findById만 알고 있다가, getReferenceById도 알게 되어 차이에 대해 찾아보았다.
find와 get 차이
- find: 찾다. 찾아보니 결과가 없을 수 있다.
Optional<T> findById(ID id) - get: 가져오다. 가져오려는 대상이 있어야 한다.
T getReferenceById(ID id);
findById
1. CrudRepository 문서
(CrudRepository interface에서도 확인할 수 있다.)
- 파라미터: id 값은 null이면 안된다.
- findById는 주어진 id값으로 entity를 반환하거나 Optional로 감싸져 있기에 비어있는 객체를 반환한다.
- id값이 null일 경우에는 IllegalArgumentException을 발생시킨다.

2. SimpleJpaRepository.java
이번에는 findById 코드를 살펴보자.
문서에서 확인한 것처럼, null이 아닐 경우 해당 값을 포함하는 Optional 객체를 반환하고, null일 경우 Optional.empty()를 반환한다.
@Override
public Optional<T> findById(ID id) {
Assert.notNull(id, ID_MUST_NOT_BE_NULL);
Class<T> domainType = getDomainClass();
if (metadata == null) {
return Optional.ofNullable(entityManager.find(domainType, id));
}
LockModeType type = metadata.getLockModeType();
Map<String, Object> hints = getHints();
return Optional.ofNullable(type == null ? entityManager.find(domainType, id, hints) : entityManager.find(domainType, id, type, hints));
}3. Transaction
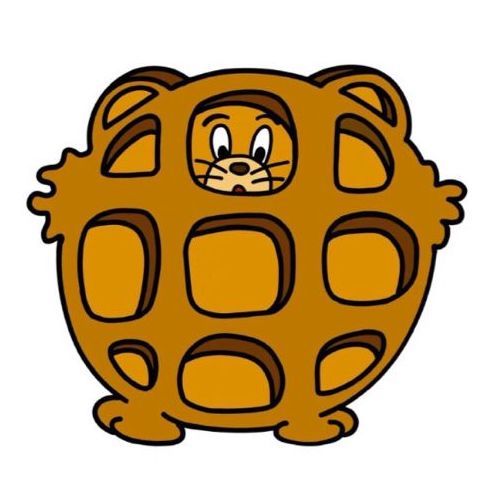
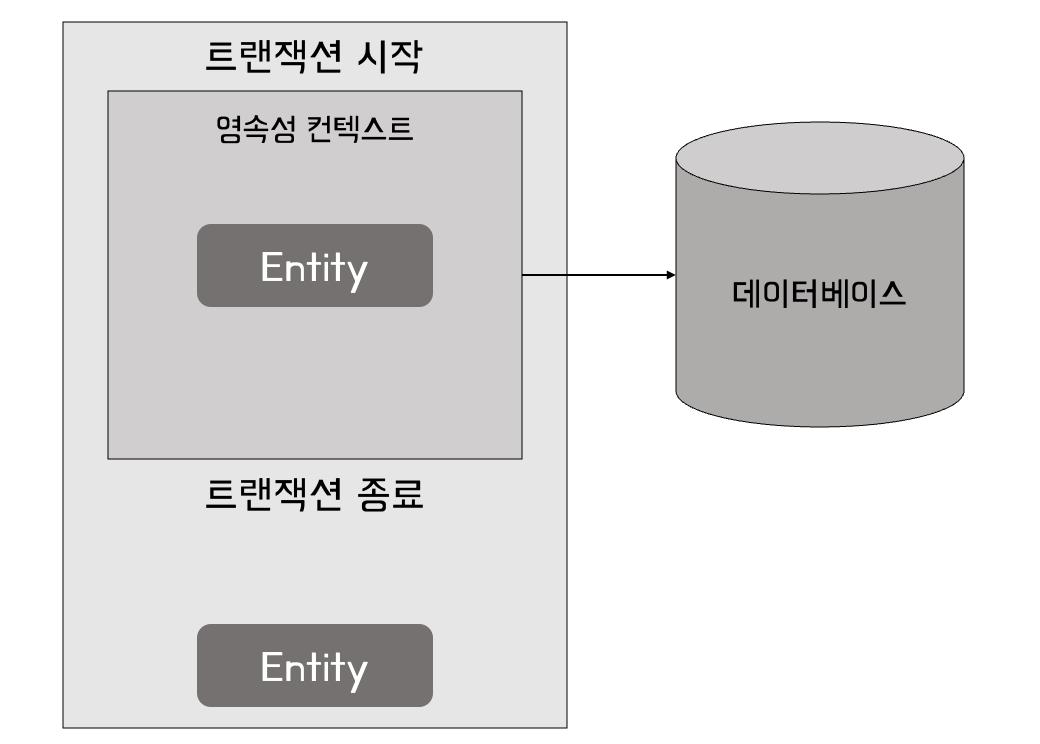
Within a transaction, all the entities inside the persistence context have a direct representation in the database. This is a managed state. Thus, all the changes to the entity will be reflected in the database. Outside the transaction, the entity moved to a detached state, and changes won’t be reflected until the entity is moved back to the managed state.
- 트랜잭션 내에서 영속성 컨텍스트 안의 모든 객체들은 데이터베이스 상태와 동기화되어 있다. 그래서 객체들에 대한 모든 변경 사항은 데이터베이스에 반영된다.
- 트랜잭션 밖의 객체, 즉, 영속성 컨텍스트의 관리 범위를 벗어난 상태의 객체는 관리 상태로 이동할 때까지 변경 사항이 반영되지 않는다.
getReferencedById
1. JpaRepository 문서
(JpaRepository interface에서도 확인할 수 있다.)
- 주어진 id에 따라 객체의 참조를 반환한다.
- JPA 영속성 제공자가 어떻게 구현한 지에 따라 인스턴스를 반환하거나
EntityNotFoundException을 발생시킬 수 있다. - 파라미터: id가 null이면 안된다.

2. SimpleJpaRepository.java
이번에는 getReferencedById 코드를 살펴보자.
문서에서 확인한 것과 마찬가지로 주어지는 식별자(id)값이 null이면 안된다.
문서와는 다르게 EntityNotFoundException이 없다. 반환하는 부분을 보면, entityManager.getReference 메서드에 의해 간접적으로 발생하는 것을 알 수 있다.
@Override
public T getReferenceById(ID id) {
Assert.notNull(id, ID_MUST_NOT_BE_NULL);
return entityManager.getReference(getDomainClass(), id);
}3. Transaction
Lazy-loaded entities behave slightly differently. Spring won’t load them until we explicitly use them in the persistence context:
Spring will allocate an empty proxy placeholder to fetch the entity from the database lazily. However, if we don’t do this, the entity will remain an empty proxy outside the transaction, and any call to it will result in a LazyInitializationException. However, if we do call or interact with the entity in the way it will require the internal information, the actual request to the database will be made:
- 지연로딩 객체는 약간 다르게 동작한다. 우리가 영속성 컨텍스트에서 명시적으로 사용하기 전까지는 스프링이 엔티티를 로드하지 않는다.
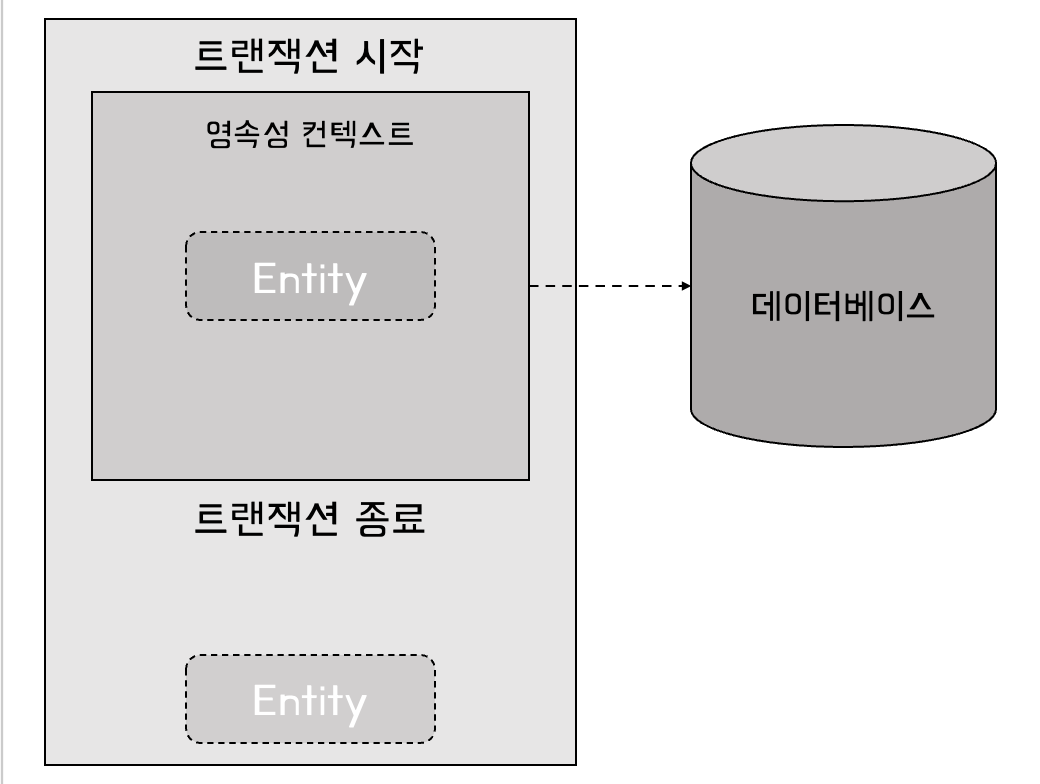
- 스프링은 데이터베이스에서 객체를 지연 로딩하기 위해 빈 프록시 자리를 할당한다. 우리가 이를 사용하지 않으면, 객체는 트랜잭션 밖에서 빈 프록시로 남게 되고 LazyInitializationException이 발생한다.
우리가 객체를 호출하거나 상호작용할 때, 데이터베이스 요청이 이루어지는 것이다.
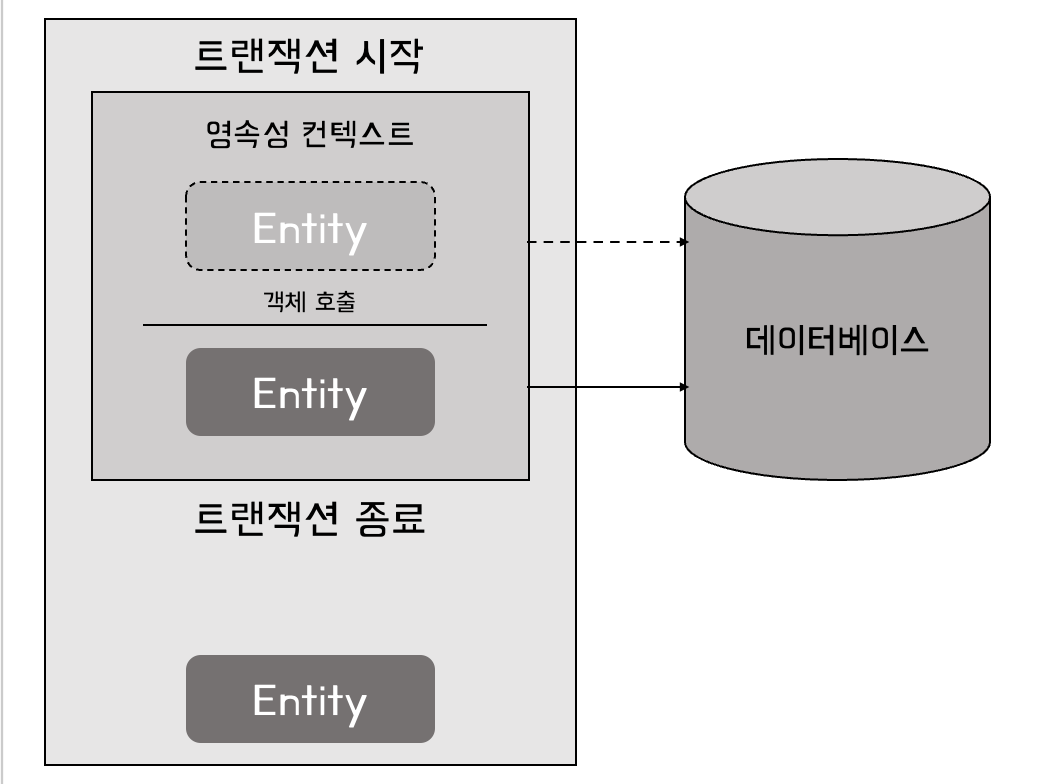
언제 사용할까?
아래 코드를 보자.
코드에서 user는 getReferencedById, study는 findById를 사용하였다.
- user: user는 엔티티 존재 여부만 확인하면 되기 때문에 getReferencedById를 사용하여 엔티티 프록시를 생성하였다.
- study: study는 객체에서 mission을 가져와야하기 때문에 findById를 사용하여 객체를 가져왔다.
User user = userRepository.getReferenceById(userId);
Study study = studyRepository.findById(studyId).orElseThrow(() -> new EntityNotFoundException("존재하지 않는 스터디입니다."));
String missionUrl = validateMissionUrl(study.getMission().getMissionType(), missionUrlRequestDTO.getMissionUrl());
StudyEnrollment studyEnrollment = studyEnrollmentRepository.findByUserAndStudy(user, study).orElseThrow(() -> new EntityNotFoundException("해당 스터디 참여 내역이 없습니다."));
studyEnrollment.updateMissionUrl(missionUrl);참고
CrudRepository
JpaRepository
When to Use the getReferenceById() and findById() Methods in Spring Data JPA

