🌟다익스트라 vs 플로이드-워셜
- 그림 필요
🎇 다익스트라
1. 정의
하나의 정점에서 출발했을 때 다른 모든 정점으로의 최단 경로 구하는 알고리즘
2. 특징
조건 : 양의 가중치에서는 상관 없지만, 음의 가중치에서는 사이클이 있을 때 무한 루프에 빠지기 때문에 사용 X -> [플로이드-워셜] 사용
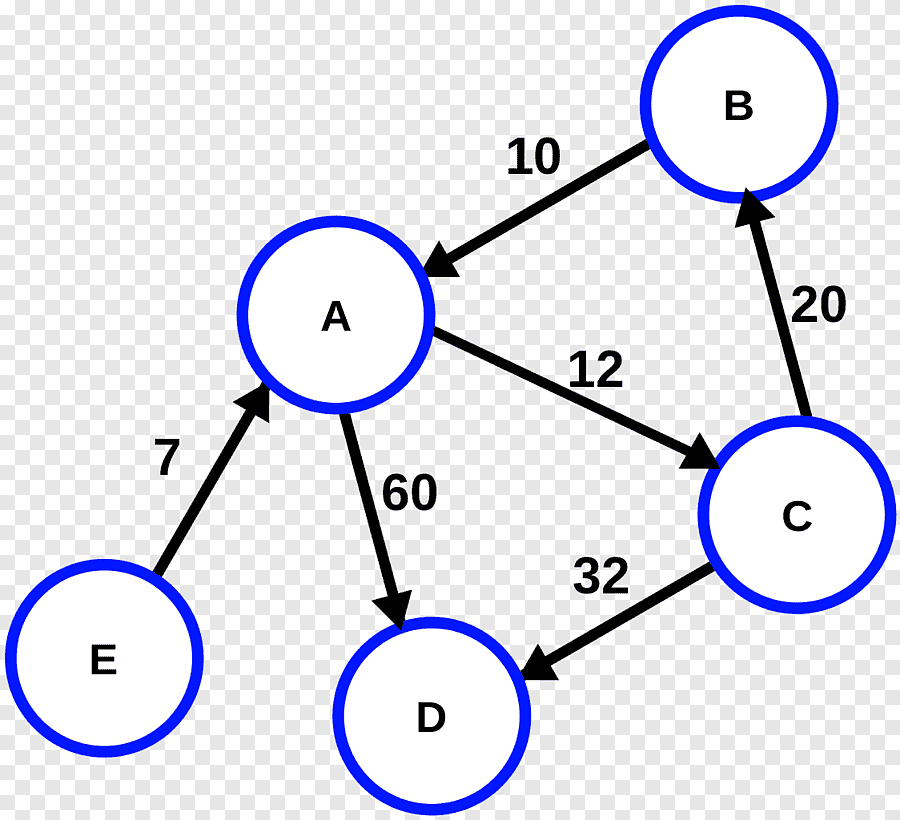
- 노드와 간선 필요
- 3개의 변수 지정 필요 : Graph, Distance, Heapq에 들어갈 리스트 q
- 시간 복잡도 : E * log(V)
- BFS, 그리디 알고리즘 계열
3.1. 기본 예시
import sys
import heapq
input = sys.stdin.readline
N, M = map(int, input().split())
graph = [[] for _ in range(N+1)]
INF = int(1e9)
# 1. 비용과 함께 그래프 노드 포함한 이중 리스트 Setting
for i in range(M):
a, b, cow = map(int, input().split())
graph[a].append((cow, b))
graph[b].append((cow, a))
def dijkstra(S):
Q = []
distance = [INF] * (N+1)
# 2. 다익스트라 함수 내에 Heapq 모듈의 heappush 함수활용하여 힙 리스트 init
heapq.heappush(Q, (0, S))
distance[S] = 0
# 3. 반복문을 활용하여 heappop 함수 활용하여 Distance 리스트의 거리를 Update
while Q:
now_dist, now_vertex = heapq.heappop(Q)
# 가지치기 함 해주고
if now_dist > distance[now_vertex]:
continue
# 애초에 설정된 거리와 a, b 거리 비교해서 a+b 크기가 작으면 이걸로 distance 갱신해줌
for next_dist, next_vertex in graph[now_vertex]:
if now_dist + next_dist < distance[next_vertex]:
distance[next_vertex] = now_dist + next_dist
heapq.heappush(Q, (now_dist + next_dist, next_vertex))
return distance
# 4. 출발지 입력하여 거리 계산
print(dijkstra(1)[N])3.2. Graph 이론 + Dijkstra - 네트워크 복구
- Parent 이용 : [Graph이론]
import sys
import heapq
input = sys.stdin.readline
INF = int(1e9)
def dijkstra(start):
q = []
distance[start] = 0
heapq.heappush(q, (0, start))
while q:
dist, now = heapq.heappop(q)
if distance[now] < dist:
continue
for next_node, next_cost in graph[now]:
cost = dist + next_cost
if distance[next_node] > cost:
# 더 짧은 거리로 갱신될 때마다 parent도 함께 갱신
parent[next_node] = now
distance[next_node] = cost
heapq.heappush(q, (cost, next_node))
n, m = map(int, input().split())
distance = [INF] * (n+1)
parent = [0] * (n+1)
graph = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
for _ in range(m):
a, b, c = map(int, input().split())
graph[a].append((b, c))
graph[b].append((a, c))
dijkstra(1)
print(n-1)
for i in range(2, n + 1):
print(i, parent[i])🎇 플로이드-워셜
1. 정의
모든 정점에서 다른 모든 정점으로의 최단 경로 구하는 알고리즘
2. 특징
- Node 개수 500개 이하일 때만 사용