들어가며
static 인스턴스, 변수, 메서드는 JVM의 heap 영역이 아닌 method area에 저장되고 GC(Garbage collector)의 대상이 아니다.
위는 내가 기존에 알고 있던 내용이다. 하지만 엄밀히 말하자면 틀렸다. 이 게시물은 Hotspot JVM의 Metaspce와 Permanent generation에 기반한다.
Java8부터 사라진 Permanent generation

Java7의 메모리 사진을 보면, 인스턴스들이 저장되는 heap, OS가 관리하는 native memory, 그리고 Permanent generation 영역이 존재한다. Permanent generation에는 Class metadata, interned Strings, class static variables 가 저장되었다. 문제는 이 영역이 제한적인 크기를 갖고 있고, 런타임에 조정 불가하다.
기본값은 64-bit version JVM에서는 82 Mb이고 32-bit JVM에서는 64 Mb였다. 자동으로 크기가 늘어나는 것이 아닌데 미리 용량을 예측하여 크기를 조정하는 일은 매우 어렵다. 그때그때 메모리 크기를 늘리는 것은 임시방편에 불과하다.
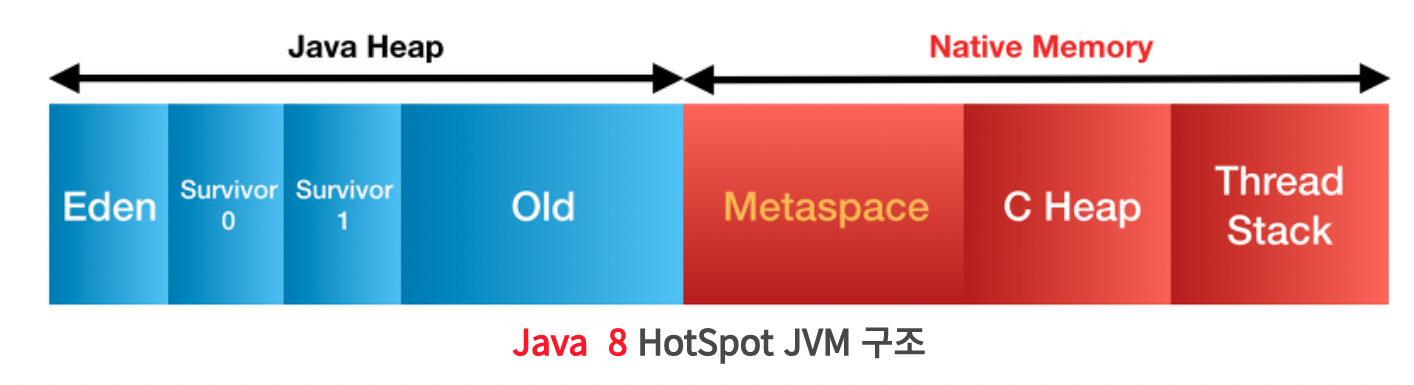
Java8부터는 Metaspace로 Permanent generation이 완전히 대체되었다. Metaspace는 Natice memory에 속해 OS가 자동으로 조절한다. (The block sizes will vary depending on the behavior of the application. [1])
interned Strings and class statics to heap
말 그대로다. Java8부터 String pool이 heap 영역으로 옮겨졌고 class statics, 즉 static object들도 heap에서 관리한다. interned String은 String pool에서 관리하는 String constant를 말한다.
String apple = "사과"; // interned String = String pool에 저장되고 재사용 됨
String banana = new String("banana"); // heap에 생성됨static object의 참조는 Metaspace에 저장된다. 참조를 잃은 static 인스턴스는 GC에 의해 제거된다.
static List<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>(); // static object본래 Permanent generation에 저장되던 것들이다. 크기 제한 문제는 개선했으나 메모리 부족이나 GC 빈도가 증가할 수 있다.
요약은 아래와 같다.
The proposed implementation(Java8에서의 업데이트) will allocate class meta-data in native memory and move interned Strings and class statics to the Java heap. [1]
출처
[1]
[2]



별생각 없이 넘어갈 수 있는 주제인데 깊게 다루어 주셔서 좋았어요 👍