문제 요구 사항
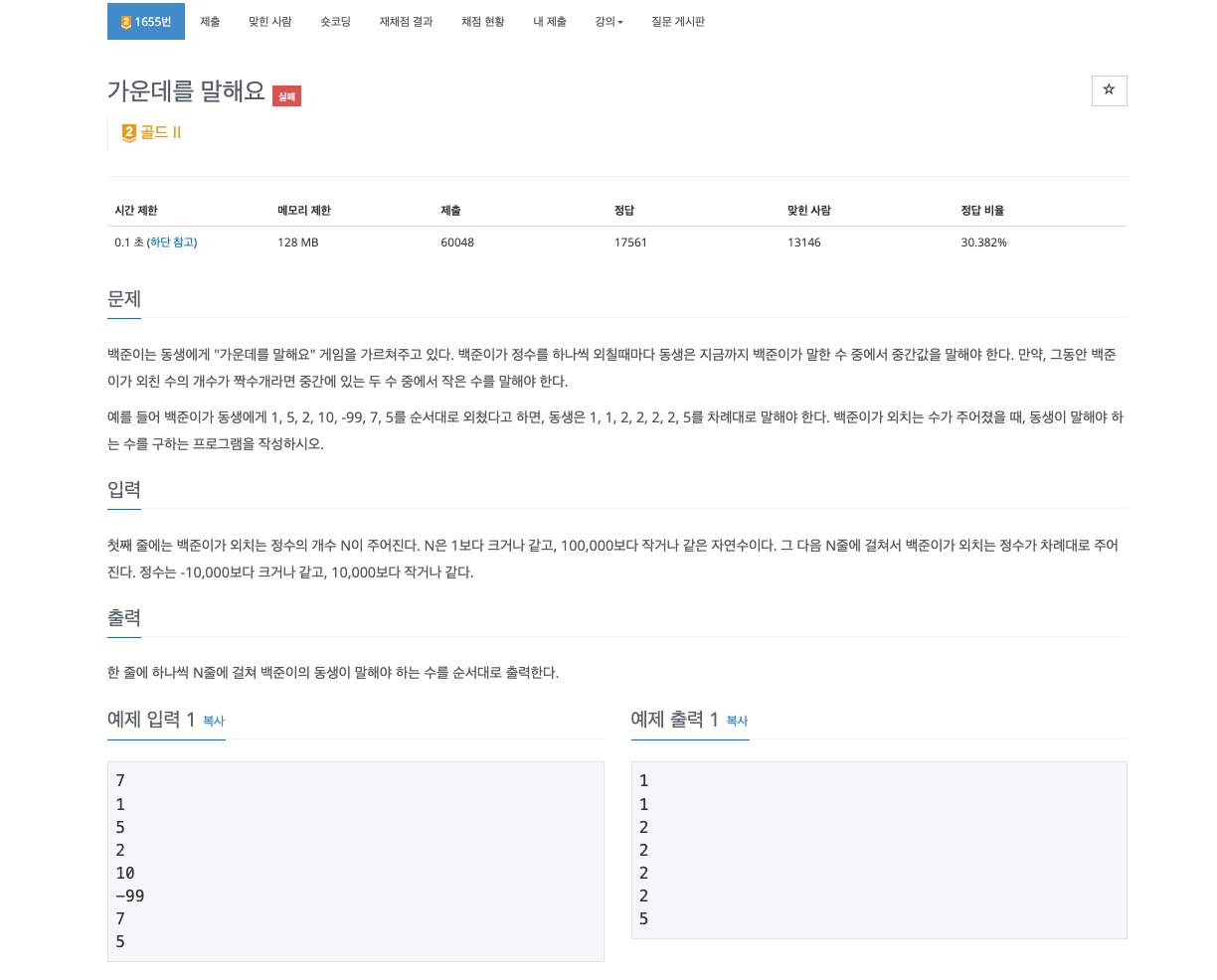
- 값이 N개가 주어진다.
- 값이 하나씩 주어질 때마다, 지금까지 입력된 값들 중 중앙값을 찾아서 출력한다.
- 중앙값을 출력하기 위해서는 입력값이 들어올 때마다 정렬되어 있어야 함. - 시간 제한은 0.1초, N은 100,000보다 작거나 같은 자연수
알고리즘 접근 회로
🤔 무식하게 접근
무식하게 생각해보자. 중앙값을 출력하기 위해서는 입력값이 들어올 때마다 정렬되어있어야 한다.
그렇다면, vector<int> v에 값을 입력 받고, 값을 입력 받을 때 마다 sort(v.begin(),v.end())하면 되지 않을까?
하지만 N의 값이 100,000이기 때문에 시간 초과가 날 것이라는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
만일 이 이라면,
시간이 엄청나게 오래 걸릴 것이다.
🥲 sort()를 호출 하지 않는다면?
그럼 매번 입력값이 들어올 때마다 vector에 정렬된 채로 값을 넣는다면? 나는 이 알고리즘이 정답일 줄 알고, 바로 코드를 작성해서 제출했다.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector <int> v;
void insertNewNumber(int n) {
const auto pos = lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), n);
v.insert(pos, n);
}
int main (void)
{
int N, next;
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cin >> next;
insertNewNumber(next);
int midIdx = (v.size() - 1) / 2;
cout << v[midIdx] << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
깔끔하게 시간 초과 났다.
값을 한번 계산해보고 접근했다면, 이런 실수를 하지 않았으리라.
만일 이 이라면,
사실 값을 비교해보면 무식하게 풀었을 때와 5배 밖에 차이나지 않는다.
정렬하는 시간에서 을 로 바꿨다고 문제가 해결 될 거라고 생각했지만, 은 정말 미미한 숫자에 불과 했다..
👀 우선순위 큐를 사용해보자
우선순위 큐를 통해서 값을 집어넣고 읽는 것은 다음과 같다.
따라서 우선순위 큐를 사용해서 코드를 작성한다면 조금 더 빠르게 알고리즘을 완성할 수 있었다.
만일 이 이라면,
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> pqGreater;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pqLess;
int main (void)
{
int N, num;
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cin >> num;
if (pqGreater.empty()) {
pqGreater.push(num);
}
else if (pqGreater.size() == pqLess.size()) {
pqGreater.push(num);
}
else if (pqGreater.size() > pqLess.size()) {
pqLess.push(num);
}
if (!pqGreater.empty() && !pqLess.empty() && (pqGreater.top() > pqLess.top())) {
int fromGreater = pqGreater.top();
int fromLess = pqLess.top();
pqGreater.pop();
pqLess.pop();
pqGreater.push(fromLess);
pqLess.push(fromGreater);
}
cout << pqGreater.top() << '\n';
}
return 0;
}