문제
(취익)B100 요원, 요란한 옷차림을 한 서커스 예술가 한 쌍이 한 도시의 거리들을 이동하고 있다. 너의 임무는 그들이 어디로 가고 있는지 알아내는 것이다. 우리가 알아낸 것은 그들이 s지점에서 출발했다는 것, 그리고 목적지 후보들 중 하나가 그들의 목적지라는 것이다. 그들이 급한 상황이기 때문에 목적지까지 우회하지 않고 최단거리로 갈 것이라 확신한다. 이상이다. (취익)
어휴! (요란한 옷차림을 했을지도 모를) 듀오가 어디에도 보이지 않는다. 다행히도 당신은 후각이 개만큼 뛰어나다. 이 후각으로 그들이 g와 h 교차로 사이에 있는 도로를 지나갔다는 것을 알아냈다.
이 듀오는 대체 어디로 가고 있는 것일까?
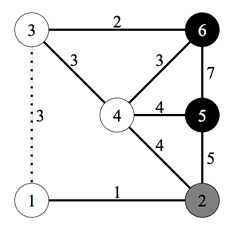
예제 입력의 두 번째 케이스를 시각화한 것이다. 이 듀오는 회색 원에서 두 검은 원 중 하나로 가고 있고 점선으로 표시된 도로에서 냄새를 맡았다. 따라서 그들은 6으로 향하고 있다.
입력
첫 번째 줄에는 테스트 케이스의 T(1 ≤ T ≤ 100)가 주어진다. 각 테스트 케이스마다
첫 번째 줄에 3개의 정수 n, m, t (2 ≤ n ≤ 2 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 50 000 and 1 ≤ t ≤ 100)가 주어진다. 각각 교차로, 도로, 목적지 후보의 개수이다.
두 번째 줄에 3개의 정수 s, g, h (1 ≤ s, g, h ≤ n)가 주어진다. s는 예술가들의 출발지이고, g, h는 문제 설명에 나와 있다. (g ≠ h)
그 다음 m개의 각 줄마다 3개의 정수 a, b, d (1 ≤ a < b ≤ n and 1 ≤ d ≤ 1 000)가 주어진다. a와 b 사이에 길이 d의 양방향 도로가 있다는 뜻이다.
그 다음 t개의 각 줄마다 정수 x가 주어지는데, t개의 목적지 후보들을 의미한다. 이 t개의 지점들은 서로 다른 위치이며 모두 s와 같지 않다.교차로 사이에는 도로가 많아봐야 1개이다. m개의 줄 중에서 g와 h 사이의 도로를 나타낸 것이 존재한다. 또한 이 도로는 목적지 후보들 중 적어도 1개로 향하는 최단 경로의 일부이다.
출력
테스트 케이스마다
- 입력에서 주어진 목적지 후보들 중 불가능한 경우들을 제외한 목적지들을 공백으로 분리시킨 오름차순의 정수들로 출력한다.
예제 입&출력
소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private static int n, m, t;
private static int s, g, h;
private static List<Node>[] lists;
private static int[] dist;
private static boolean[] visit;
private static List<Integer> destinations;
private static final int INF = 50_000_000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
int tc = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
while ((tc--) > 0) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 정점
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 간선
t = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 목적지 갯수
lists = new ArrayList[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
lists[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
dist = new int[n + 1];
visit = new boolean[n + 1];
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
s = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 시작점
g = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 무조건 지나가는 정점 1
h = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 무조건 지나가는 정점 2
while ((m--) > 0) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int cost = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
/**
* 무조건 지나가는 정점에 해당하는 간선이면 가중치를 홀수로,
* 그렇지 않다면 가중치를 짝수로
*/
if ((a == g && b == h) || (a == h && b == g)) {
lists[a].add(new Node(b, cost * 2 - 1));
lists[b].add(new Node(a, cost * 2 - 1));
} else {
lists[a].add(new Node(b, cost * 2));
lists[b].add(new Node(a, cost * 2));
}
}
destinations = new ArrayList<>(t);
while ((t--) > 0) {
destinations.add(Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()));
}
/**
* 다익스트라 알고리즘을 통해서 시작점으로부터의 최단경로의 dist[]를 구하고
* 목적지 후보가 되는 곳들의 dist[목적지]가 홀 수 일때 정답
*/
getAns(s);
Collections.sort(destinations);
for (Integer destination : destinations) {
if(dist[destination] % 2 != 0) System.out.println(destination);
}
}
}
private static void getAns(int s) {
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
Arrays.fill(visit, false);
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add(new Node(s, 0));
dist[s] = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node node = pq.poll();
int cur = node.next;
if (!visit[cur]) visit[cur] = true;
for (Node nNode : lists[cur]) {
if (!visit[nNode.next] && dist[nNode.next] > dist[cur] + nNode.cost) {
dist[nNode.next] = dist[cur] + nNode.cost;
pq.add(new Node(nNode.next, dist[nNode.next]));
}
}
}
}
private static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int next;
int cost;
public Node(int next, int cost) {
this.next = next;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.cost - o.cost;
}
}
}
Comment
- 전형적인 다익스트라 알고리즘이지만 가중치에 대한 조건 부여를 생각하기가 오래 걸렸다.
- 코딩에 대한 이해는 주석을 통해 알아보자.
