버블링과 캡처링
코드
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>버블링&캡처링</title>
<style>
div {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.one {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: red;
}
.two {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
}
.three {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="one">one
<div class="two">two
<div class="three">three</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const divs = document.querySelectorAll('div');
const showLog = (e) => console.log(e.currentTarget.className);
// 버블링
divs.forEach((div) => {
div.addEventListener('click', showLog);
});
// 캡처링
divs.forEach((div) => {
div.addEventListener('click', showLog, true);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>결과 화면
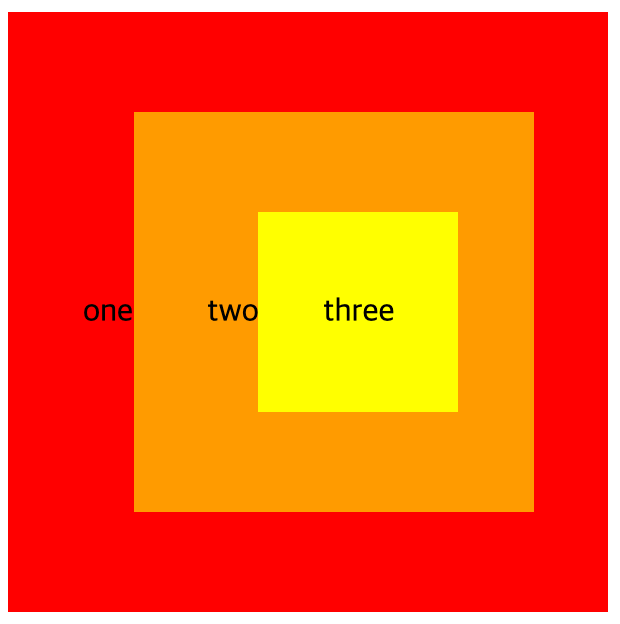
// 캡처링도 켜둔 상태
1) three 요소를 눌렀을 때

2) two 요소를 눌렀을 때

3) one 요소를 눌렀을 때

활용 예시 (Event Delegation)
1) 동적으로 생성된 요소 이벤트 핸들링
예를 들면 Todo list에서 ul에 태그(요소들의 공통 조상)에 이벤트 리스너를 사용하면
동적으로 생성된 하위 li 태그에서도 클릭을 했을 때 버블링으로 인해 상위 ul 태그까지 도달할 수 있기 때문에
이벤트 핸들링이 가능하며 일일이 모든 li 태그에 이벤트 리스너를 달 필요가 없어지게 된다.
2) 팝업창
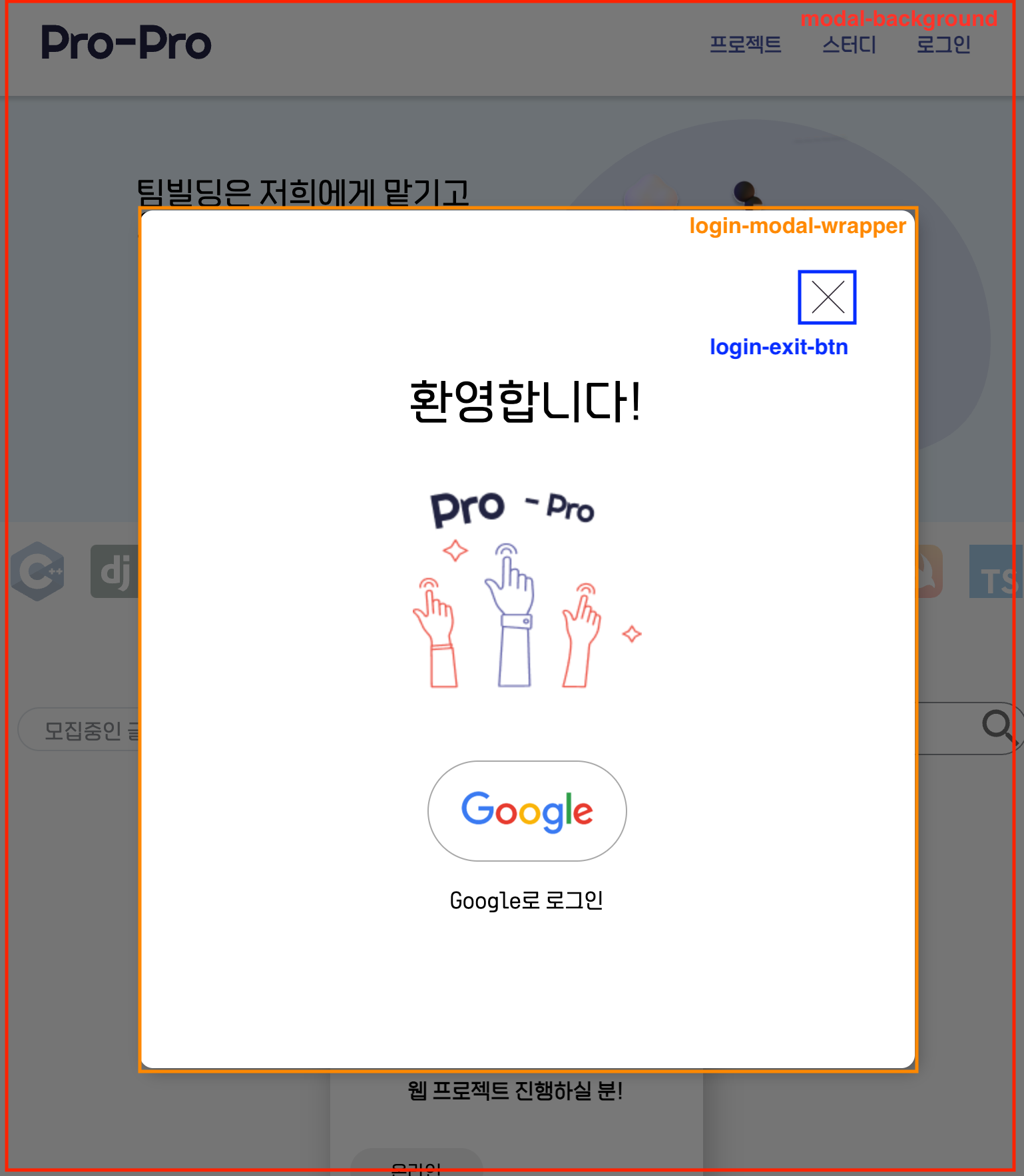
// this.$dom = this.createDom('div', {
// className: 'modal-background hidden',
// });
const $loginModalWrapper = this.$dom.querySelector('.login-modal-wrapper');
this.$dom.addEventListener('click', e => {
// login-modal-wrapper 범위 바깥을 클릭 시 모달창 off
if (!$loginModalWrapper.contains(e.target)) {
this.$dom.classList.add('hidden');
}
// login-exit-btn 버튼 클릭 시 모달창 off
if (e.target.classList.contains('login-exit-btn')) {
this.$dom.classList.add('hidden');
}
});이벤트 발생시 동적으로 생성되는 이벤트 객체 (event)의
event.target
event.currentTarget의 차이를 알아두면 좋다.event.target:
event handler가 붙여진 요소를 참조
event.currentTarget:실제로 이벤트를 발생시킨 요소를 참조
거의 모든 이벤트는 버블링이 되지만 focus 이벤트와 같이 버블링 되지 않는 이벤트도 존재
어떤 이벤트는 버블링이 window까지 도달하기도함 (document까지만 가는 이벤트도 존재)
