오늘은 JWT에 대해서 공부했다. 그리고 JWT 인코딩 과정과 디코딩 과정을 직접 파이썬으로 구현해 보았다. 이번 TIL에서는 이 두 가지를 정리해보고자 한다.
🎟️ JWT (JSON Web Token)
JWT에 대해서는 RFC 7519에 정의되어 있다.
JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe means of representing claims to be transferred between two parties. The claims in a JWT are encoded as a JSON object that is used as the payload of a JSON Web Signature (JWS) structure or as the plaintext of a JSON Web Encryption (JWE) structure, enabling the claims to be digitally signed or integrity protected with a Message Authentication Code (MAC) and/or encrypted.
JSON Web Token은 두 당사자 간에 주고받는 클레임을 나타내는 간결하고, URL-safe한 방법의 하나이다. JWT에 있는 클레임은 JSON 웹 서명 (JWS) 구조의 payload나 JSON 웹 암호화 (JWE) 구조의 평문으로 쓰이는 JSON 객체로 인코딩된다. 이는 클레임이 디지털 서명되거나 메시지 인증 코드 (MAC)를 통해 무결성이 보장되거나 그리고/또는 암호화될 수 있게 한다.
해석은 내 뇌에서 나온 번역과 GPT의 번역을 적절히 섞었다.
위 글에서 알 수 있는 것은, JWT가 URL-safe한 방법으로 인코딩되어 있다는 점과, JWS 구조와 JWE 구조로 나눌 수 있다는 것이다.
클레임
그런데 첫 문장을 보면 두 당사자 간에 주고받는 클레임이라고 했다. 그럼 클레임은 무슨 뜻일까? RFC 7519의 Terminology 부분을 보면 알 수 있다.
A piece of information asserted about a subject. A claim is represented as a name/value pair consisting of a Claim Name and a Claim Value.
한 주체에 대해 주장된 어떤 정보. 클레임은 클레임 이름과 클레임 값으로 구성된 이름/값 쌍으로 표현된다.
조금 더 쉽게 생각해보면, 서버로부터 인증을 받기 위해 서버에 전달하는 주체의 정보라고 볼 수 있겠다.
클레임 이름의 구분
클레임 이름은 3가지로 구분된다.
- Registered Name: 이게 인터넷을 찾아보면 어떤 글은 RFC 7519에 있는 최초 7개를 가리키고, 어떤 글은 IANA의 JSON Web Token 클레임 저장소에 저장되어 있는 클레임 이름 모두를 가리키고 있다. 그래서 원문을 남겨둘 테니, 어떻게 해석할 것인가는 각자의 몫으로...
The following Claim Names are registered in the IANA "JSON Web Token Claims" registry established by Section 10.1. None of the claims defined below are intended to be mandatory to use or implement in all cases, but rather they provide a starting point for a set of useful, interoperable claims. Applications using JWTs should define which specific claims they use and when they are required or optional. All the names are short because a core goal of JWTs is for the representation to be compact.
- Public Name: 충돌을 피하는 이름을 의마한다. 여기서 충돌이라 함은 서로 다른 서비스인데 같은 이름을 다른 의미나 다른 형태로 사용하는 것을 뜻한다.
- Private Name: Registered Name도 아니고 Public Name도 아닌 이름이다. 충돌의 위험성이 있다.
Compact Serialization과 JSON Serialization
JWS와 JWE는 모두 Compact Serialization과 JSON Serialization을 통해 직렬화할 수 있다. Compact Serialization은 BASE64URL 문자열로 직렬화하는 방법으로, JWT의 표현에는 이 방법을 사용한다. (JWTs are always represented using the JWS Compact Serialization or the JWE Compact Serialization.)
JWS와 JWE
JWS
JWS는 JSON Web Signature의 약자로, Signature라는 말이 암시하듯 서명을 통해 데이터의 무결성을 보장한다. 보통 인터넷에서 JWT의 예시로 나오는 것들은 JWS 구조로 되어 있는 것이다.
JWS는 RFC 7515에 정의되어 있다.
JWS의 구성
JWS represents digitally signed or MACed content using JSON data structures and base64url encoding. These JSON data structures MAY contain whitespace and/or line breaks before or after any JSON values or structural characters, in accordance with Section 2 of RFC 7159 [RFC7159]. A JWS represents these logical values (each of which is defined in Section 2):
o JOSE Header
o JWS Payload
o JWS SignatureJWS는 JSON 데이터 구조와 base64url 인코딩을 사용하는 디지털 서명되거나 MAC(메시지 인증 코드)된 컨텐츠를 나타낸다. 이러한 JSON 데이터 구조는 RFC 7159의 섹션 2에 따라 어떤 JSON 값이나 구조 문자 앞뒤에 공백이나 개행을 포함할 수 있다. JWS는 다음의 논리적 값을 나타낸다 (섹션 2에 정의된 각 값들):
o JOSE Header
o JWS Payload
o JWS Signature
JWS는 JOSE Header, JWS Payload, JWS Signature로 구성된다. JOSE Header에서 JOSE는 JSON Object Signing and Encryption의 약자로 JOSE Header는 JSON 객체를 서명하고 암호화하는 방법이 있는 헤더이다. JWS Payload는 아까 보았듯 클레임들을 모아둔 것을 의미한다. JWS Signature는 JOSE Header에서 정의한 알고리즘으로 서명한 것으로, 서명 방법은 아래와 같다.
- Compute the JWS Signature in the manner defined for the particular algorithm being used over the JWS Signing Input ASCII(BASE64URL(UTF8(JWS Protected Header)) || '.' || BASE64URL(JWS Payload)). The "alg" (algorithm) Header Parameter MUST be present in the JOSE Header, with the algorithm value accurately representing the algorithm used to construct the JWS Signature.
- Compute the encoded signature value BASE64URL(JWS Signature).
- JWS 서명 입력 ASCII(BASE64URL(UTF8(JWS 보호된 헤더)) || '.' || BASE64URL(JWS Payload))에 대해 사용되는 특정한 알고리즘에 대해 정의된 방법으로 JWS 서명을 계산한다.
- BASE64URL(JWS Signature) 인코딩된 서명값을 계산한다.
Message Signature or MAC Computation에 적혀 있는 순서의 일부분이다. 서명하는 부분에 해당하는 내용만 인용했다. 번역이 좀 매끄럽게 되질 않는데, 쉽게 말하면 ASCII(BASE64URL(UTF8(JWS 보호된 헤더)) || '.' || BASE64URL(JWS Payload))를 입력값으로 하여 특정 알고리즘을 사용해서 JWS 서명을 계산하라는 뜻이다. 그리고 그렇게 나온 JWS 서명을 BASE64URL 인코딩하면 된다.
그렇게 하여 최종적으로는 Compact Serialization 기준으로 아래의 문자열이 된다.
BASE64URL(UTF8(JWS Protected Header)) || '.' ||
BASE64URL(UTF8(JWS Payload)) || '.' ||
BASE64URL(UTF8(JWS Signature))JWE
JSON Web Encryption (JWE)은 Encryption이라는 단어에서 알 수 있듯 암호화를 통해 무결성을 보장한다. RFC 7516에 정의되어 있다.
BASE64URL(UTF8(JWE Protected Header)) || '.' ||
BASE64URL(JWE Encrypted Key) || '.' ||
BASE64URL(JWE Initialization Vector) || '.' ||
BASE64URL(JWE Ciphertext) || '.' ||
BASE64URL(JWE Authentication Tag)이건 JWE의 Compact Serialization (BASE64URL 문자열)인데, JWS와는 다르게 5개의 부분으로 구성되어 있는 것을 알 수 있다.
JWE를 만드는 방법은 너무 복잡하기 때문에 지금은 다루지 않겠다. 궁금하다면 Producing and Consuming JWEs에서 구경해보길..
🖥️ JWT를 파이썬으로 구현하기
JWT를 파이썬에서 구현해보자.
목표
구글에 JWT decoder라고 치면 나오는 사이트 중 https://www.jwt.io/ 라는 사이트가 있다.

이 사이트의 JWT Decoder에 BASE64URL 문자열의 JWS 토큰을 입력하고 SECRET에 시크릿 키를 입력하면, 오른쪽과 같이 디코딩된 JOSE Header와 JWS Payload가 나타난다. 시크릿 키를 바탕으로 서명 검증에 성공한다면 위처럼 Valid secret이 나타난다.
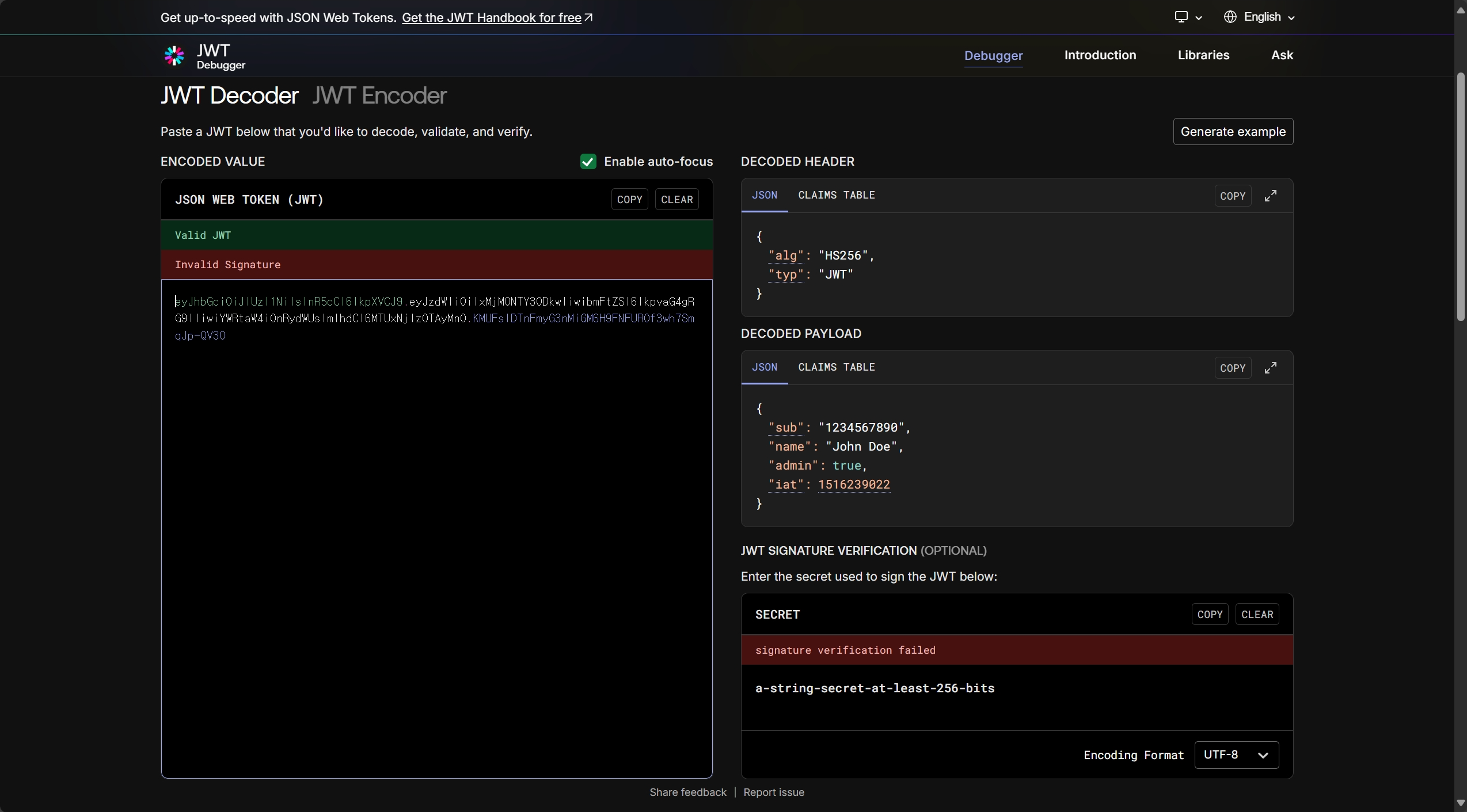
서명 검증에 실패한다면 이런 식으로 signature verification failed가 나타나게 된다.
구현한 프로그램으로 얻은 BASE64URL 문자열의 JWT와, 키 정보를 위 사이트에 넣어서 디코딩된 JOSE Header와 JWS Payload가 잘 나타나고, 서명 검증에 성공하는 것이 이번 실습의 목표이다.
전제
- JWS 구조를 사용할 것이다.
- Compact Serialization, 즉 BASE64URL 문자열로 표현한다.
- 알고리즘은 HS256을 사용한다. HS256은 HMAC와 SHA256 방식을 합친 것이다.
- JWS Payload는
sub,name,iss클레임으로 구성할 것이다.sub는1234567890,name은Homer Simpson,iss는 현재 시간으로 지정할 것이다.
- 서명에 사용하는 키는
key-for-test이다.
인코딩
인코딩의 과정은 다음과 같다.
- JOSE Header, JWS Payload를 각각 딕셔너리로 선언한다.
- JOSE Header, JWS Payload를 딕셔너리 -> JSON 객체 문자열 -> trailing
=를 제거한 BASE64URL 문자열 과정을 거쳐 인코딩한다.- RFC 7515의 Terminology를 보면, Base64url 인코딩에 trailing
=를 제거하는 내용을 적어두었다. 그리고, 위 사이트에서도 trailing=를 제거하지 않으면 RFC 7519에 정의되어 있는 방식대로 인코딩되지 않았다고 오류가 난다.
- RFC 7515의 Terminology를 보면, Base64url 인코딩에 trailing
- BASE64URL 문자열인 JOSE Header와 JWS Payload를
.구분자로 합치고 (join), 합친 문자열과 키, HMAC 및 SHA256 알고리즘을 이용해서 JWS Signature를 계산한다. - 계산한 JWS Signature를 BASE64URL 문자열로 인코딩한다.
- BASE64URL 문자열인 JOSE Header, JWS Payload, JWS Signature를
.구분자로 합친다.
코드
1단계: JOSE Header와 JWS Payload
from time import time
jose_header = {
'alg': 'HS256',
'typ': 'JWT'
}
jws_payload = {
'sub': '1234567890',
'name': 'Homer Simpson',
'iss': int(time()) # 현재 시간을 유닉스 초로 나타낸 후 소숫점은 버린
}jose_header와jws_payload를 딕셔너리로 선언하였다.time모듈의time은 현재 시간을 유닉스 초로 반환하는데,float타입으로 반환한다.float에int를 적용하면 소숫점이 절삭(양수의 경우math.floor적용한 결과와 같다)된다.
2단계: JOSE Header와 JWS Payload를 인코딩
from json import dumps
from base64 import urlsafe_b64encode
def encode_to_base64url_bytes(segment: dict) -> bytes:
json_str: str = dumps(segment)
base64_bytes = urlsafe_b64encode(json_str.encode(encoding='utf-8')).rstrip(b'=')
return base64_bytes
def encode_to_base64url(segment: dict) -> str:
return encode_to_base64url_bytes(segment).decode('utf-8')
jose_header_base64url_bytes = encode_to_base64url_bytes(jose_header)
jws_payload_base64url_bytes = encode_to_base64url_bytes(jws_payload)
jose_header_base64url = encode_to_base64url(jose_header)
jws_payload_base64url = encode_to_base64url(jws_payload)- 여러 번 활용할 것이므로 함수로 선언했다.
bytes타입의 바이트 문자열에서rstrip메소드를 사용할 수 있다. 이때rstrip의 인자로 bytes-like object가 들어간다.encode_to_base64_url_bytes를 선언한 이유는, 후술할 3단계에서 HMAC에서bytes를 필요로 하기 때문이다.
3단계: JWS Signature를 계산
import hmac
from hashlib import sha256
jws_signature_input = jose_header_base64url_bytes + b'.' + jws_payload_base64url_bytes
jws_signature = hmac.new(key=b'key-for-test', msg=jws_signature_input, digestmod=sha256).digest()
jws_signature_base64url = urlsafe_b64encode(jws_signature).rstrip(b'=').decode(encoding='utf-8')
print(jws_signature_base64url)hmac.new에서key와msg모두str타입은 받지 않는다.
4단계: JOSE Header + JWS Payload + JWS Signature
jws_compact = jws_signature_input.decode(encoding='utf-8') + '.' + jws_signature_base64url- JOSE Header와 JWS Payload는 이미
jws_signature_input으로 합쳐놨으니 이것을 디코딩해서str타입으로 바꿔준 후,.으로 구분해서 JWS Signature를 BASE64URL 문자열로 인코딩한 것과 합친다.
5단계: 테스트
print(jws_compact)출력된 토큰을 사이트에 넣고, SECRET에는 key-for-test라고 입력한다.
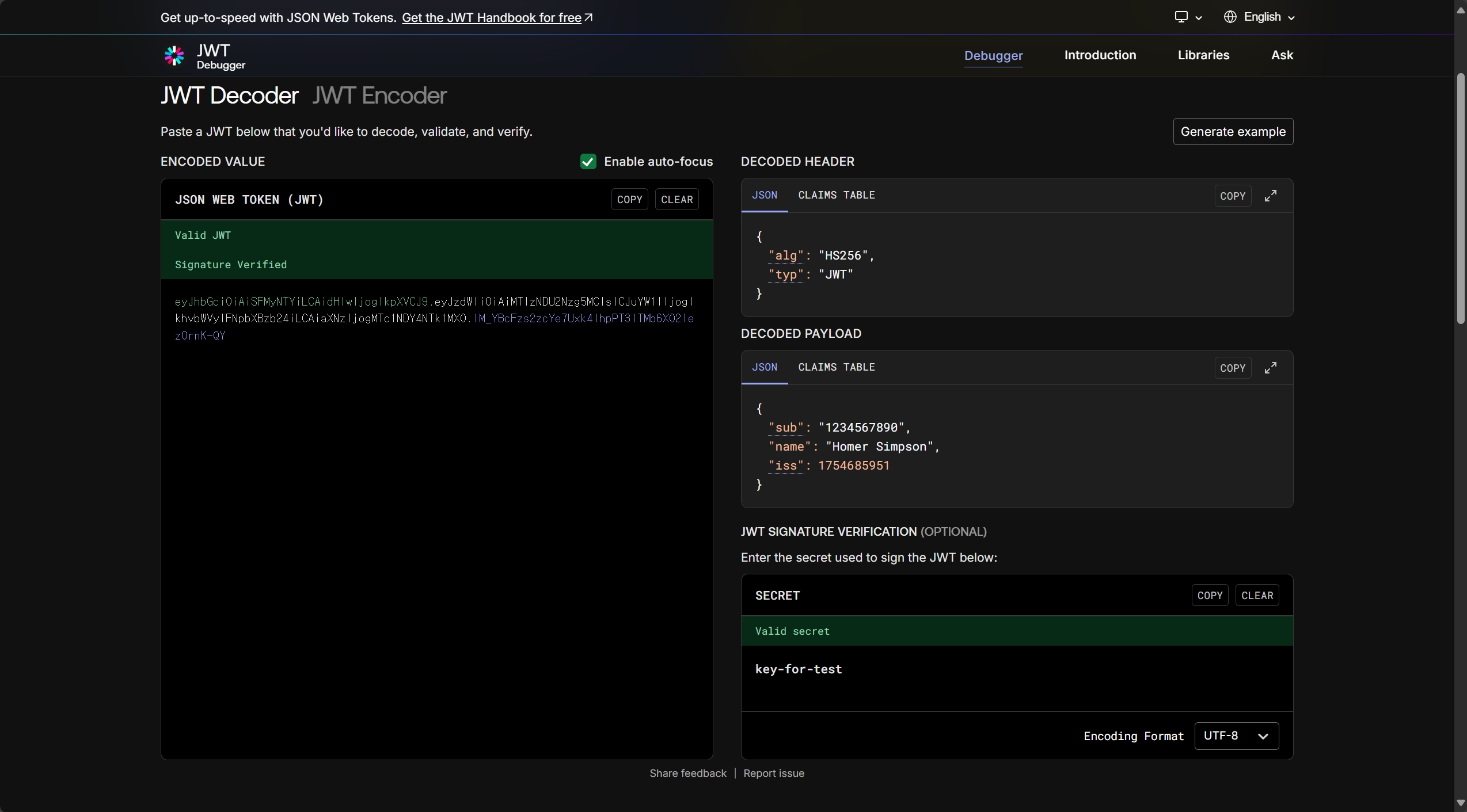
디코딩과 서명 검증 모두 성공적으로 되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
디코딩
- BASE64URL 문자열을
.을 기준으로 분리한다. 그러면 JOSE Header, JWS Payload, JWS Signature로 나눠지게 된다. - JOSE Header와 JWS Payload는 끝에
==를 추가한 BASE64URL 문자열 -> JSON 객체 문자열 -> 딕셔너리 과정을 거쳐 디코딩하면 된다. - JWS Signature는 디코딩이 불가능한데, HMAC과 SHA256은 해싱 알고리즘이므로 복호화가 불가능하기 때문이다. 대신, 인코딩 때 JWS Signature를 계산하는 방법과 같은 방법으로 JWS Signature를 계산 및 인코딩한 후 BASE64URL 문자열에 있는 JWS Signature와 일치하는지 확인해서 서명 검증을 할 수 있다.
코드
1단계: BASE64URL 문자열을 . 기준으로 분리
jose_header_base64url, jws_payload_base64url, jws_signature_base64url = jws_compact.split('.')2단계: JOSE Header와 JWS Payload 디코딩
from base64 import urlsafe_b64decode
from json import loads
def decode_to_dict(base64url: str) -> dict:
json_bytes = urlsafe_b64decode(base64url + '==')
dictionary = loads(json_bytes)
return dictionary
jose_header_decoded = decode_to_dict(jose_header_base64url)
jws_payload_decoded = decode_to_dict(jws_payload_base64url)base64url문자열의 뒤에==를 추가하는 이유는 패딩이 없으면base64.urlsafe_b64decode에서 오류가 발생하기 때문이다. 이때 추가적인 패딩은 디코딩 단계에서 절삭되므로, 문제가 되지 않는다.json.dumps는str타입만을 반환하던 것과 달리,json.loads는bytes타입을 받을 수 있다. 그래서bytes에서str로 변환하는 과정이 필요하지 않다.
3단계: JWS Signature 서명 검증
import hmac
from hashlib import sha256
jws_signature_input = jose_header_base64url.encode(encoding='utf-8') + b'.' + jws_payload_base64url.encode(encoding='utf-8')
jws_signature_target = hmac.new(key=b'key-for-test', msg=jws_signature_input, digestmod=sha256).digest()
jws_signature_target_base64url = urlsafe_b64encode(jws_signature_target).rstrip(b'=').decode(encoding='utf-8')
print(jws_signature_base64url == jws_signature_target_base64url)- 앞의 인코딩 과정의 JWS Signature 계산 과정을 수행한 후에 원본 JWS Signature와 같은지 비교하는 과정이 추가되었다.
True가 출력되면 서명 검증이 성공한 것이다.
🔚 결론
이렇게 해서 JWT에 대해 알아보고, JWT(JWS)를 파이썬으로 구현해 보았다. 물론, 이렇게 간단하게 구현한 JWS는 실제로 사용할 수 있는 정도라고는 할 수 없을 것이다. 사실, 이렇게 직접 안 만들어도 이미 JWT를 구현한 패키지가 존재하고, 훨씬 정교하고 잘 만들어져 있다. 그러니, 직접 만들지 말고 사서 먹자.
8월 8일의 TIL이라면서 다음날 6시 반에 올리는 거면 이건 사실상 9일의 TIL 아닌가..? 싶긴 한데 8일에 공부하고 실습한 내용이니깐 8일로 올린다. 실제로 공부할 때에는 객체 단위로 분리해가며 복잡하게 만들어서 시간이 오래 걸렸었다. 블로그에서는 그 코드를 그대로 옮기면 너무 읽기 힘들어질 것 같아 구현 과정을 간단히 적었다.
