알고리즘에서 그래프를 활용 가능하다.
그래프는 사물들과 이들 사이의 연결 관계를 표현하는 자료 구조이다.
그래프 관련 핵심 용어는 아래와 같다.
- 정점(V) : 그래프의 구성요소로 하나의 사물
- 간선(E) : 두 정점을 연결하는 선
- 차수 : 정점에 연결된 간선의 수 (최대 차수는 정점의 개수 - 1)
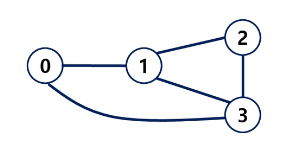
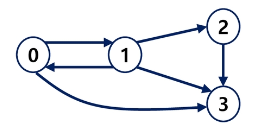
그래프의 종류는 아래와 같다.
- 무향 그래프 (그래프의 최대 간선 수는 V * (V - 1) / 2)
- 유향 그래프 (그래프의 최대 간선 수는 V * (V - 1))
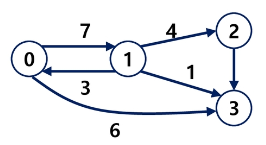
- 가중치 그래프
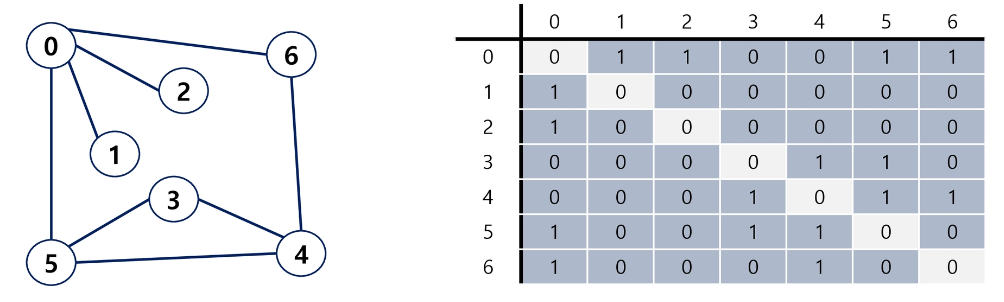
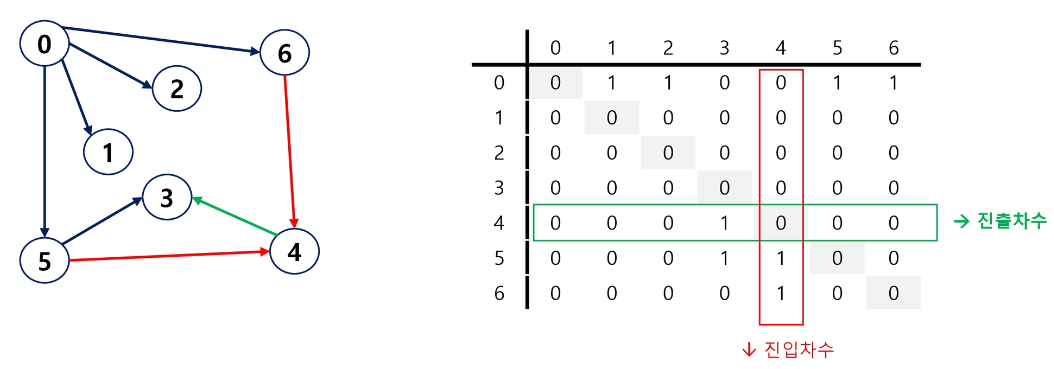
알고리즘에서 그래프를 인접 행렬로 표현할 수 있다.
먼저 인접 행렬로 그래프를 표현하면 아래와 같다.
- 무향 그래프
- 유향 그래프
무향 그래프를 인접 행렬로 구현하면 아래와 같다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjacencyMatrix {
static int[][] adjMatrix;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
adjMatrix = new int[V][V];
int from, to;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
from = sc.nextInt();
to = sc.nextInt();
adjMatrix[from][to] = adjMatrix[to][from] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
System.out.print(adjMatrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}입력값과 출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
- 입력값
7
8
0 1
0 2
0 5
0 6
4 3
5 3
5 4
6 4
- 출력 결과
0 1 1 0 0 1 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 1 1
1 0 0 1 1 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0
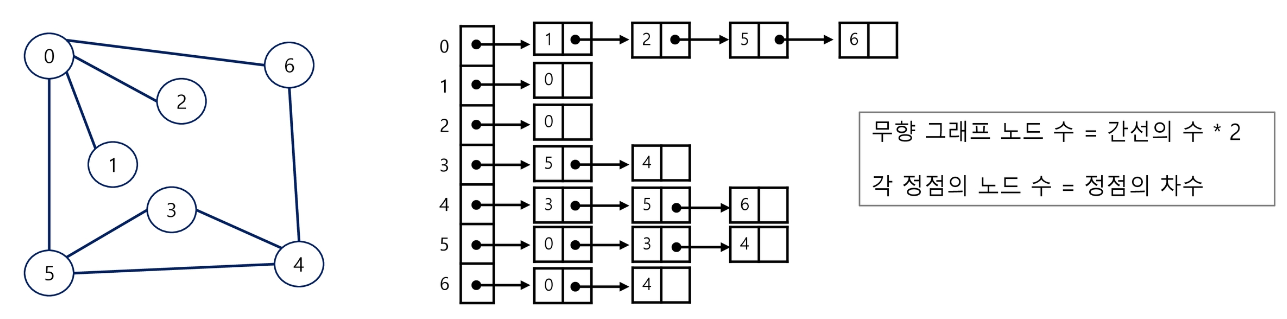
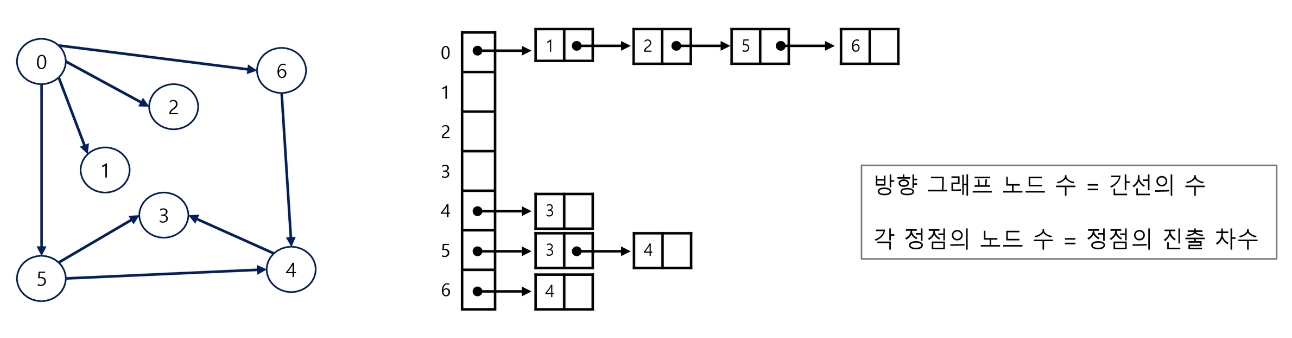
알고리즘에서 그래프를 인접 리스트로 표현할 수 있다.
인접 행렬은 정점에 비해 간선이 적으면 필요없는 공간이 할당된다는 게 단점이다.
따라서 이를 극복하고자 인접 리스트를 활용한다.
인접 리스트로 그래프를 표현하면 아래와 같다.
- 무향 그래프
- 유향 그래프
무향 그래프를 Node 클래스로 구현하면 아래와 같다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjacencyList {
static class Node {
int V;
Node node;
public Node(int v, Node node) {
super();
V = v;
this.node = node;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [V=" + V + ", node=" + node + "]";
}
}
static Node[] adjList;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
adjList = new Node[V];
int from, to;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
from = sc.nextInt();
to = sc.nextInt();
adjList[from] = new Node(to, adjList[from]);
adjList[to] = new Node(from, adjList[to]);
}
for (Node node : adjList) {
System.out.println(node);
}
sc.close();
}
}입력값과 출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
- 입력값
7
8
0 1
0 2
0 5
0 6
4 3
5 3
5 4
6 4
- 출력결과
Node [V=6, node=Node [V=5, node=Node [V=2, node=Node [V=1, node=null]]]]
Node [V=0, node=null]
Node [V=0, node=null]
Node [V=5, node=Node [V=4, node=null]]
Node [V=6, node=Node [V=5, node=Node [V=3, node=null]]]
Node [V=4, node=Node [V=3, node=Node [V=0, node=null]]]
Node [V=4, node=Node [V=0, node=null]]
무향 그래프를 List로 구현하면 아래와 같다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjacencyList2 {
static List<Integer>[] adjList;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
adjList = new ArrayList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adjList[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
int from, to;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
from = sc.nextInt();
to = sc.nextInt();
adjList[from].add(to);
adjList[to].add(from);
}
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
System.out.println(adjList[i]);
}
sc.close();
}
}입력값과 출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
- 입력값
7
8
0 1
0 2
0 5
0 6
4 3
5 3
5 4
6 4
- 출력 결과
[1, 2, 5, 6]
[0]
[0]
[4, 5]
[3, 5, 6]
[0, 3, 4]
[0, 4]
알고리즘에서 가중치 그래프를 인접 리스트로 표현할 수 있다.
간선의 연결 간 가중치가 각기 다른 그래프를 가중치 그래프라고 한다.
가중치 그래프를 List로 구현하면 아래와 같다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class WeightAdjacencyList {
static int V, E;
static List<Data>[] graph;
static class Data {
int to, weight;
public Data(int to, int weight) {
super();
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Data [to=" + to + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
V = sc.nextInt();
E = sc.nextInt();
graph = new ArrayList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<Data>();
}
int from, to, weight;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
from = sc.nextInt();
to = sc.nextInt();
weight = sc.nextInt();
graph[from].add(new Data(to, weight));
}
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
System.out.println(graph[i]);
}
sc.close();
}
}입력값과 출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
- 입력값
7
7
0 1 2
0 2 4
0 5 1
4 3 4
5 3 6
5 4 2
6 4 6
- 출력결과
[Data [to=1, weight=2], Data [to=2, weight=4], Data [to=5, weight=1]]
[]
[]
[]
[Data [to=3, weight=4]]
[Data [to=3, weight=6], Data [to=4, weight=2]]
[Data [to=4, weight=6]]