FrontEnd에서 AJAX를 사용할 수 있다.
AJAX(Asynchronous Javascript & XML)의 특징은 아래와 같다.
- 언어나 프레임워크가 아닌 구현하는 방식을 의미한다.
- 웹에서 화면을 갱신하지 않고 데이터를 서버로부터 가져와 처리하는 방법을 의미한다.
- XHR 객체로 데이터를 전달하고 비동기 방식으로 결과를 조회한다.
- 화면 갱신이 없으므로 사용자 입장에서는 편리하지만, 구현이 복잡하다.
아래 사진을 참고하자.
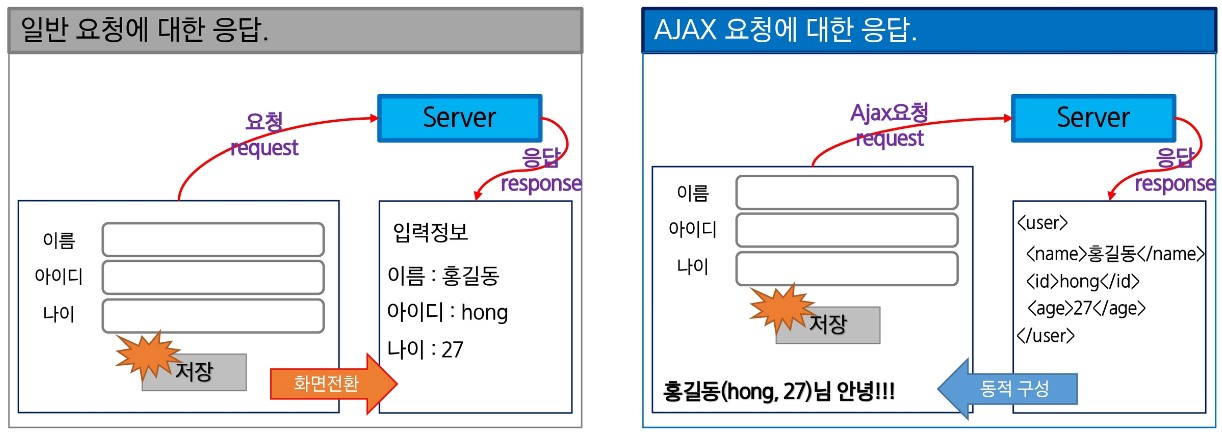
일반 요청에 대한 응답 (SSR)은 아래와 같다.
- data 입력 후 event가 발생한다.
- 서버에서 logic을 처리한 후 응답 html page를 생성 후 클라이언트에 전송한다.
- client에서 받은 page로 화면 전환이 일어난다.
AJAX 요청에 대한 응답 (CSR)은 아래와 같다.
- data 입력 후 event가 발생한다.
- Ajax를 적용하면 서버에서 요청을 처리한 후 Text, XML 또는 JSON으로 응답한다.
- Client에서는 응답 data를 이용하여 화면 전환없이 동적으로 화면을 재구성한다.
AJAX 사용방식은 3가지가 있다.
- XMLHttpRequest 이용 방식 -> 너무 복잡함
- fetch() 이용 방식
- 외부라이브러리 이용 방식(jQuery 등) -> 최근에 많이 안쓰임
※ GET방식과 POST방식의 차이는 아래와 같다.
GET 방식의 특징은 아래와 같다.
- URL에 변수를 노출한다. -> 보안에 취약하다.
- 전송하는 길이에 제한이 있다.
- 캐싱할 수 있다.
POST 방식의 특징은 아래와 같다.
- URL에 변수를 노출하지 않고 요청한다. -> 기본 보안은 유지된다.
- 전송하는 길이에 제한이 없다.
- 캐싱할 수 없다.
Fetch()로 AJAX를 사용할 수 있다.
fetch 메서드의 특징은 아래와 같다.
- fetch(url, [options]) 방식으로 사용한다.
- option의 default값은 GET방식이며, url로부터 contents가 다운로드된다.
- 실행 결과 Promise 타입의 객체를 반환한다.
data를 받는 방법은 아래와 같다.
- response.text() : 응답을 읽고 text를 반환한다.
- response.json() : 응답을 JSON 형식으로 파싱한다.
- response.formData() : 응답을 FormData 객체 형태로 반환한다.
- response.blob() : 응답을 Blob 형태로 반환한다.
fetch 메서드의 실행 예시는 아래와 같다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>fetch()</title>
<script>
window.onload = async function () {
let url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1";
let response = await fetch(url);
console.log(response);
data = await response.json(); // await가 있을 때와 없을 때 비교.
console.log(data.userId);
};
</script>
</head>
<body></body>
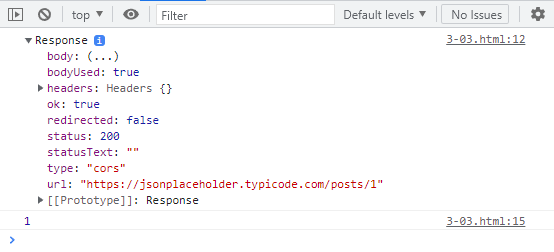
</html>만약 data 줄에 await가 없으면 data를 아직 다 받지 않은 pending 상태로 남아 undefined가 출력될 수 있다.
하지만 await가 있으면 확실히 data를 다 받았기 때문에 1이 정상적으로 출력된다.
실행 결과는 아래와 같다.
await 대신 fetch와 .then 개념을 사용 가능하다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>fetch() - GET</title>
<script>
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1")
.then((response) => response.json()) // = function (response) { return response.json() }
.then((data) => console.log(data.userId));
</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>response와 data는 변수 이름일 뿐이므로 다른 걸로도 설정 가능하다.
실행 결과는 아래와 같다.

CSV, XML, JSON으로 데이터를 전송할 수 있다.
첫 번째로 CSV 파일을 보낼 수 있다. 예시는 아래와 같다.
// 4-01.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>CSV</title>
<style type="text/css">
table {
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
}
th, td {
text-align: center;
}
.first-view-bg {
background-color: darkblue;
}
.first-view-color {
color: ivory;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Samsung 분반</h3>
<button id="listBtn">학생정보보기</button>
<table style="display: none">
<tr>
<th>학번</th>
<th>이름</th>
<th>분반</th>
<th>성적</th>
</tr>
<tbody id="studentinfo"></tbody>
</table>
<script>
let btn = document.querySelector("#listBtn");
btn.addEventListener("click", function () {
fetch("4-01csv.jsp")
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((data) => makeList(data))
});
function makeList(data) {
document.querySelector("table").setAttribute("style", "display: ;");
let tbody = document.querySelector("#studentinfo");
let students = data.split("\n");
initTable();
students.forEach((student) => {
let tr = document.createElement("tr");
let infos = student.split(",");
infos.forEach(function (info, i) {
let td = document.createElement("td");
td.appendChild(document.createTextNode(info));
tr.appendChild(td);
});
tbody.appendChild(tr);
});
let first = document.querySelector("tr:first-child");
first.className = "first-view-bg";
first.classList.add("first-view-color");
let even = document.querySelectorAll("tr:nth-child(even)");
even.forEach(function (td) {
td.setAttribute("style", "background: lightgray;");
});
}
function initTable() {
let tbody = document.querySelector("#studentinfo");
let len = tbody.rows.length;
for (let i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
tbody.deleteRow(i);
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>// 4-01csv.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/plain; charset=UTF-8"
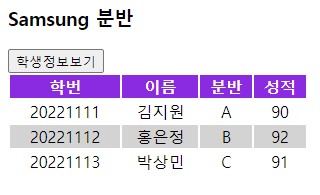
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>20221111,김지원,A,90
20221112,홍은정,B,92
20221113,박정민,C,91버튼을 누른 후 실행 결과는 아래와 같다.
두 번째로 XML 파일을 보낼 수 있다. 예시는 아래와 같다.
// 4-02.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>XML</title>
<style type="text/css">
table {
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
}
th,
td {
text-align: center;
}
.first-view-bg {
background-color: darkgreen;
}
.first-view-color {
color: ivory;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Samsung 분반</h3>
<button id="listBtn">학생정보보기</button>
<table style="display: none">
<tr>
<th>학번</th>
<th>이름</th>
<th>분반</th>
<th>성적</th>
</tr>
<tbody id="studentinfo"></tbody>
</table>
<script>
let btn = document.querySelector("#listBtn");
btn.addEventListener("click", function () {
fetch("4-02.xml")
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((data) => makeList(data))
});
function makeList(data) {
document.querySelector("table").setAttribute("style", "display: ;");
let tbody = document.querySelector("#studentinfo");
let parser = new DOMParser();
const xml = parser.parseFromString(data, "application/xml");
// console.log(xml);
initTable();
let students = xml.querySelectorAll("student");
students.forEach((student) => {
let tr = document.createElement("tr");
let idTd = document.createElement("td");
idTd.appendChild(document.createTextNode(student.querySelector("id").textContent));
tr.appendChild(idTd);
let nameTd = document.createElement("td");
nameTd.appendChild(document.createTextNode(student.querySelector("name").textContent));
tr.appendChild(nameTd);
let classTd = document.createElement("td");
classTd.appendChild(document.createTextNode(student.querySelector("class").textContent));
tr.appendChild(classTd);
let gradeTd = document.createElement("td");
gradeTd.appendChild(document.createTextNode(student.querySelector("grade").textContent));
tr.appendChild(gradeTd);
tbody.appendChild(tr);
});
let first = document.querySelector("tr:first-child");
first.className = "first-view-bg";
first.classList.add("first-view-color");
let odd = document.querySelectorAll("tr:nth-child(even)");
odd.forEach(function (td) {
td.setAttribute("style", "background: lightgray;");
});
}
function initTable() {
let tbody = document.querySelector("#studentinfo");
let len = tbody.rows.length;
for (let i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
tbody.deleteRow(i);
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>// 4-02.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<students>
<student>
<id>20221111</id>
<name>김지원</name>
<class>A</class>
<grade>90</grade>
</student>
<student>
<id>20221112</id>
<name>홍은정</name>
<class>B</class>
<grade>92</grade>
</student>
<student>
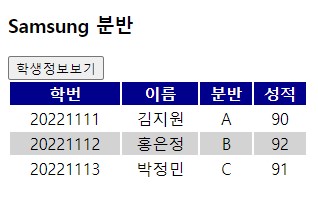
<id>20221113</id>
<name>박상민</name>
<class>C</class>
<grade>91</grade>
</student>
</students>버튼을 누른 후 실행 결과는 아래와 같다.
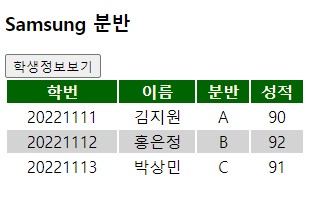
마지막으로 JSON 파일을 보낼 수 있다.
// 4-03.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>JSON</title>
<style type="text/css">
table {
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
}
th,
td {
text-align: center;
}
.first-view-bg {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.first-view-color {
color: ivory;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Samsung 분반</h3>
<button id="listBtn">학생정보보기</button>
<table style="display: none">
<tr>
<th>학번</th>
<th>이름</th>
<th>분반</th>
<th>성적</th>
</tr>
<tbody id="studentinfo"></tbody>
</table>
<script>
let btn = document.querySelector("#listBtn");
btn.addEventListener("click", function () {
fetch("4-03.json")
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => makeList(data))
});
function makeList(data) {
// console.log(typeof data);
document.querySelector("table").setAttribute("style", "display: ;");
let tbody = document.querySelector("#studentinfo");
// let students = data.split("\n");
initTable();
data.forEach((student) => {
let tr = document.createElement("tr");
let idTd = document.createElement("td");
idTd.appendChild(document.createTextNode(student.id));
tr.appendChild(idTd);
let nameTd = document.createElement("td");
nameTd.appendChild(document.createTextNode(student.name));
tr.appendChild(nameTd);
let classTd = document.createElement("td");
classTd.appendChild(document.createTextNode(student.class));
tr.appendChild(classTd);
let gradeTd = document.createElement("td");
gradeTd.appendChild(document.createTextNode(student.grade));
tr.appendChild(gradeTd);
tbody.appendChild(tr);
});
let first = document.querySelector("tr:first-child");
first.className = "first-view-bg";
first.classList.add("first-view-color");
let odd = document.querySelectorAll("tr:nth-child(even)");
odd.forEach(function (td) {
td.setAttribute("style", "background: lightgray;");
});
}
function initTable() {
let tbody = document.querySelector("#studentinfo");
let len = tbody.rows.length;
for (let i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
tbody.deleteRow(i);
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>// 4-03.json
[
{
"id" : "20221111",
"name" : "김지원",
"class" : "A",
"grade" : "90"
},
{
"id" : "20221112",
"name" : "홍은정",
"class" : "B",
"grade" : "92"
},
{
"id" : "20221113",
"name" : "박상민",
"class" : "C",
"grade" : "91"
}
]버튼을 누른 후 실행 결과는 아래와 같다.