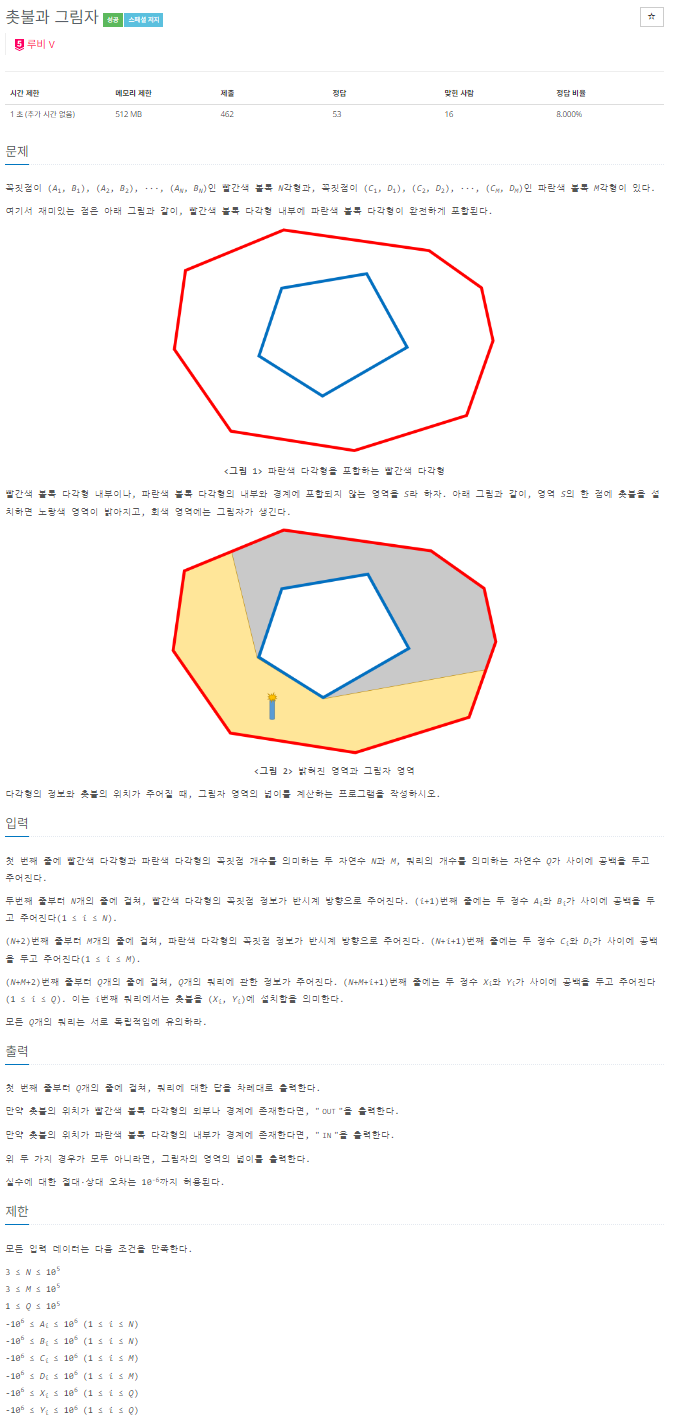
문제 접근 방법
-
다각형 포함 여부 판별: 주어진 점이 빨간색 다각형이나 파란색 다각형 내부에 포함되는지를 확인해야 한다. 이 작업을 위해 외적(cross product)과 내적(dot product)을 활용한 방향 판별을 이용했다.
-
그림자 영역의 넓이 계산: 주어진 점이 빨간색 다각형 내부에 있으면서 파란색 다각형에는 포함되지 않는 경우, 그림자가 생기는 영역의 넓이를 계산한다. 이를 위해 주어진 점이 두 다각형 사이의 구간에 있을 때, 두 다각형 간 그림자의 넓이를 구하는 방법을 설계했다.
-
효율적인 계산: 다각형의 점 개수와 쿼리 개수가 매우 크기 때문에 모든 연산을 빠르게 수행해야 한다. 점이 다각형 내부에 있는지 판별하거나 그림자 영역을 구할 때 이진 탐색과 기하학적 계산을 조합해 시간 복잡도를 최적화했다.
코드
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
typedef long long int64;
typedef long double float64;
const int MAX_VERTICES = 1e5;
struct Vertex { int64 x, y; };
// 벡터의 외적을 계산하는 함수
int64 calculateCrossProduct(const Vertex& p1, const Vertex& p2, const Vertex& p3) {
return (p2.x - p1.x) * (p3.y - p2.y) - (p2.y - p1.y) * (p3.x - p2.x);
}
// 벡터의 내적을 계산하는 함수
int64 calculateDotProduct(const Vertex& p1, const Vertex& p2, const Vertex& p3) {
return (p2.x - p1.x) * (p3.x - p2.x) + (p2.y - p1.y) * (p3.y - p2.y);
}
// 벡터의 방향을 계산하는 함수
int calculateDirection(const Vertex& p1, const Vertex& p2, const Vertex& p3) {
int64 cross = calculateCrossProduct(p1, p2, p3);
return cross > 0 ? 1 : cross < 0 ? -1 : 0;
}
// 벡터가 교차하는지 확인하는 함수
bool checkIntersection(const Vertex& p1, const Vertex& p2, const Vertex& p3) {
return !calculateDirection(p1, p2, p3) && calculateDotProduct(p1, p3, p2) >= 0;
}
std::vector<Vertex> outerPolygon, innerPolygon;
int64 outerAreaSums[MAX_VERTICES], innerAreaSums[MAX_VERTICES];
int outerVertexCount, innerVertexCount, queryCount;
// 점이 다각형 내에 있는지 판별하는 함수
int isPointInsidePolygon(const std::vector<Vertex>& polygon, const Vertex& point) {
int left = 1, right = polygon.size() - 1, mid, direction;
if (calculateDirection(polygon[0], polygon[left], point) <= 0)
return -1 * !checkIntersection(polygon[0], polygon[left], point);
if (calculateDirection(polygon[0], polygon[right], point) >= 0)
return -1 * !checkIntersection(polygon[0], polygon[right], point);
while (left < right - 1) {
mid = left + right >> 1;
direction = calculateDirection(polygon[0], polygon[mid], point);
if (direction >= 0) left = mid;
else right = mid;
}
direction = calculateDirection(polygon[left], polygon[right], point);
if (direction > 0) return direction;
return -1 * !checkIntersection(polygon[left], polygon[right], point);
}
// 특정 범위 내에서 최대 혹은 최소 경계 인덱스를 반환
int getBoundaryIndex(const std::vector<Vertex>& h, const Vertex& p, int start, int end, bool forward) {
while (start < end) {
int mid = start + end >> 1;
Vertex currentPoint = p, startPoint = h[mid], nextPoint = h[(mid + 1) % h.size()];
if (!forward) std::swap(currentPoint, startPoint);
if (calculateDirection(currentPoint, startPoint, nextPoint) > 0) start = mid + 1;
else end = mid;
}
return start;
}
// 다각형 내부의 특정 범위 내 면적을 계산
int64 calculateInnerArea(const Vertex& point, int& left, int& right) {
left = 0, right = 0;
int directionLeft = calculateDirection(point, innerPolygon[0], innerPolygon[1]);
int directionRight = calculateDirection(point, innerPolygon[0], innerPolygon[innerVertexCount - 1]);
if (directionLeft * directionRight >= 0) {
if (!directionLeft && calculateDotProduct(point, innerPolygon[1], innerPolygon[0]) > 0) left = 1;
if (!directionRight && calculateDotProduct(point, innerPolygon[innerVertexCount - 1], innerPolygon[0]) > 0) left = innerVertexCount - 1;
int start = 0 + !directionLeft, end = innerVertexCount - 1 - !directionRight;
bool forward = calculateDirection(point, innerPolygon[start], innerPolygon[start + 1]) >= 0;
right = getBoundaryIndex(innerPolygon, point, start, end, forward);
if (!calculateDirection(point, innerPolygon[right], innerPolygon[(right + 1) % innerVertexCount]) && calculateDotProduct(point, innerPolygon[(right + 1) % innerVertexCount], innerPolygon[right]) > 0)
right = (right + 1) % innerVertexCount;
} else {
int start = 0, end = innerVertexCount - 1, mid, direction;
bool isLeftSide = directionLeft > 0 && directionRight < 0;
while (start < end - 1) {
mid = start + end >> 1;
direction = calculateDirection(innerPolygon[0], innerPolygon[mid], point);
if (!isLeftSide) direction *= -1;
if (direction > 0) start = mid;
else end = mid;
}
left = getBoundaryIndex(innerPolygon, point, 0, start, isLeftSide);
if (!calculateDirection(point, innerPolygon[left], innerPolygon[(left + 1) % innerVertexCount]) && calculateDotProduct(point, innerPolygon[(left + 1) % innerVertexCount], innerPolygon[left]) > 0)
left = (left + 1) % innerVertexCount;
right = getBoundaryIndex(innerPolygon, point, end, innerVertexCount - 1, !isLeftSide);
if (!calculateDirection(point, innerPolygon[right], innerPolygon[(right + 1) % innerVertexCount]) && calculateDotProduct(point, innerPolygon[(right + 1) % innerVertexCount], innerPolygon[right]) > 0)
right = (right + 1) % innerVertexCount;
}
if (left > right) std::swap(left, right);
int64 area = innerAreaSums[right] - innerAreaSums[left] - calculateCrossProduct(innerPolygon[0], innerPolygon[left], innerPolygon[right]);
int64 triangleArea = calculateCrossProduct(point, innerPolygon[left], innerPolygon[right]);
if (triangleArea < 0) area = innerAreaSums[innerVertexCount - 1] - area - triangleArea, std::swap(left, right);
else area += triangleArea;
return area;
}
// 외부 다각형의 그림자 영역을 계산
std::pair<int64, float64> calculateOuterShadow(const Vertex& point, int& left, int& right, const int leftInner, const int rightInner) {
left = 0, right = 0;
int start = 0, end = outerVertexCount - 1, mid;
float64 leftWing = 0, rightWing = 0;
const Vertex& leftInnerPoint = innerPolygon[leftInner];
const Vertex& rightInnerPoint = innerPolygon[rightInner];
while (start < end - 1) {
mid = start + end >> 1;
if (calculateDirection(outerPolygon[0], outerPolygon[mid], point) >= 0) start = mid;
else end = mid;
}
int startLeft = 0, endLeft = 0;
if (calculateDirection(point, outerPolygon[start], leftInnerPoint) >= 0 && calculateDirection(point, outerPolygon[end], leftInnerPoint) <= 0) {
startLeft = start, endLeft = end;
} else {
if (calculateDirection(outerPolygon[0], point, leftInnerPoint) < 0) startLeft = 0, endLeft = start;
if (calculateDirection(outerPolygon[0], point, leftInnerPoint) > 0) startLeft = end, endLeft = outerVertexCount;
while (startLeft < endLeft - 1) {
mid = startLeft + endLeft >> 1;
if (calculateDirection(point, outerPolygon[mid % outerVertexCount], leftInnerPoint) > 0) startLeft = mid;
else endLeft = mid;
}
}
startLeft %= outerVertexCount, endLeft %= outerVertexCount; left = endLeft;
if (calculateCrossProduct(point, leftInnerPoint, outerPolygon[left])) {
int64 triangleLeft = std::abs(calculateCrossProduct(point, outerPolygon[startLeft], outerPolygon[endLeft]));
int64 areaLeft = std::abs(calculateCrossProduct(point, leftInnerPoint, outerPolygon[startLeft]));
int64 areaRight = std::abs(calculateCrossProduct(point, leftInnerPoint, outerPolygon[endLeft]));
leftWing = triangleLeft * ((float64)areaRight / (areaLeft + areaRight));
}
int startRight = 0, endRight = 0;
if (calculateDirection(point, outerPolygon[start], rightInnerPoint) >= 0 && calculateDirection(point, outerPolygon[end], rightInnerPoint) <= 0) {
startRight = start, endRight = end;
} else {
if (calculateDirection(outerPolygon[0], point, rightInnerPoint) < 0) startRight = 0, endRight = start;
if (calculateDirection(outerPolygon[0], point, rightInnerPoint) > 0) startRight = end, endRight = outerVertexCount;
while (startRight < endRight - 1) {
mid = startRight + endRight >> 1;
if (calculateDirection(point, outerPolygon[mid % outerVertexCount], rightInnerPoint) > 0) startRight = mid;
else endRight = mid;
}
}
startRight %= outerVertexCount, endRight %= outerVertexCount; right = startRight;
if (calculateCrossProduct(point, rightInnerPoint, outerPolygon[right])) {
int64 triangleRight = std::abs(calculateCrossProduct(point, outerPolygon[startRight], outerPolygon[endRight]));
int64 areaRight1 = std::abs(calculateCrossProduct(point, rightInnerPoint, outerPolygon[startRight]));
int64 areaRight2 = std::abs(calculateCrossProduct(point, rightInnerPoint, outerPolygon[endRight]));
rightWing = triangleRight * ((float64)areaRight1 / (areaRight1 + areaRight2));
}
bool isReverse = left > right;
int64 triangleArea = calculateCrossProduct(outerPolygon[left], outerPolygon[right], point);
if (startLeft == startRight) return { -std::abs(triangleArea), leftWing + rightWing };
if (isReverse) std::swap(left, right);
int64 totalArea = outerAreaSums[right] - outerAreaSums[left] - calculateCrossProduct(outerPolygon[0], outerPolygon[left], outerPolygon[right]);
if (isReverse) totalArea = outerAreaSums[outerVertexCount - 1] - totalArea;
totalArea += triangleArea;
return { totalArea, leftWing + rightWing };
}
// 주어진 점에 대한 그림자 영역 계산
float64 calculateShadowArea(const Vertex& point) {
int leftInner, rightInner, leftOuter, rightOuter;
int64 innerArea = calculateInnerArea(point, leftInner, rightInner);
std::pair<int64, float64> outerArea = calculateOuterShadow(point, leftOuter, rightOuter, leftInner, rightInner);
return ((outerArea.first - innerArea) + outerArea.second) * 0.5l;
}
int main() {
std::cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
std::cout << std::fixed;
std::cout.precision(7);
std::cin >> outerVertexCount >> innerVertexCount >> queryCount;
for (int i = 0, x, y; i < outerVertexCount; ++i) {
std::cin >> x >> y;
outerPolygon.push_back({ x, y });
}
for (int i = 2; i < outerVertexCount; ++i) {
outerAreaSums[i] = calculateCrossProduct(outerPolygon[0], outerPolygon[i - 1], outerPolygon[i]);
outerAreaSums[i] = outerAreaSums[i] + outerAreaSums[i - 1];
}
for (int i = 0, x, y; i < innerVertexCount; ++i) {
std::cin >> x >> y;
innerPolygon.push_back({ x, y });
}
for (int i = 2; i < innerVertexCount; ++i) {
innerAreaSums[i] = calculateCrossProduct(innerPolygon[0], innerPolygon[i - 1], innerPolygon[i]);
innerAreaSums[i] = innerAreaSums[i] + innerAreaSums[i - 1];
}
for (int i = 0, x, y; i < queryCount; ++i) {
std::cin >> x >> y;
Vertex queryPoint = { x, y };
if (isPointInsidePolygon(outerPolygon, queryPoint) <= 0) std::cout << "OUT\n";
else if (isPointInsidePolygon(innerPolygon, queryPoint) >= 0) std::cout << "IN\n";
else std::cout << calculateShadowArea(queryPoint) << '\n';
}
}코드 설명
- 벡터의 내적과 외적 계산:
calculateCrossProduct와 calculateDotProduct 함수는 각각 두 벡터의 외적과 내적을 계산하여 다각형의 방향과 위치 관계를 파악하는 데 사용된다.
- 점이 다각형 내에 있는지 확인:
isPointInsidePolygon 함수는 주어진 점이 다각형 내부에 있는지를 확인하는 함수다. 외적과 내적을 이용해 점이 내부에 있는지, 외부에 있는지를 확인한다.
- 다각형의 특정 영역 내 그림자 면적 계산:
calculateInnerArea 함수는 주어진 점이 특정 구간에서 다각형 내에 포함되는지를 계산하고 해당 영역의 면적을 반환한다.
calculateOuterShadow는 외부 다각형 내에서 그림자 영역을 계산하는 함수로, 다각형을 따라 그림자 경계를 계산한다.
- 그림자 영역 계산:
calculateShadowArea 함수는 점의 위치를 기준으로 내부와 외부의 그림자 영역을 계산하여 최종 넓이를 반환한다.
So...
빨간색 다각형과 파란색 다각형이 주어졌을 때, 특정 점에서 생기는 그림자 영역의 넓이를 계산하는 문제를 풀었는데 이 코드에서는 기하학적 알고리즘을 사용해 다각형 내 위치 판별과 그림자 면적 계산을 효율적으로 수행했다. 각 단계에서 벡터 연산을 통해 다각형의 내부, 외부를 판별하고, 경계 부분의 면적을 계산하여 최종 넓이를 구하는 방식이 핵심이다.
