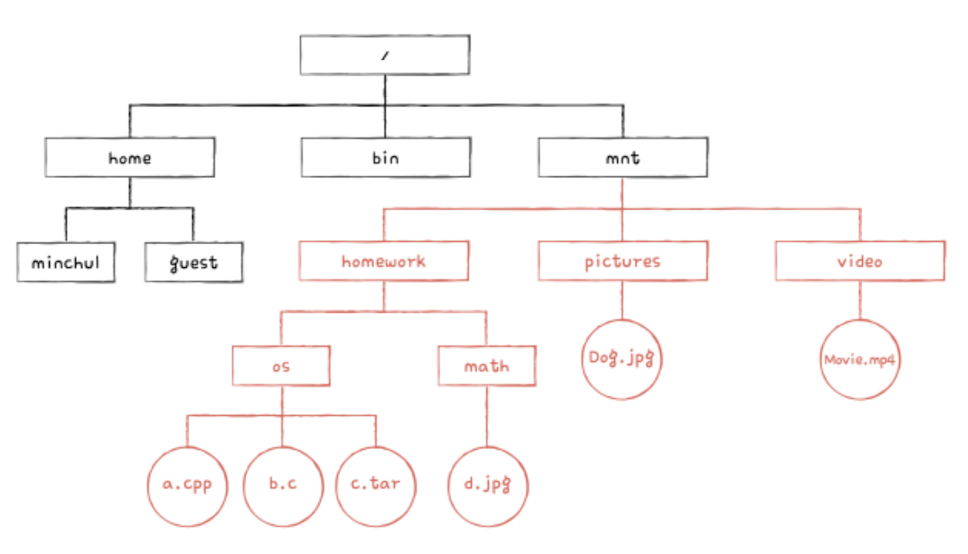
📁 Files, Directories, and File Systems
File: A logical unit of related data, stored as a bundle in secondary memory
Directory: fundemantaly directory is a special type of file that stores metadata about other files. It stores this in a table format.
Directory Entry: entry of the table that includes file name and its location in hard dist etc.
File System: a component of the OS that manages how files and directories are stored, retrieved, and organized on secondary storage
🧱 How the File System Works
- Partitioning
: Divides a physical storage into logical sections called partitions
: Each partition has different file system - Formatting
: Configure file system and ready to write new data on the storage
📦 How Data is Stored
- Files are broken into blocks, each made up of multiple sectors
- Theses blocks are the basic units used to allocate space on disk
📚 Allocation Strategies
Contiguous allocation
: Like a linked list with a directory table
: Simple and fast, but suffers from external fragmentation
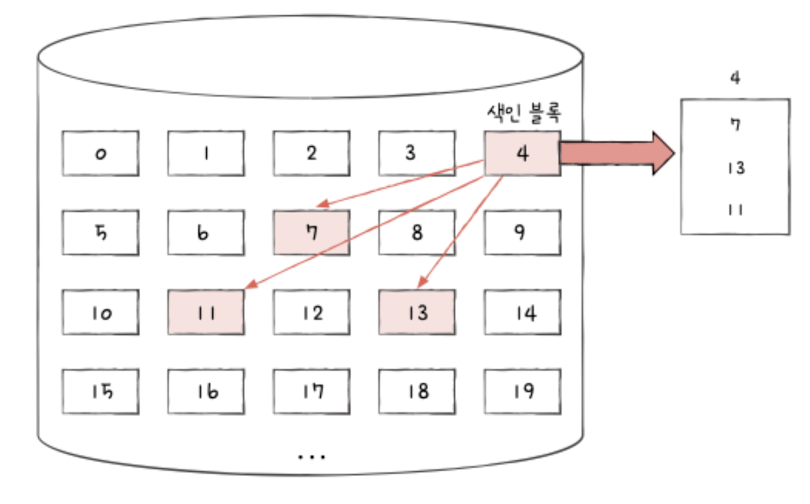
Indexed allocation
: Each file has a dedicated index block that stores the addresses of all its data blocks
: Enables fast random access by using the index to look up any block directly
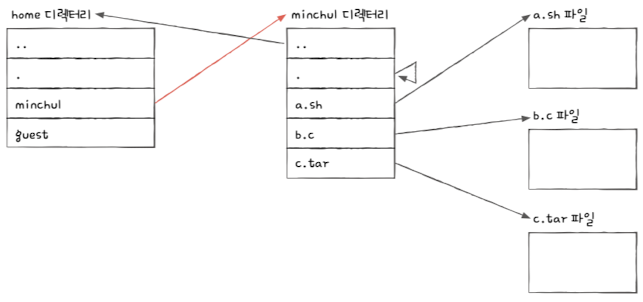
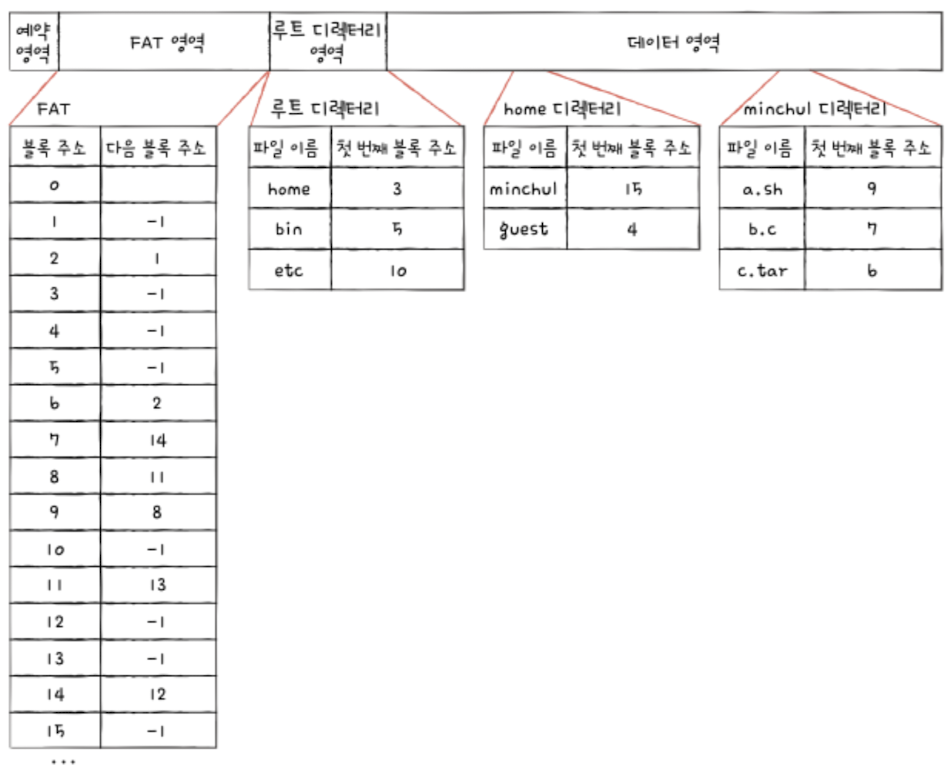
FAT(File Allocation Table) File System
: Uses a table that stores (current block → next block) pairs
: The FAT is located at the beginning of the partition
: Even though it's a form of linked allocation, it can be cached in memory, making lookup fast
ex) /home/mincul/a.sh file look up meachnism in FAT system
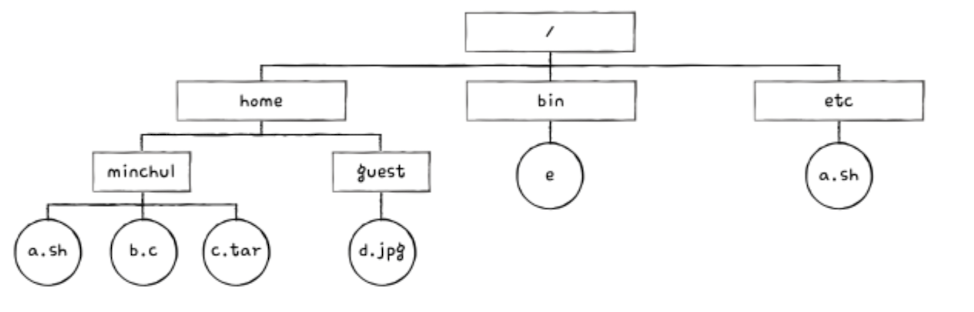
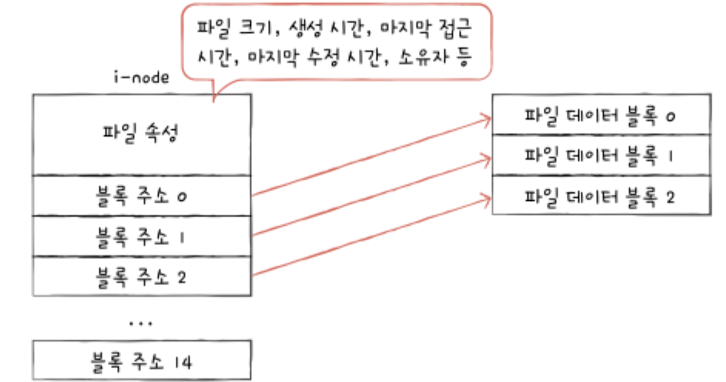
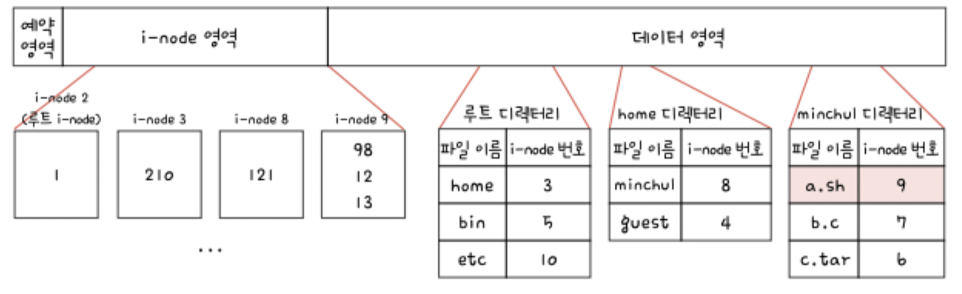
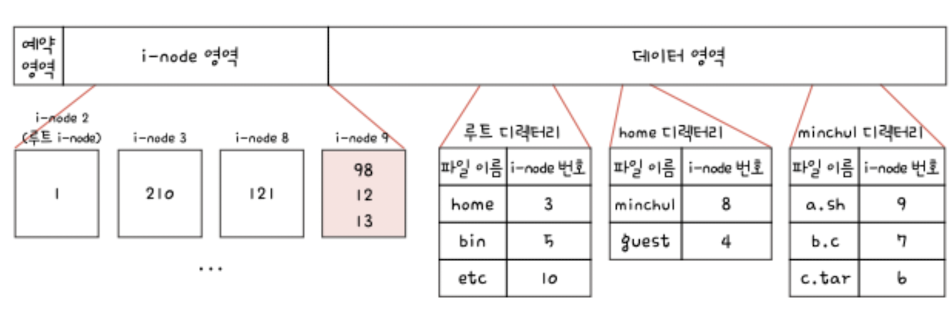
Unix File System
: Uses i-nodes (index nodes) to store:
- File metadata (size, permissions, timestamps)
- Block addresses for data
The directory only stores: - File name
- i-node number (acts like a pointer to the file metadata and data blocks)
Mount
: Merge one file system to another file system
ex) Use USB connecting to a computer