데이터 살펴보기
Pandas 불러오기 & csv파일 읽어오기
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('파일위치')기본 정보 확인
df.columns: 전체 컬럼명(리스트) 확인df.info(): 요약 정보 확인(행/열 갯수, 전체 컬럼 정보 - null값 유무, 데이터 타입)df.duplicated().sum(): 중복값 갯수df.describe(): 통계값 확인(수치형 데이터만) > 이상치 확인df.describe().round(0).T: 컬럼이 많은 경우, 행열 전환하여 확인- mean(평균)은 이상치에 크게 영향 받고, median(중앙값)은 크게 영향 받지 x
df.nunique(): 컬럼별로 고유한 항목 갯수 (고유값이 하나인 경우는 분석에 필요없을 확률 ↑)df.drop(['컬럼1', '컬럼2', .. ], axis = 1, inplace = True): 불필요 컬럼 제거axis = 0: 행,axis = 1: 열 /inplace = True: 데이터 객체에 바로 적용
df.select_dtypes(include = 'object'): 문자형 데이터 확인df.select_dtypes(include = 'int64'): 숫자형 데이터 확인
Groupby() / Pivot_table()
Groupby()
tmp0 = df[['Department', 'EducationField','JobRole','JobLevel', 'Attrition']].copy()
tmp0.groupby('Department').size()
# tmp0.groupby('Department')['Department'].count() # 동일한 결과
### 결과
Department
Human Resources 63
Research & Development 961
Sales 446
dtype: int64size(): null을 포함하여 센다 vscount(): null은 제외하고 센다 (집계함수)
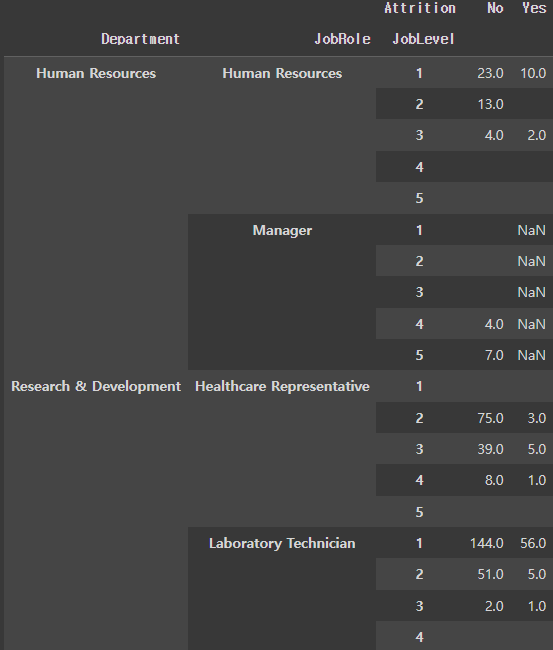
tmp0.groupby(['Department','JobRole','JobLevel','EducationField']).size().sort_values(ascending=False).reset_index(name='Emp Count')
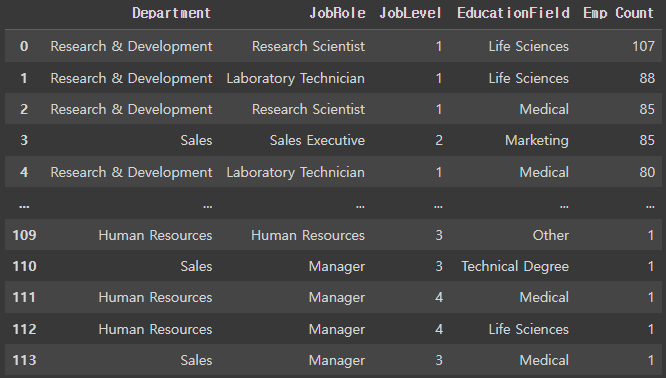
- 여러 기준으로 그룹핑 가능
reset_index()사용하면 데이터 프레임 형태로 출력- ( )안에
size()로 count한 컬럼명 지정 가능
- ( )안에
tmp1 = df[['Department','JobRole', 'JobLevel', 'Age','Attrition']].copy()
tmp1.groupby(['Department','JobRole'])['Age'].agg(['count','max','min'])- 여러 개의 집계를 사용할 때
agg([])사용
Pivot_table
pt2 = pd.pivot_table(tmp1,
index=['Attrition','Department','JobRole'],
columns='JobLevel',
values='Age',
aggfunc='count',
fill_value='' # null값이 있는 경우 채울 값
)
pt2
# pt2.index # 전체 인덱스 확인
# pt2.index.names # 인덱스 이름 리스트 (pt2는 멀티인덱스)
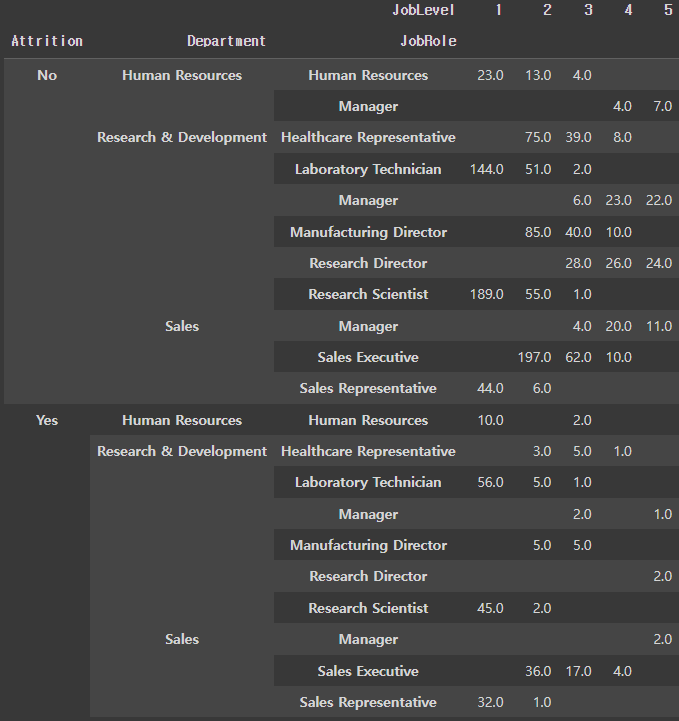
위 데이터 프레임에서 인덱스는 3개('Attrition','Department','JobRole')
└ unstack할 때 순서는 0 : 'Attrition', 1 : 'Department', 2 : 'JobRole'
└ -1은 맨 뒤에서 첫번째 인덱스인 JobRole
unstack, stack 항목은 멀티 인덱스를 가진 데이터프레임에 적합
unstack / stack : default level = -1unstack : index -> columnstack : column -> index
pt1.unstack(level=0) : 0번 인덱스 'Attrition'을 열 위치로 옮기겠다
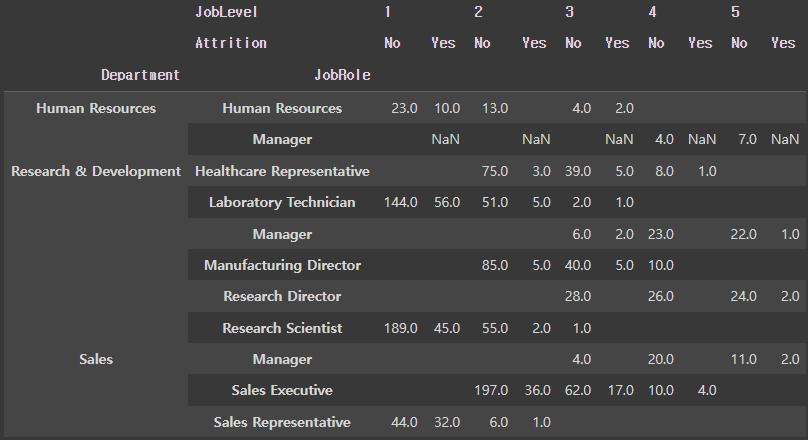
pt2.unstack(level=0).stack(level=0) : 위 unstack된 상태에서 column 0번 인덱스인 'JobLevel'을 행 위치로 옮기겠다
Visualization
matplotlib
- python 대표 시각화 라이브러리
- 기본 그래프부터 통계, image 처리까지 가능
- Documentation과 Cheatsheet 참고
seaborn
- matplotlib 기반의 adds-on 성격의 라이브러리
- 간단한 메서드로 다양한 통계 그래픽
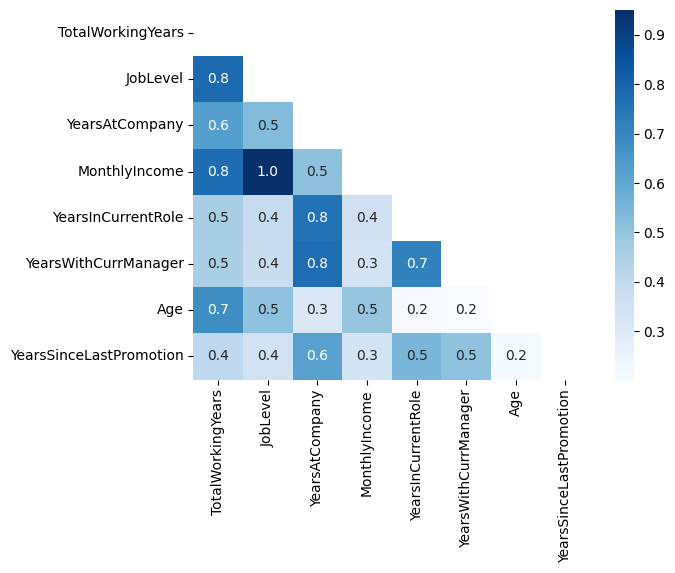
히트맵 (Heatmap)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
plt.figure(figsize=(15,10))
sns.heatmap(cor_df.corr()
, annot=True # 히트맵에 숫자 표기
, fmt='.1f' # 소수점 표기
, linewidth=0.5 # 라인 두께
, cmap='YlGnBu' # 색상 color map
)
plt.show()
# 상관관계(컬럼 합계) 높은 변수 top8 리스트 추리기
top8_cols = df.select_dtypes(include='int64').corr().sum().sort_values(ascending=False)[:8].index.tolist()
cor_df2 = df[top8_cols].corr()
sns.heatmap(cor_df2, annot=True, fmt='.1f', cmap='Blues')
# 삼각형 Mask 씌워서 Heatmap 깔끔하게 그려보기
import numpy as np
mask = np.zeros_like(cor_df2, dtype=bool)
mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True
sns.heatmap(cor_df2, annot=True, fmt='.1f', cmap='Blues', mask=mask)
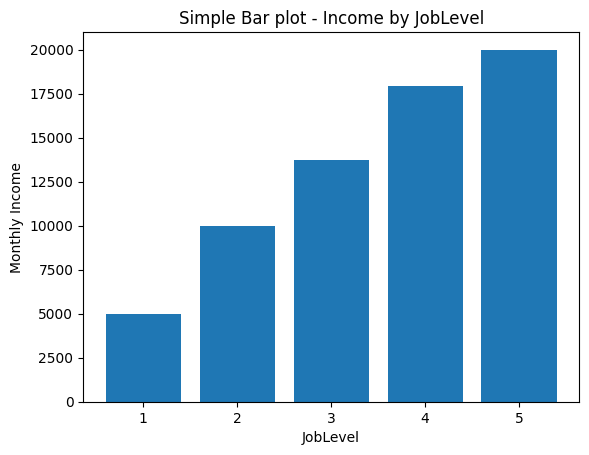
bar graph (barplot)
# JobLevel별 income
plt.title('Simple Bar plot - Income by JobLevel')
plt.bar(df['JobLevel'], df['MonthlyIncome']) #plt.bar(x, y)
plt.xlabel('JobLevel')
plt.ylabel('Monthly Income')
plt.show()
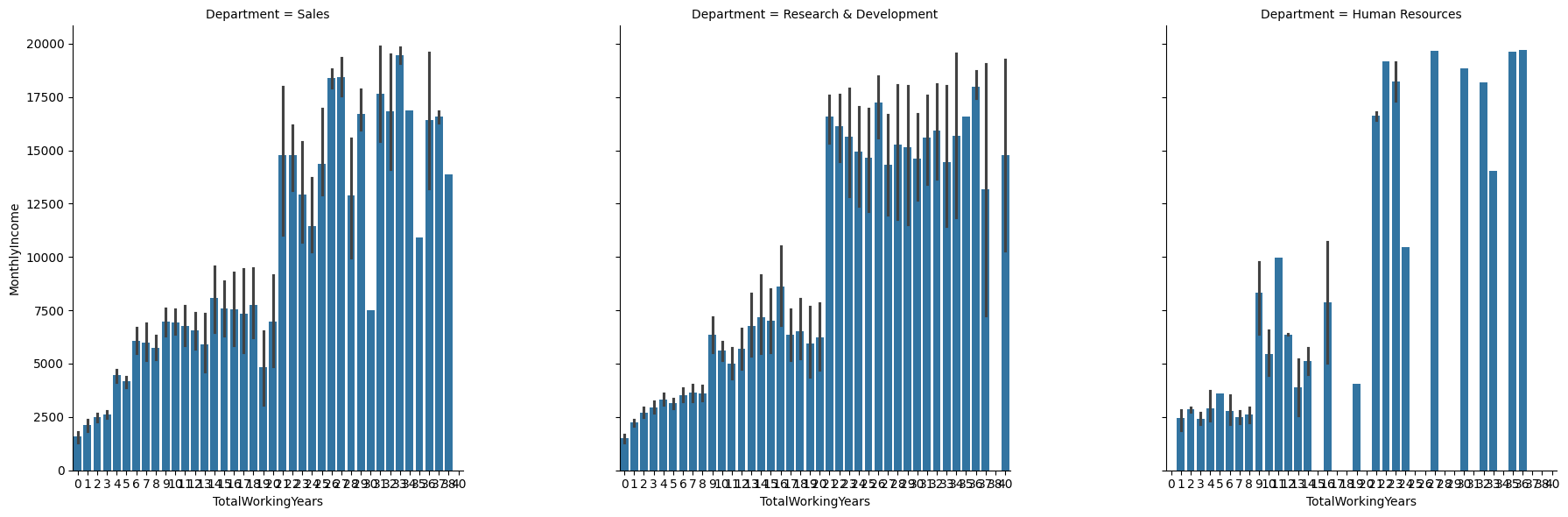
bar graph with FacetGrid (FacetGrid)
# 부서별 근속연수별 income
# FacetGrid >> x,y축 고정 column과 row 추가하여 다양한 차원에서 어느 특징을 가진 구간에서 발생한 것인지 확인 가능
# monthlyincome과 totalworkingyears 상관계수가 0.8 > 강한 양의 상관관계를 갖지만, 드릴다운하여 부서별로 보면, 계단이 확 뛰는 구간이 다르게 존재함
facet = sns.FacetGrid(df, col='Department', height=6)
facet.map_dataframe(sns.barplot, x='TotalWorkingYears', y='MonthlyIncome')
facet = facet.fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=.4, hspace=.2) # 각 그래프 크기 조정
Regplot (regplot)
: 산점도(scatter plot) + 선형회귀선
facet = sns.FacetGrid(df, col='EducationField', row='Gender', hue='Attrition', height=5, palette={'Yes':'red', 'No':'gray'})
facet = facet.map_dataframe(sns.regplot, x='Age', y='MonthlyIncome') # fit_reg = False 옵션으로 회귀선 안보이게 설정 가능
facet = facet.add_legend()
# R&D 팀은 퇴사여부가 연봉 차이에 영향을 미치는 것으로 보이는 반면 이외 팀은 그렇지 않은 경향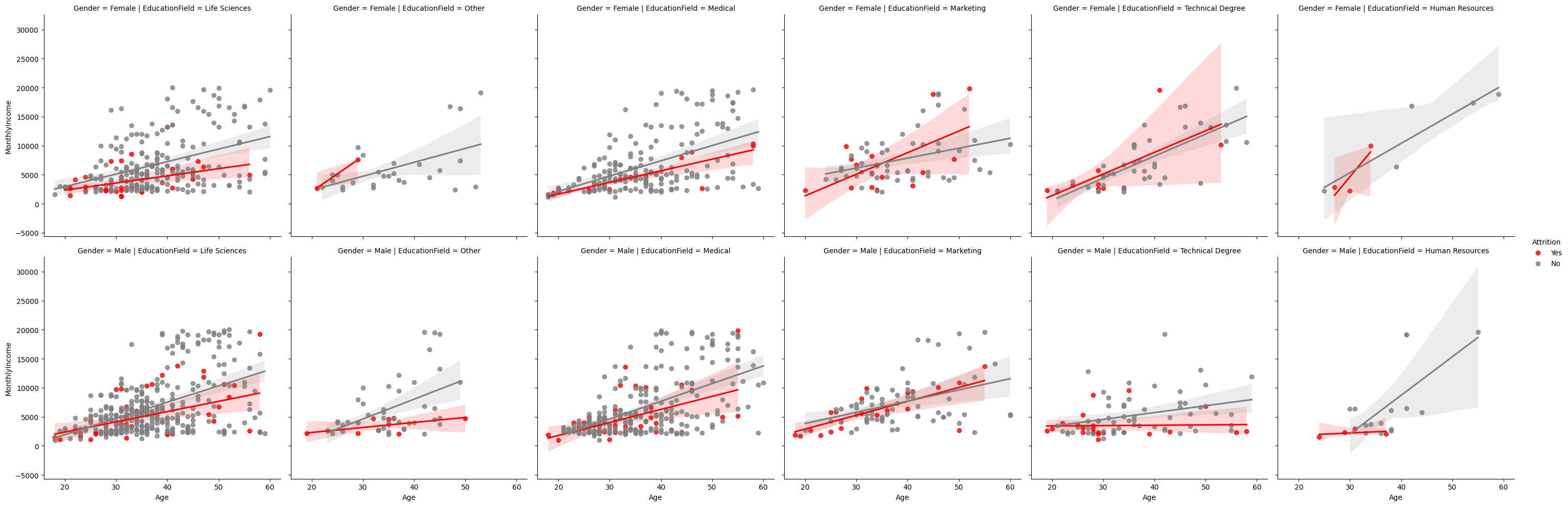
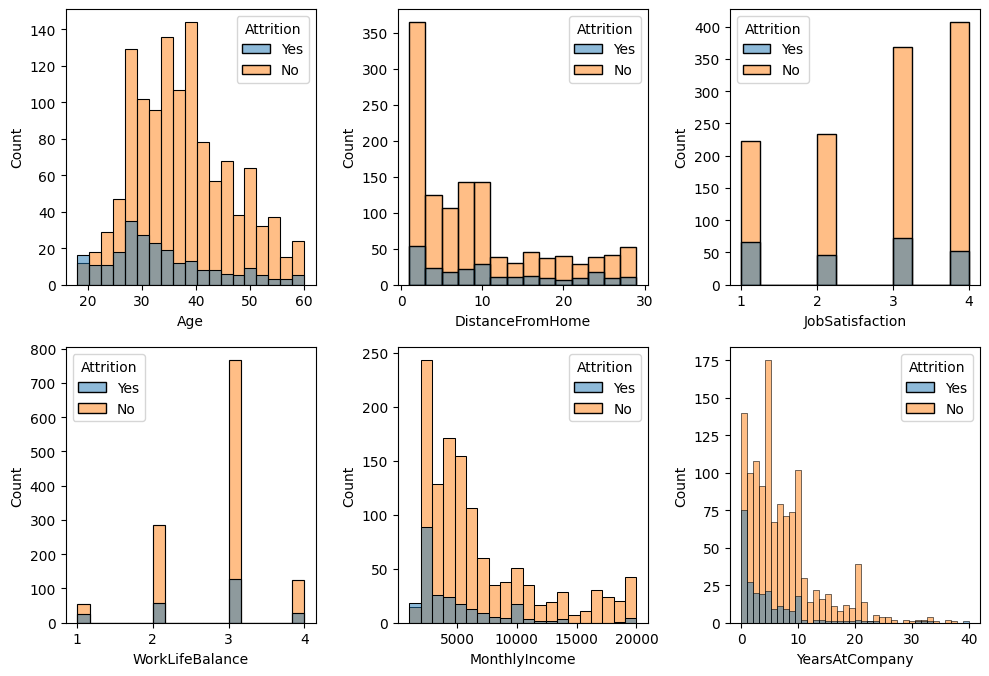
Histplot + Enumerate 반복문 (histplot)
# enumerate : 리스트 내에 값을 인덱스와 함께 반환
hist = ['Age', 'DistanceFromHome', 'JobSatisfaction', 'WorkLifeBalance','MonthlyIncome','YearsAtCompany']
plt.figure(figsize=(10,20))
for i,col in enumerate(hist):
axes = plt.subplot(6,3,i+1)
sns.histplot(x=df[col], hue=df['Attrition'])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
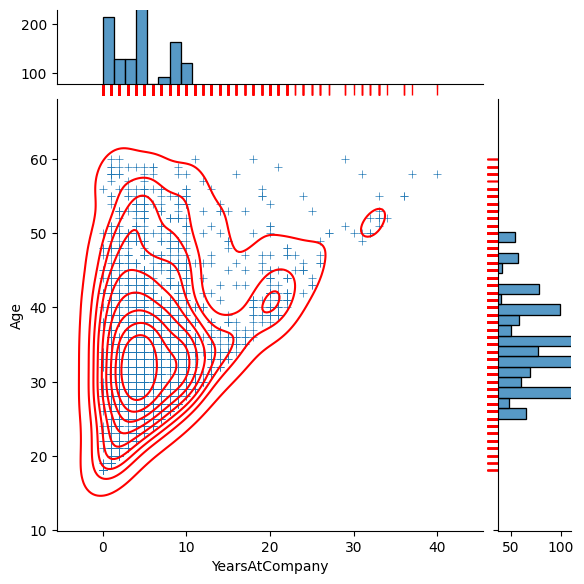
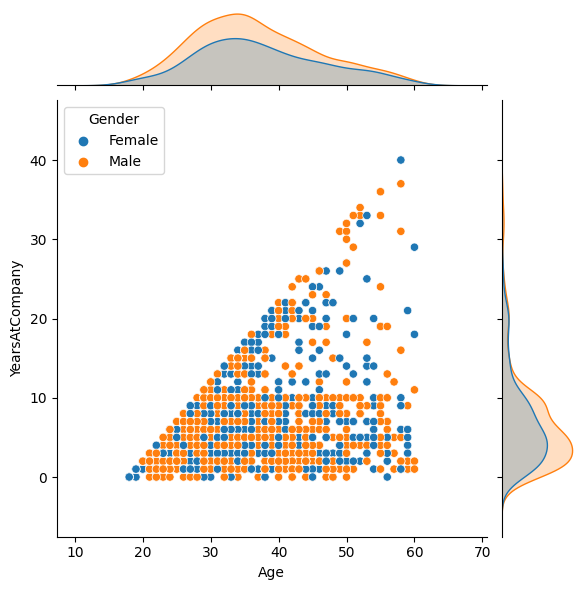
Jointplot (jointplot)
: 다양한 그래프를 한 번에 볼 수 있는 형태 > 빠르게 데이터를 확인할 때 도움
sns.jointplot(df, x='Age', y='YearsAtCompany', hue='Gender')
j = sns.jointplot(df, x='YearsAtCompany', y='Age'
, marker='+' # main data scatter 표시 마커
, marginal_ticks=True # marginal data에 y축 추가
, marginal_kws=dict(bins=30, rug=True) # marginal data의 세부 디자인 조정
)
j.plot_joint(sns.kdeplot, color='r') # 등고선 추가
j.plot_marginals(sns.rugplot, color='r',height=-.15, clip_on=False)
# ↑ 각 요소 존재하는지 표시, clip_on=False : 막대그래프 각 축 0값을 기준으로 반대편에