lower_bound
- 이진탐색 기반의 탐색 방법
- 찾고자 하는 key 값이 없으면 key 값보다 큰 가장 작은 정수(크면서 가장 가까운) 값을 찾는다.
arr[mid-1] < key && arr[mid] >= key인 mid를 찾는다.
// 벡터는 (오름차순)정렬되어 있어야 함.
int lower_bound(const vector<int>& vec, int start, int end, int key) {
int ret = vec.size();
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
//if (vec[mid] == key)
// return mid;
// 벡터에 key가 중복되게 존재할 수 있음.
//else if (vec[mid] > key) {
if(vec[mid] >= key){
ret = mid;
end = mid - 1;
}
else
start = mid + 1;
}
return ret;
}upper_bound
- 이진탐색 기반의 탐색 방법
찾고자 하는 key 값이 없으면
key 값보다 큰 가장 작은 정수(크면서 가장 가까운) 값을 찾는다.
=> key 값을 초과하는 숫자가 배열 몇 번째에서 처음 등장하는지 탐색arr[mid-1] <=key && arr[mid] > key인 mid를 찾는다.
int my_upper_bound(const vector<int>& vec, int start, int end, int key) {
int ret = vec.size();
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (vec[mid] == key)
start = mid + 1;
else if (vec[mid] > key) {
ret = mid;
end = mid - 1;
}
else
start = mid + 1;
}
return ret;
}예제
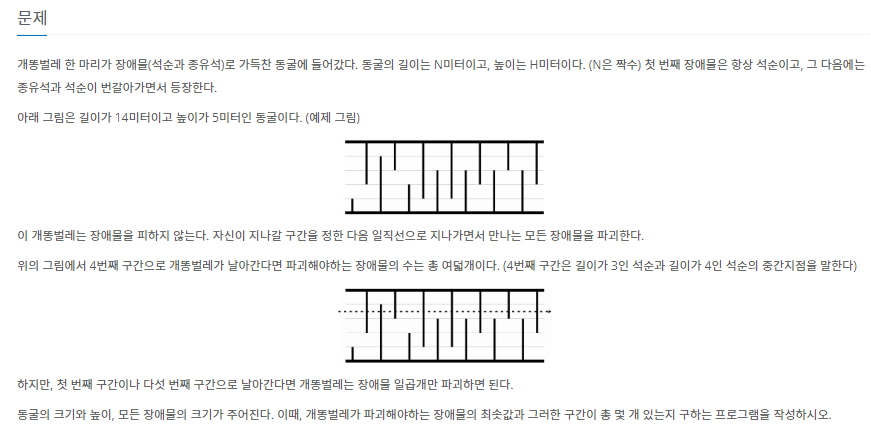
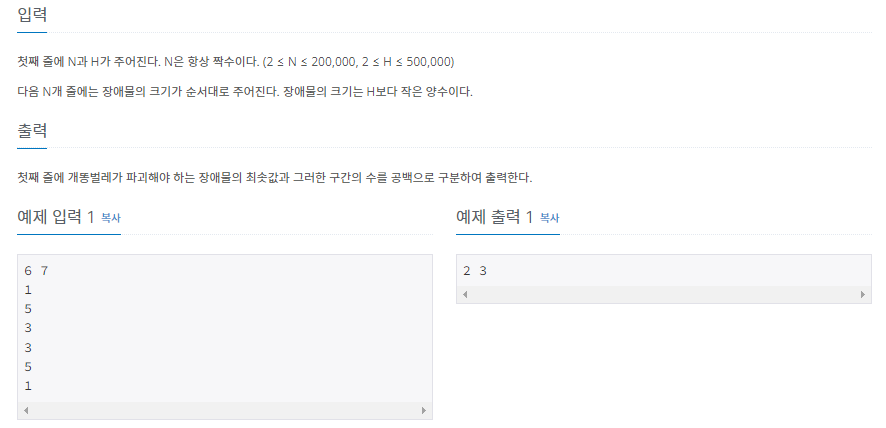
백준(3020): 개똥벌레
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int N, H;
int my_lower_bound(const vector<int>& vec, int start, int end, int key) {
int ret = vec.size();
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
//if (vec[mid] == key)
// return mid;
// key가 중복되게 나올 수 있다..
//else if (vec[mid] > key) {
if(vec[mid] >= key){
ret = mid;
end = mid - 1;
}
else
start = mid + 1;
}
return ret;
}
int my_upper_bound(const vector<int>& vec, int start, int end, int key) {
int ret = vec.size();
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (vec[mid] == key)
//return mid;
start = mid + 1;
else if (vec[mid] > key) {
ret = mid;
end = mid - 1;
}
else
start = mid + 1;
}
return ret;
}
pair<int, int> solution(vector<int>& bottom, vector<int>& top) {
int minContactNum = 1e9;
int cnt = 0;
sort(bottom.begin(), bottom.end());
sort(top.begin(), top.end());
for (int nowH = 1; nowH <= H; nowH++) {
// 내가 구현한 lower_bound, upper_bound 함수 사용
int contactBottomNum = (N / 2) - my_lower_bound(bottom, 0, N / 2 - 1, nowH);
int contactTopNum = (N / 2) - my_upper_bound(top, 0, N / 2 - 1, H - nowH);
// 표준 라이브러리 제공 lower_bound, upper_bound 함수 사용
//int contactBottomNum = (N / 2) - (lower_bound(bottom.begin(), bottom.end(), nowH) - bottom.begin());
//int contactTopNum = (N / 2) - (upper_bound(top.begin(), top.end(), H-nowH) - top.begin());
int totalContactNum = contactBottomNum + contactTopNum;
if (minContactNum > totalContactNum) {
minContactNum = totalContactNum;
cnt = 1;
}
else if (minContactNum == totalContactNum) {
cnt++;
}
}
return { minContactNum, cnt };
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> H;
vector<int> bottom(N / 2);
vector<int> top(N / 2);
for (int i = 0; i < N / 2; i++) {
cin >> bottom[i];
cin >> top[i];
}
pair<int, int> result = solution(bottom, top);
cout << result.first << " " << result.second << endl;
return 0;
}