알고리즘에서 최소 신장 트리를 활용할 수 있다.
신장 트리란 n개의 정점으로 이루어진 무향 그래프에서 n개의 정점과 n-1개의 간선으로 이뤄진 트리이다.
최소 신장 트리란 무향 가중치 그래프에서 간선들의 가중치 합이 최소인 신장 트리이다.
최소 신장 트리의 예시는 아래와 같다.
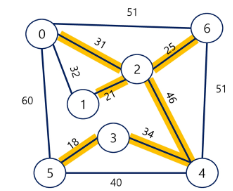
최소 신장 트리가 이뤄질 모든 경우를 찾게되면 그 경우의 수는 eCv-1이다.
즉, 간선이 30개이고 정점이 16개면 30C15로 시간 복잡도가 터지게 된다.
그래서 KRUSKAL 알고리즘과 PRIM 알고리즘을 활용한다.
최소 신장 트리를 구하는 데 KRUSKAL 알고리즘을 활용할 수 있다.
KRUSKAL 알고리즘은 아래와 같다.
- 모든 간선을 가중치에 따라 오름차순으로 정렬한다.
- 가중치가 가장 낮은 간선부터 선택하며 트리를 증가시킨다.
(이 때, 사이클이 존재하면 그 다음 간선으로 넘어간다.)- n-1개의 정점이 선택될 때까지 2를 반복한다.
정점의 서로소 집합이 합쳐지지 않으면 사이클이라고 생각하여 사이클을 검사한다.
이를 구현하면 아래와 같다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Kruskal {
static int[] set;
static int n;
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int from;
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
super();
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge e) {
return this.weight - e.weight;
}
}
static void makeSet() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
set[i] = i;
}
}
static boolean unionSet(int first, int second) {
int one = findSet(first);
int two = findSet(second);
if (one == two) {
return false;
}
set[two] = one;
return true;
}
static int findSet(int find) {
if (set[find] == find) {
return find;
}
return set[find] = findSet(set[find]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int order = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
Edge[] edgeList = new Edge[order];
for (int i = 0; i < order; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int first = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int second = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int third = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
edgeList[i] = new Edge(first, second, third);
}
Arrays.sort(edgeList);
set = new int[n];
makeSet();
int result = 0;
int check = 0;
for (Edge edge : edgeList) {
if (unionSet(edge.from, edge.to)) {
result += edge.weight;
check++;
if (check == n - 1) {
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}입력값과 출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
- 입력값
7 11
0 1 32
0 2 31
0 5 60
0 6 51
1 2 21
2 4 46
2 6 25
3 4 34
3 5 18
4 5 40
4 6 51
- 출력 결과
175
이 때, 여러 연산 중 정렬이 Elog(E)로 시간 복잡도가 가장 크다.
따라서 KRUSKAL 알고리즘은 간선 수가 많으면 효율적이지 않다.
최소 신장 트리를 구하는 데 Prim 알고리즘을 활용할 수 있다.
Prim 알고리즘은 아래와 같다.
- 초기에는 모든 정점 간 관계가 무한대이다.
- 임의의 정점을 하나 선택한다.
- 선택한 정점(들)과 인접하는 정점(들)의 최소 비용을 갱신한다.
- 선택한 정점(들)과 인접한 정점(들) 중 최소 비용으로 연결되는 정점 하나를 선택한다.
- 모든 정점이 연결될 때까지 3, 4를 반복한다.
이를 구현하면 아래와 같다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Prim {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[][] arr = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
boolean[] V = new boolean[n];
int[] D = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
D[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
D[0] = 0;
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int minValue = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int minIndex = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (V[j] == false && D[j] < minValue) {
minValue = D[j];
minIndex = j;
}
}
V[minIndex] = true;
result += minValue;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (V[j] == true || arr[minIndex][j] == 0) {
continue;
}
if (D[j] > arr[minIndex][j]) {
D[j] = arr[minIndex][j];
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}입력값과 출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
- 입력값
7
0 32 31 0 0 60 51
32 0 21 0 0 0 0
31 21 0 0 46 0 25
0 0 0 0 34 18 0
0 0 46 34 0 40 51
60 0 0 18 40 0 0
51 0 25 0 51 0 0
- 출력 결과
175
이 때의 시간 복잡도는 O(V^2)이다.
따라서 간선 수가 많으면 비효율적인 KRUSKAL 알고리즘의 단점을 극복했다.
PRIM 알고리즘을 우선순위 큐로 구현하면 아래와 같다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class PrimPriority {
static class Data implements Comparable<Data> {
int idx;
int weight;
public Data(int idx, int weight) {
super();
this.idx = idx;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Data d) {
return this.weight - d.weight;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[][] arr = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
boolean[] v = new boolean[n];
int[] d = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
d[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
int start = 3;
d[start] = 0;
PriorityQueue<Data> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(new Data(start, 0));
int result = 0;
int res = 0;
while(!pq.isEmpty()) {
Data data = pq.poll();
if (v[data.idx] == true) {
continue;
}
v[data.idx] = true;
result += data.weight;
res++;
if (res == n) {
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (v[i] == false && arr[data.idx][i] != 0 && arr[data.idx][i] < d[i]) {
d[i] = arr[data.idx][i];
pq.offer(new Data(i, d[i]));
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}입력값과 출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
- 입력값
7
0 32 31 0 0 60 51
32 0 21 0 0 0 0
31 21 0 0 46 0 25
0 0 0 0 34 18 0
0 0 46 34 0 40 51
60 0 0 18 40 0 0
51 0 25 0 51 0 0
- 출력 결과
175
