깊이를 내려가면서 브랜치가 뻗어나가는 방식의 재귀호출 시간복잡도
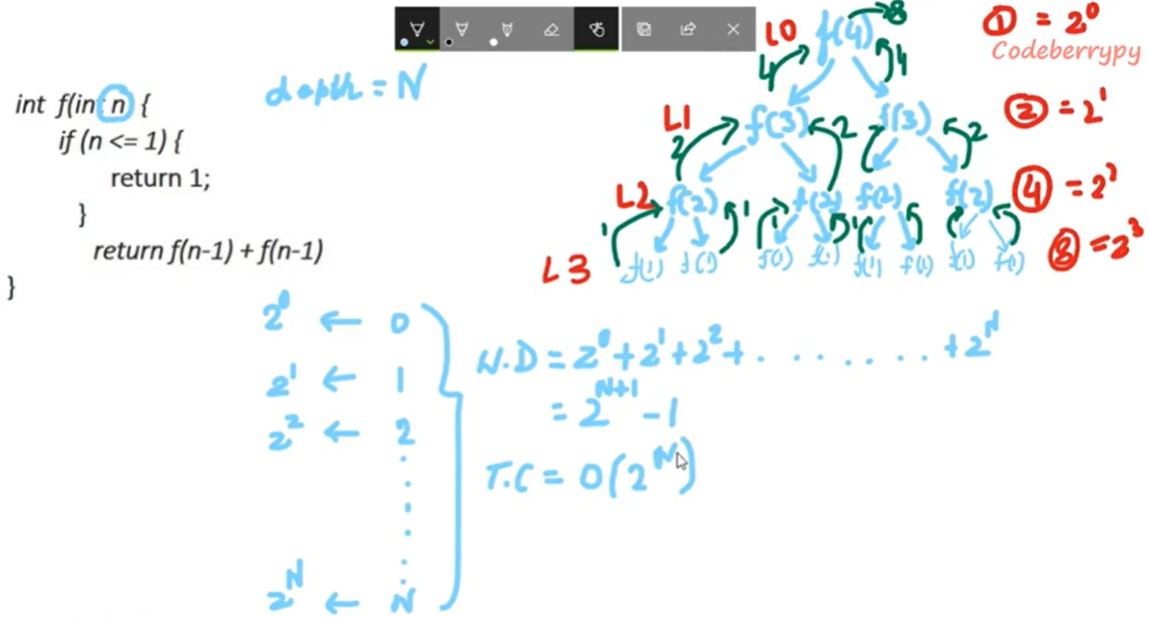
source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NyV0d5QadWM
=> 시간 복잡도: O(branch^depth)
ex) 재귀호출 방식의 피보나치 수열 시간복잡도
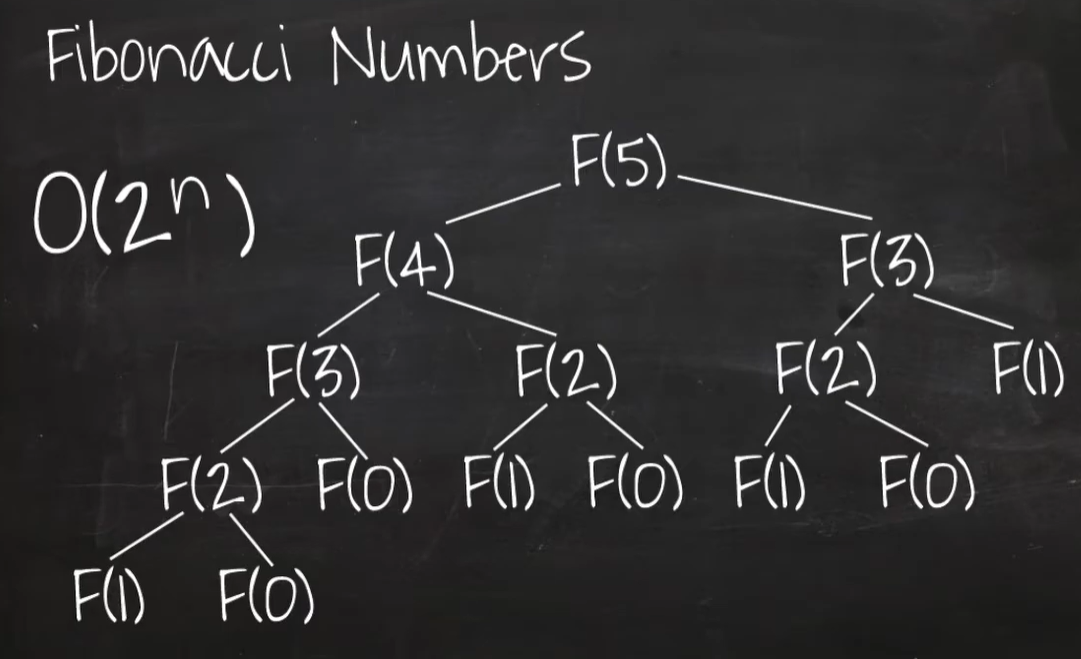
=> O(2^n)
source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VcCkPrGaKrs&t=3s
(백준) 2×n 타일링 2

_
source: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/117271) 단순 DFS(재귀) 풀이
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int MOD = 10007;
int N;
int DFS(int width) {
// 종료조건
if (width > N)
return 0;
else if (width == N)
return 1; // 한가지 방법 완성
// 탐색
int totalCnt = 0;
// 3가지 방법 탐색
// 1) 1x2 직사각형
if (width + 1 <= N) {
totalCnt += DFS(width + 1);
}
// 2) 2x2 정사각형
if (width + 2 <= N) {
totalCnt += DFS(width + 2);
}
// 3) 2x1 직사각형 두개
if (width + 2 <= N) {
totalCnt += DFS(width + 2);
}
return totalCnt % MOD;
}
int solution() {
// DFS 방식
int answer = DFS(0) % MOD;
return answer;
}
int main() {
cin >> N;
cout << solution() << endl;
}==> 시간초과!
시간 복잡도: O(3^n)
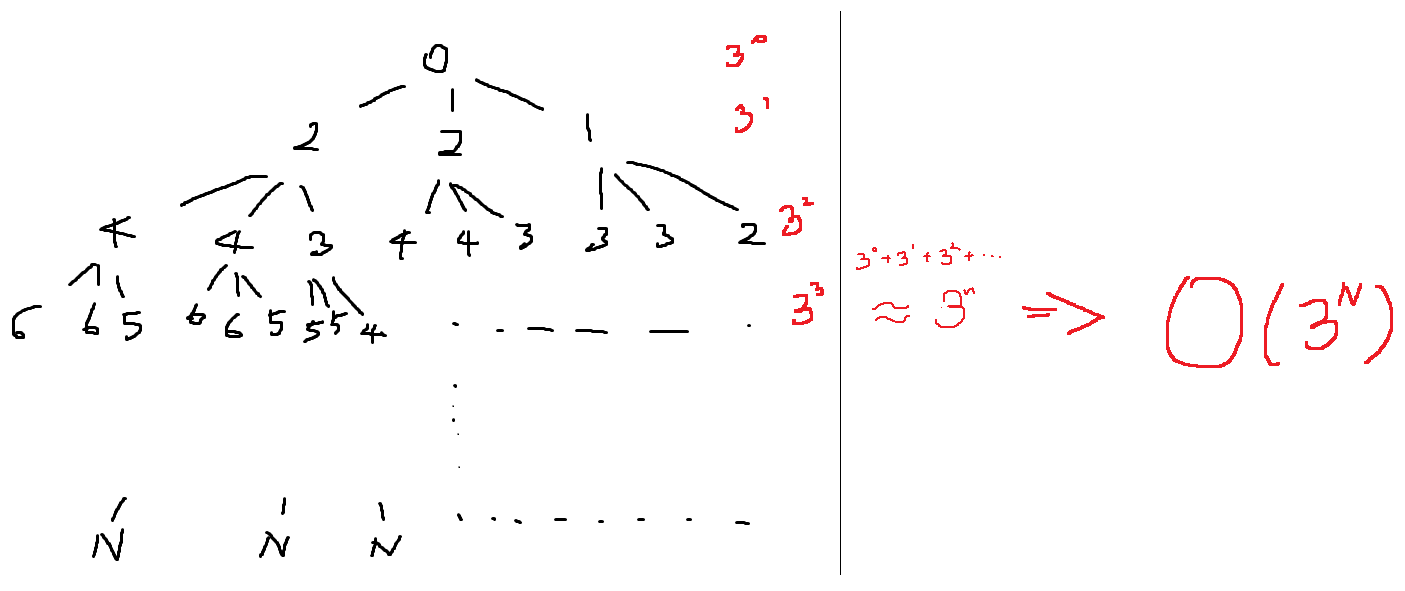
2) 메모제이션 활용
// 메모제이션 기법
int DP[1000 + 1];
int DFS(int width) {
// 메모 활용
if (DP[width])
return DP[width];
// 종료조건
if (width > N)
return 0;
else if (width == N)
return 1; // 한가지 방법 완성
// 탐색
int totalCnt = 0;
// 3가지 방법 탐색
// 1) 1x2 직사각형
if (width + 1 <= N) {
totalCnt += DFS(width + 1);
}
// 2) 2x2 정사각형
if (width + 2 <= N) {
totalCnt += DFS(width + 2);
}
// 3) 2x1 직사각형 두개
if (width + 2 <= N) {
totalCnt += DFS(width + 2);
}
// memozation
DP[width] = totalCnt % MOD;
return totalCnt % MOD;
}=> 통과
+) Bottom-Up 방식
=> 시간 복잡도: O(n)
int BOTTOM_UP() {
// 초기화
DP[0] = 0;
DP[1] = 1;
DP[2] = 3;
for (int i = 3; i <= N; i++) {
// 1x2 // 2x2 사각형, 2*1 사각형(두개)
DP[i] = (DP[i - 1] + DP[i - 2] * 2) % MOD;
}
return DP[N] % MOD;
}
int solution() {
// DFS 방식(top-down 방식)
//int answer = DFS(0) % MOD;
// Bottom-up 방식
int answer = BOTTOM_UP() % MOD;
return answer;
}