source: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/12764, https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/13334
아래 두 우선순위 큐 응용 문제의 공통점으로는 모든 인덱스를 선형으로 탐색해야 하는 오버헤드를 우선순위 큐를 사용함으로써 줄이는 것에 초점을 두었다.
우선순위 큐를 몇 개 사용할 것인지, 우선순위 큐의 힙 정렬 전략은 어떻게 짜야할 것인지가 문제 풀이의 포인트가 되었다.
예제 문제1: 싸지방에 간 준하_백준
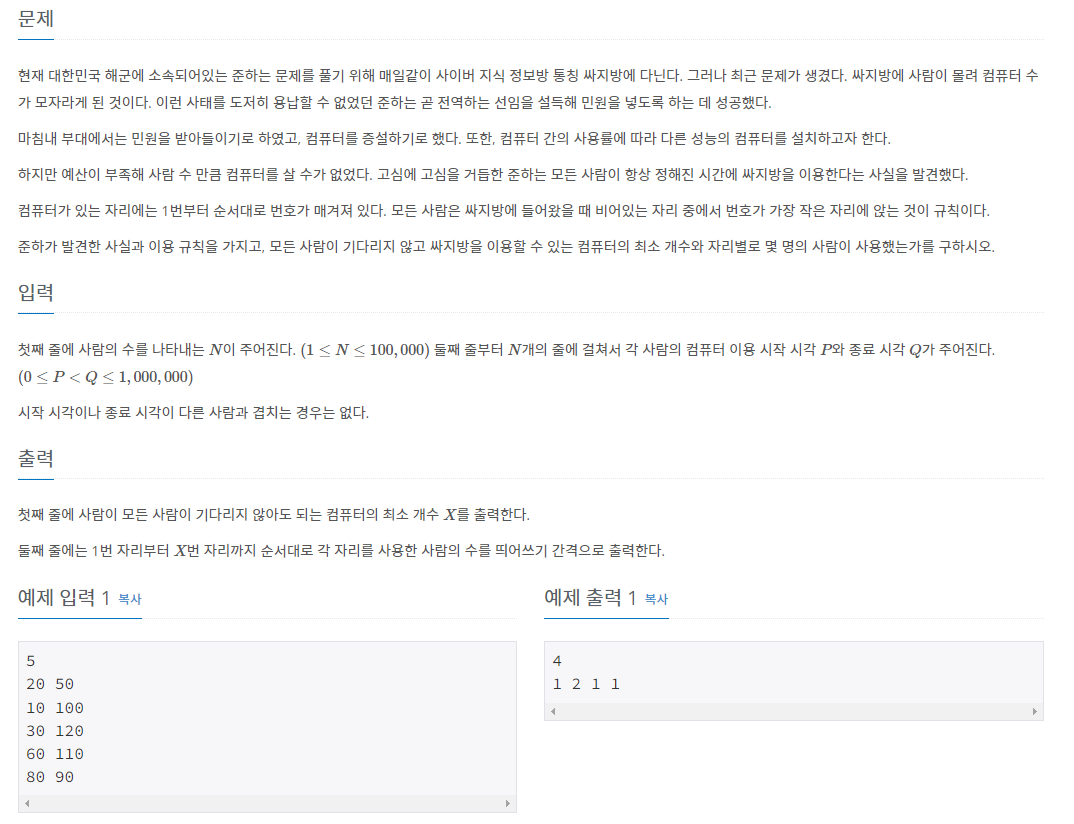
풀이
// 사실
// : 모든 사람이 항상 정해진 시간에 싸지방을 이용
// 규칙
// : 모든 사람은 싸지방에 들어왔을 때 비어있는 자리 중에서 번호가 가장 작은 자리에 앉는 것이 규칙
// 출력
// (1) 모든 사람이 기다리지 않고 싸지방을 이용할 수 있는 컴퓨터의 최소 수
// (2) 자리별로 몇명의 사람들이 사용했는지
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int N;
vector<pair<int, int>> UsingTime;
bool compare(const pair<int, int>& p1, const pair<int, int>& p2) {
if (p1.first != p2.first)
return p1.first < p2.first;
else
return p1.second < p2.second;
}
struct cmp {
bool operator()(const pair<int, int>& p1, const pair<int, int>& p2) {
// 1) 종료 시간 기준 오름차순
if (p1.first != p2.first)
return p1.first > p2.first;
// 2) 종료 시간이 같다면, 좌석 번호가 작은 것이 우선
else
return p1.second > p2.second;
}
};
struct cmp2 {
bool operator()(const pair<int, int>& p1, const pair<int, int>& p2) {
// 좌석 번호 기준 최소 힙
return p1.second > p2.second;
}
};
vector<int> solution() {
// (1) 시작 시간 기준으로 오름차순 정렬
sort(UsingTime.begin(), UsingTime.end(), compare);
// (2) 오름차순 정렬된 벡터를 탐색하며 동시에,
// 두 개의 우선순위 큐(pq, readyq)를 이용하여 최소 컴퓨터 자리 생성 및 할당을 진행한다.
int sequence = 0; // 할당 시퀀스
vector<int> retVec(1000000, 0);
// pq는 현재 점유중인 컴퓨터 좌석들을 나타낸다.
// 종료시간 기준 최소힙이다.
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, cmp> pq;
// readyq는 비어있는 컴퓨터 좌석들을 나타낸다.
// 좌석 번호 기준 최소힙이다.
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, cmp2> readyq;
for (int i = 0; i < UsingTime.size(); i++) {
int start = UsingTime[i].first;
int end = UsingTime[i].second;
// 모두 빈좌석이라면 가장 첫번째 번호인 0번에 해당하는 자리에 앉는다.
if (pq.empty()) {
pq.push({ end, 0 });
retVec[0]++;
}
else {
// 새로 온 사람이 앉을 수 있는 자리들을 정리한다(readyq로 보낸다).
while (!pq.empty()) {
int topEnd = pq.top().first;
int comNum = pq.top().second;
if (topEnd < start) {
readyq.push(pq.top());
pq.pop();
}
else
break;
}
// 빈 좌석이 하나도 없다면 새로운 좌석을 만든다.
if (readyq.empty()) {
sequence++;
pq.push({ end, sequence });
retVec[sequence]++;
}
// 빈 좌석들 중 좌석 번호가 가장 작은 좌석을 택하여 앉는다.
else {
int comNum = readyq.top().second;
readyq.pop();
pq.push({ end, comNum });
retVec[comNum]++;
}
}
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < retVec.size(); i++) {
if (retVec[i] == 0)
break;
cnt++;
}
retVec.resize(cnt);
return retVec;
}
int main() {
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int start, end;
cin >> start >> end;
UsingTime.push_back({ start, end });
}
vector<int> answerVec = solution();
// (1) 최소 컴퓨터 대수
cout << answerVec.size() << endl;
// (2) 각 컴퓨터당 사용한 사람 수
for (int i = 0; i < answerVec.size(); i++) {
if (answerVec[i] == 0)
break;
cout << answerVec[i] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}예제 문제2: 싸지방에 간 준하_백준

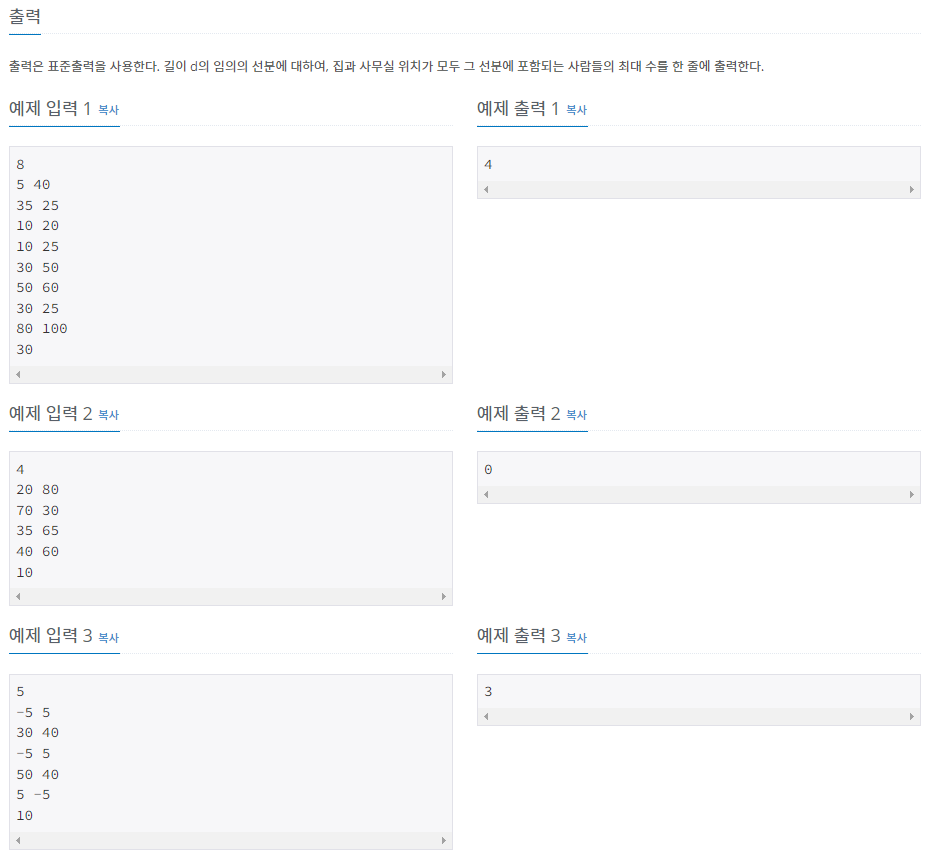
풀이
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int N;
vector<pair<int, int>> PersonLoc;
int LEN;
struct cmp {
bool operator()(int a, int b) {
return a > b; // 오름차순 정렬
}
};
bool compare(const pair<int, int>& p1, const pair<int, int>& p2) {
if (p1.second != p2.second)
return p1.second < p2.second;
else
return p1.first < p2.first;
}
int solution() {
int maxCnt = 0;
// (1) 도착 위치를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬한다.
sort(PersonLoc.begin(), PersonLoc.end(), compare);
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, cmp> pq;
// (2-1) 도착 위치 기준으로 오름차순 정렬되어 있는 것들을 탐색한다.
for (int i = 0; i < PersonLoc.size(); i++) {
int start = PersonLoc[i].first;
int end = PersonLoc[i].second;
// 길이가 기준 길이보다 길다면
if (end - start > LEN)
continue;
else
pq.push(start);
// (2-2) pq에 담겨있것들은 후보군이다.
// 후보들의 시작점을 비교하며, 제거할 수 있는 후보는 제거한다.
while (!pq.empty()) {
int topStart = pq.top();
if (topStart < end - LEN)
pq.pop();
else {
maxCnt = max(maxCnt, static_cast<int>(pq.size()));
break;
}
}
}
return maxCnt;
}
int main() {
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int homeLoc, officeLoc;
cin >> homeLoc >> officeLoc;
if (homeLoc < officeLoc)
PersonLoc.push_back({ homeLoc, officeLoc });
else
PersonLoc.push_back({ officeLoc, homeLoc });
}
cin >> LEN;
int answer = solution();
cout << answer << endl;
return 0;
}