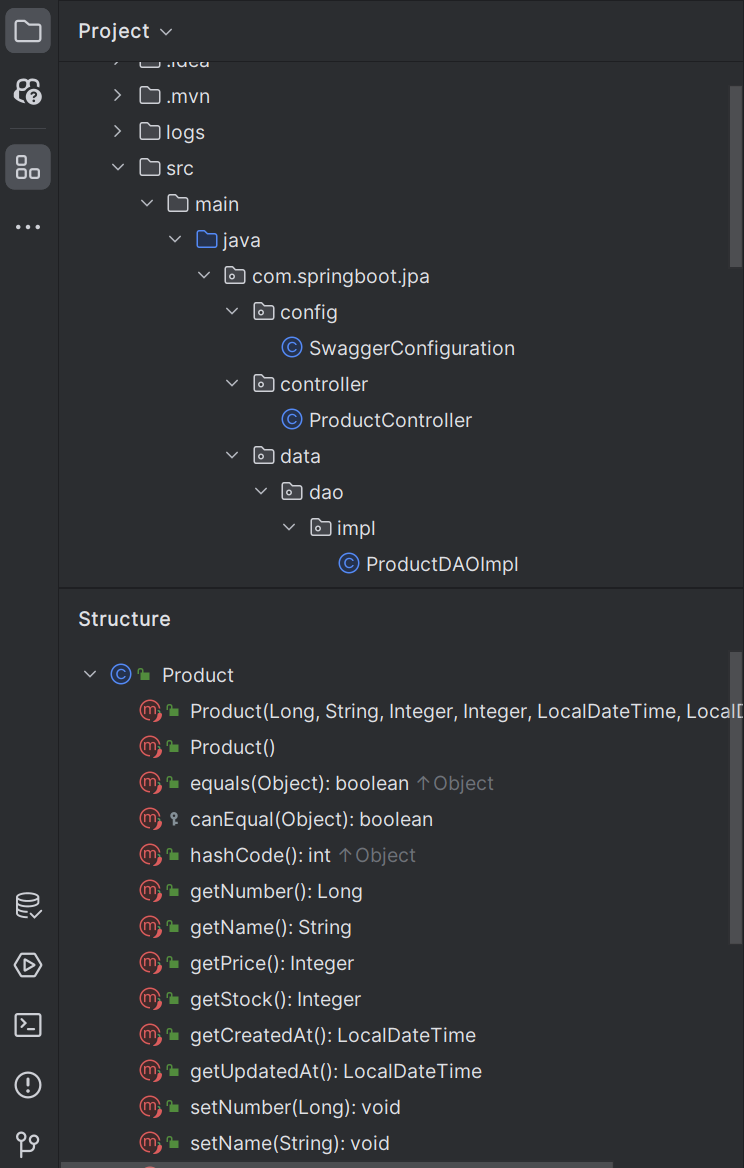
@NoArgsConstructor, @AllArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor(생성자 자동 생성)
@NoArgsConstructor, @AllArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor 이 세가지 어노테이션은 데이터 클래스의 초기화를 위한 생성자를 자동으로 만들어주는 어노테이션이다.
@NoArgsConstructor : 매개변수 없는 생성자를 자동 생성한다.
public Product() { }@AllArgsConstructor : 모든 필드를 매개변수로 갖는 생성자를 자동 생성한다.
public Product(Long number, String name, Integer price, Integer stock, LocalDateTime createdAt, LocalDateTime updatedAt) { this.number = number; this.name = name; this.price = price; this.stock = stock; this.createdAt = createdAt; this.updatedAt = updatedAt; }@RequiredArgsConstructor : 필드 중 final이나 @NotNull이 설정된 변수를 매개변수로 갖는 생성자를 자동 생성한다.
@ToString
toString() 메서드를 생성하는 어노테이션이다.
toString() 메서드
public String toString() { return "Product(number=" + this.getNumber() + ", price=" + this.getPrice() + ", stock=" + this.getStock() + ", createdAt=" + this.getCreatedAt() + ", updatedAt=" + this.getUpdatedAt() + ")"; }
- @ToString 어노테이션의 exclude 속성을 활용해 특정 필드를 자동생성에서 제외할 수 있다.
@ToString(exclude = "name")
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long number;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false)
private Integer price;
@Column(nullable = false)
private Integer stock;
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
private LocalDateTime updatedAt;
}@EqualsAndHashCode
@EqualsAndHashCode는 객체의 동등성과 동일성을 비교하는 연산 메서드를 생성한다.
- equals : 두 객체의 내용이 같은지 동등성을 비교한다.
- hashCode : 두 객체가 같은 객체인지 동일성을 비교한다.
부모 클래스의 필드까지 비교해야하는 경우, @EqualsAndHashCode의 callSuper 속성을 true로 해주면 된다. 기본값은 false이다.
- 자동생성되는 equals()와 hashCode() 메서드
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Product)) return false;
final Product other = (Product) o;
if (!other.canEqual((Object) this)) return false;
final Object this$number = this.getNumber();
final Object other$number = other.getNumber();
if (this$number == null ? other$number != null : !this$number.equals(other$number)) return false;
final Object this$name = this.getName();
final Object other$name = other.getName();
if (this$name == null ? other$name != null : !this$name.equals(other$name)) return false;
final Object this$price = this.getPrice();
final Object other$price = other.getPrice();
if (this$price == null ? other$price != null : !this$price.equals(other$price)) return false;
final Object this$stock = this.getStock();
final Object other$stock = other.getStock();
if (this$stock == null ? other$stock != null : !this$stock.equals(other$stock)) return false;
final Object this$createdAt = this.getCreatedAt();
final Object other$createdAt = other.getCreatedAt();
if (this$createdAt == null ? other$createdAt != null : !this$createdAt.equals(other$createdAt)) return false;
final Object this$updatedAt = this.getUpdatedAt();
final Object other$updatedAt = other.getUpdatedAt();
if (this$updatedAt == null ? other$updatedAt != null : !this$updatedAt.equals(other$updatedAt)) return false;
return true;
}
protected boolean canEqual(final Object other) {
return other instanceof Product;
}
public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
final Object $number = this.getNumber();
result = result * PRIME + ($number == null ? 43 : $number.hashCode());
final Object $name = this.getName();
result = result * PRIME + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
final Object $price = this.getPrice();
result = result * PRIME + ($price == null ? 43 : $price.hashCode());
final Object $stock = this.getStock();
result = result * PRIME + ($stock == null ? 43 : $stock.hashCode());
final Object $createdAt = this.getCreatedAt();
result = result * PRIME + ($createdAt == null ? 43 : $createdAt.hashCode());
final Object $updatedAt = this.getUpdatedAt();
result = result * PRIME + ($updatedAt == null ? 43 : $updatedAt.hashCode());
return result;
}@Data
@Data는 앞의 모든 어노테이션을 포함하는 어노테이션이다.
마치며
Lombok은 자주 사용되는 라이브러리이므로 기본적인 사용법은 알고있도록 하자.

