알고리즘에서 이항 계수를 구하는 데 DP를 사용할 수 있다.
nCk는 n-1Ck-1 + n-1Ck로 정의된다. 따라서 nCk를 구하는 재귀 함수는 아래와 같다.
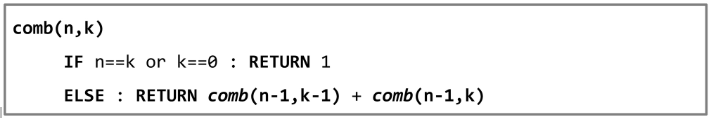
위 함수는 순수 함수이다.
이 때, 아래처럼 호출의 중복이 일어난다.
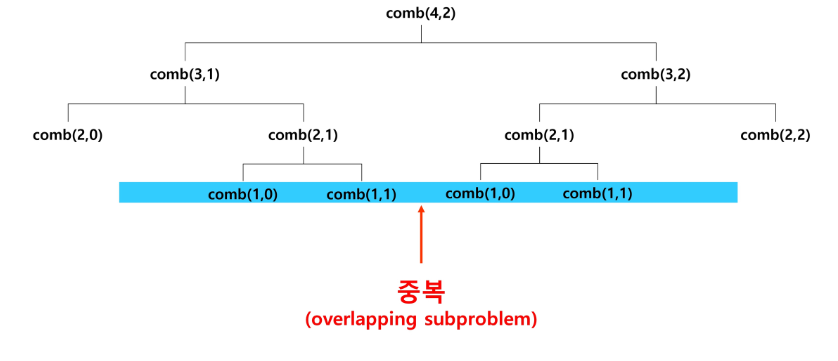
따라서 이를 해결하고자 메모이제이션을 활용할 수 있다. 이를 활용한 코드는 아래와 같다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class KnapsackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int[][] arr = new int[31][31];
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
arr[i][i] = 1;
arr[i][1] = i;
}
for (int i = 3; i <= 30; i++) {
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) {
arr[i][j] = arr[i-1][j-1] + arr[i-1][j];
}
}
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
System.out.println(arr[M][N]);
}
}입력값은 아래와 같다.
30 15
출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
155117520
이러면 일반 조합으로는 무리가 있던 30C15를 무리 없이 구할 수 있다.
알고리즘에서 동전 거스름돈을 구할 때 DP를 사용할 수 있다.
동전 거스름돈을 주는 문제 정의는 아래와 같다.
최소한의 동전을 사용해 고객에게 거스름돈을 준다.
이는 동전들이 배수가 아니라면 탐욕 기법으로 문제를 풀 수 없다.
따라서 DP로 이를 풀어보면 아래와 같다.
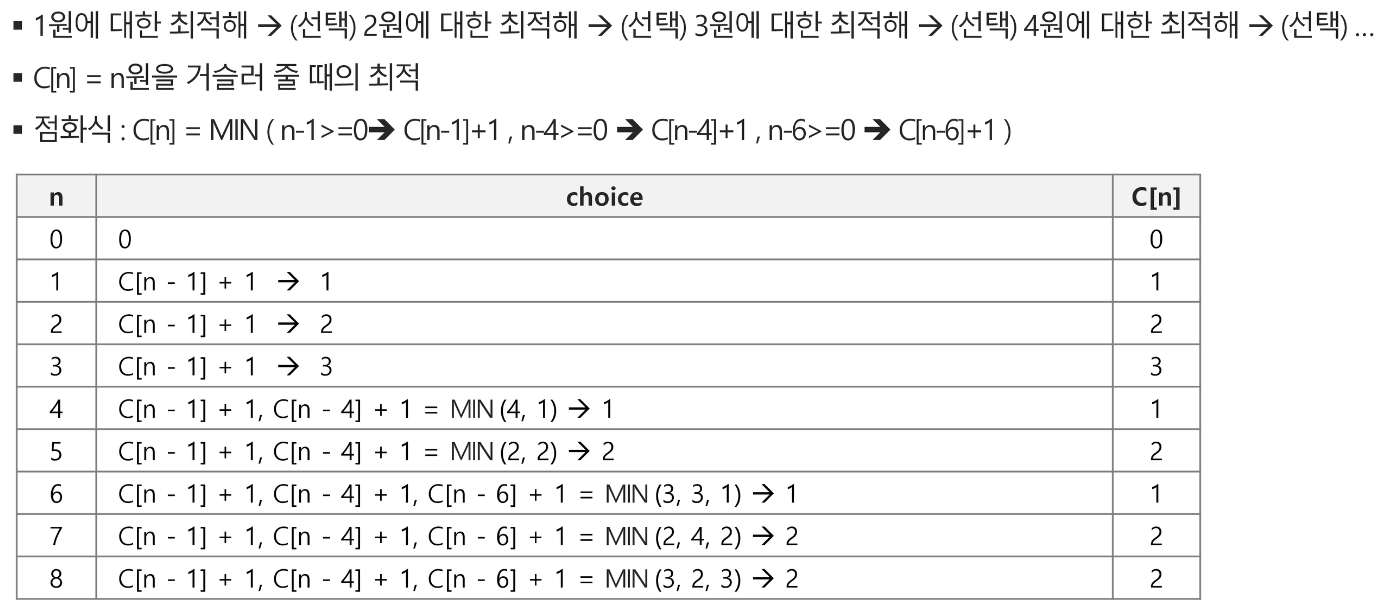
동전 거스름돈 문제를 실제로 구현하면 아래와 같다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Coin {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int target = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[] arr = new int[N];
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
Arrays.sort(arr);
int[] dynamic = new int[target+1];
Arrays.fill(dynamic, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dynamic[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= target; i++) {
int threshold = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (i >= arr[j]) {
threshold = j;
continue;
}
break;
}
for (int j = 0; j <= threshold; j++) {
dynamic[i] = Math.min(dynamic[i], dynamic[i - arr[j]] + 1);
}
}
System.out.println(dynamic[target]);
}
}입력값은 아래와 같다.
8
3
1 4 6
출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
2
