알고리즘에서 그래프를 dfs로 완전 탐색할 수 있다.
그래프에서 dfs는 아래와 같이 진행된다.
- 시작 정점을 잡고, 해당 정점을 방문한다.
- 해당 정점을 방문했음을 표시한다.
- 방문한 정점의 모든 정점을 살펴본다.
- 살펴보다가 방문하지 않은 정점을 방문할 시 그 정점을 기준으로 1, 2, 3 과정을 반복한다.
알고리즘에서 인접 행렬를 dfs로 완전 탐색할 수 있다.
아래와 같은 그래프가 있다.
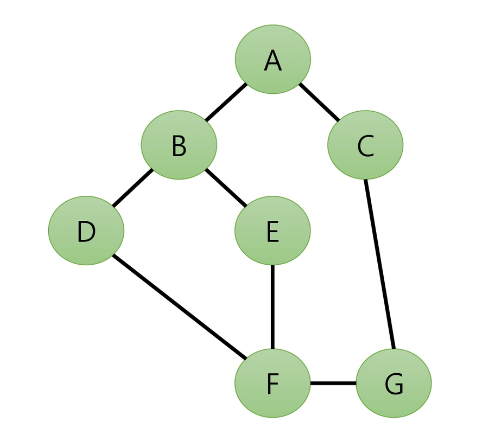
위 그래프가 인접 행렬로 표현되어 있을 때, dfs로 완전 탐색하는 코드는 아래와 같다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MatrixDFS {
static int[][] adjMatrix;
static int V;
static void dfs(int current, boolean[] visited) {
visited[current] = true;
System.out.print((char)(current + 65) + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (adjMatrix[current][i] != 0 && !visited[i]) {
dfs(i, visited);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
adjMatrix = new int[V][V];
int from, to;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
from = sc.nextInt();
to = sc.nextInt();
adjMatrix[from][to] = adjMatrix[to][from] = 1;
}
dfs(0, new boolean[V]);
sc.close();
}
} 입력값과 출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
- 입력값
7
8
0 1
0 2
1 3
1 4
3 5
4 5
5 6
2 6
- 출력 결과
A B D F E G C
알고리즘에서 인접 리스트를 dfs로 완전 탐색할 수 있다.
위 그래프가 Node 클래스를 직접 구현한 인접 리스트로 표현되어 있을 때,
dfs로 완전 탐색하는 코드는 아래와 같다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ListBFS {
static Node[] adjList;
static int V;
static class Node {
int V;
Node node;
public Node(int v, Node node) {
super();
V = v;
this.node = node;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [V=" + V + ", node=" + node + "]";
}
}
static void dfs(int current, boolean[] visited) {
visited[current] = true;
System.out.print((char)(current + 65) + " ");
for (Node node = adjList[current]; node != null; node = node.node) {
if (visited[node.V] != true) {
dfs(node.V, visited);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
adjList = new Node[V];
int from, to;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
from = sc.nextInt();
to = sc.nextInt();
adjList[from] = new Node(to, adjList[from]);
adjList[to] = new Node(from, adjList[to]);
}
dfs(0, new boolean[V]);
sc.close();
}
}입력값과 출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
- 입력값
7
8
0 1
0 2
1 3
1 4
3 5
4 5
5 6
2 6
- 출력 결과
A C G F E B D
위 그래프가 List를 이용한 인접 리스트로 표현되어 있을 때,
dfs로 완전 탐색하는 코드는 아래와 같다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ListDFS2 {
static List<Integer>[] adjList;
static int V;
static void dfs(int current, boolean[] visited) {
visited[current] = true;
System.out.print((char)(current + 65) + " ");
for (int value : adjList[current]) {
if (visited[value] != true) {
dfs(value, visited);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
adjList = new ArrayList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adjList[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
int from, to;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
from = sc.nextInt();
to = sc.nextInt();
adjList[from].add(to);
adjList[to].add(from);
}
dfs(0, new boolean[V]);
sc.close();
}
}입력값과 출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
- 입력값
7
8
0 1
0 2
1 3
1 4
3 5
4 5
5 6
2 6
- 출력 결과
A B D F E G C
