목표
이번에 진행하는 목표는 다음과 같습니다.
YOLO를 이용해서 RGB에 대한 Classificiaton을 진행할거에요
근데 ONNX포맷을 사용할겁니다.
우선 그러려면 YOLO pt파일부터 만들어야겠죠? 데이터세트도 있어야겠고요
만들어봅시다. 우선 YOLO import 부터 해봅시다.
import ultralytics
ultralytics.checks()Ultralytics 8.3.59 🚀 Python-3.11.9 torch-2.5.1 CUDA:0 (NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop GPU, 8188MiB)
Setup complete ✅ (22 CPUs, 31.1 GB RAM, 258.8/1006.9 GB disk)
제대로 인식되는걸 볼 수 있습니다.
1.데이터 파일 만들기
우선 rgb로 랜덤하게 이미지 100장씩만 만들어봅시다.
import os
import random
import shutil
# (1) 무작위 시드 고정 (재현성을 위해)
random.seed(0)
# (2) 원본 이미지와 새로 구성할 데이터 디렉토리 지정
src_dir = "/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images" # 원본 데이터
dst_dir = "/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/classification_data" # MNIST 스타일 구조로 변환할 경로
# (3) 사용할 클래스 목록
classes = ['blue', 'red', 'green']
# (4) 훈련/테스트 분할 비율
split_ratio = 0.8 # 예: 80%는 train, 20%는 test
# (5) 폴더 구조 생성
for phase in ['train', 'test']:
for cls in classes:
os.makedirs(os.path.join(dst_dir, phase, cls), exist_ok=True)
# (6) 각 클래스별로 이미지를 읽고, train/test로 나눠서 복사
for cls in classes:
# 원본 이미지 목록
src_cls_dir = os.path.join(src_dir, cls)
images = os.listdir(src_cls_dir)
# 이미지 무작위 셔플
random.shuffle(images)
# train/test로 나눌 위치
cut_idx = int(len(images) * split_ratio)
train_images = images[:cut_idx]
test_images = images[cut_idx:]
# train 폴더로 복사
for img in train_images:
src_path = os.path.join(src_cls_dir, img)
dst_path = os.path.join(dst_dir, 'train', cls, img)
shutil.copy2(src_path, dst_path)
# test 폴더로 복사
for img in test_images:
src_path = os.path.join(src_cls_dir, img)
dst_path = os.path.join(dst_dir, 'test', cls, img)
shutil.copy2(src_path, dst_path)
print("데이터셋 분할 및 복사가 완료되었습니다!")


잘 생성됐네요.
2. 데이터셋 YAML 파일 생성
Ultralytics YOLO 분류 모델을 학습하려면, 데이터 경로와 클래스 이름 등을 .yaml 파일에 지정해주어야 합니다. 아래 예시는 custom_data.yaml 파일을 생성합니다.
data_yaml_content = f"""# YOLO Classification Data
path: {dst_dir} #
train: train #
val: test #
test: test #
names:
0: blue
1: red
2: green
"""
# 파일 생성
yaml_path = os.path.join(dst_dir, "custom_data.yaml")
with open(yaml_path, 'w') as f:
f.write(data_yaml_content)
print(f"데이터 설정 파일이 생성되었습니다: {yaml_path}")출력결과:
데이터 설정 파일이 생성되었습니다: /home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/classification_data/custom_data.yaml
3. YOLO v11 분류 모델 학습
이제 Ultralytics YOLO 객체를 이용해, 기존에 제공되는 yolo11n-cls.pt 사전 학습 가중치를 로드하고, 우리가 준비한 custom_data.yaml로 학습을 진행해볼 수 있습니다.
from ultralytics import YOLO
# (A) 사전학습 가중치 로드
model = YOLO('yolo11n-cls.pt') # 분류 모델
# (B) 모델 학습 (epochs=3, 출력 폴더 name='my_custom_train')
results = model.train(
data="/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/classification_data",
epochs=3,
imgsz=96, # 원하는 이미지 크기 지정
name="my_custom_train",
project="runs/classify"
)주의: imgsz 지정 안해주시면 224로 통일됩니다.
4. 결과확인하기
import os
import time
from ultralytics import YOLO
# (A) 학습 완료된 모델 로드
# (위에서 학습된 최적 가중치 위치)
trained_model = YOLO("/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/runs/classify/my_custom_train3/weights/best.pt")
# (B) 추론할 폴더 목록
folders = [
"/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/blue",
"/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/red",
"/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/green"
]
# (C) 이미지 확장자 목록
valid_exts = (".jpg", ".jpeg", ".png", ".bmp")
# (D) 결과 로그를 기록할 txt 파일
output_txt_path = "inference_results.txt"
# 총 추론시간 및 이미지 수를 추적하기 위한 변수
total_inference_time = 0.0
total_images = 0
with open(output_txt_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
# (E) 폴더별로 순회하며 추론
for folder_path in folders:
f.write(f"\n=== Inference in folder: {folder_path} ===\n")
print(f"\n=== Inference in folder: {folder_path} ===")
image_files = [img for img in os.listdir(folder_path) if img.lower().endswith(valid_exts)]
for img_file in image_files:
img_path = os.path.join(folder_path, img_file)
start_time = time.time()
# 추론 수행
results = trained_model.predict(img_path)
end_time = time.time()
inference_time = end_time - start_time
total_inference_time += inference_time
total_images += 1
# 결과 해석: 가장 확률 높은 클래스 인덱스/확률
top1_index = results[0].probs.top1
top1_conf = float(results[0].probs.top1conf)
# (F) 화면 출력
print(f"Image: {img_path}")
print(f" - Predicted Class Index: {top1_index}")
print(f" - Confidence: {top1_conf:.4f}")
print(f" - Inference Time: {inference_time:.4f} s")
# (G) TXT 파일에도 기록
f.write(f"\nImage: {img_path}\n")
f.write(f" - Predicted Class Index: {top1_index}\n")
f.write(f" - Confidence: {top1_conf:.4f}\n")
f.write(f" - Inference Time: {inference_time:.4f} s\n")
# (H) 전체 이미지에 대한 총 추론 시간 기록
f.write("\n==================== SUMMARY ====================\n")
print("\n==================== SUMMARY ====================")
if total_images > 0:
average_time = total_inference_time / total_images
summary_str = (
f"Total Images: {total_images}\n"
f"Total Inference Time: {total_inference_time:.4f} s\n"
f"Average Inference Time per Image: {average_time:.4f} s\n"
)
else:
summary_str = "No images were found for inference.\n"
f.write(summary_str)
print(summary_str)
print(f"Inference results saved to: {output_txt_path}")출력결과:
=== Inference in folder: /home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/blue ===
image 1/1 /home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/blue/image_b200_199.png: 96x96 blue 1.00, green 0.00, red 0.00, 16.0ms
Speed: 4.7ms preprocess, 16.0ms inference, 0.2ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 96, 96)
Image: /home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/blue/image_b200_199.png
- Predicted Class Index: 0
- Confidence: 1.0000
- Inference Time: 0.3022 s
image 1/1 /home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/blue/image_b200_225.png: 96x96 blue 1.00, red 0.00, green 0.00, 16.8ms
Speed: 4.0ms preprocess, 16.8ms inference, 0.1ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 96, 96)
Image: /home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/blue/image_b200_225.png
- Predicted Class Index: 0
- Confidence: 1.0000
- Inference Time: 0.0283 s
image 1/1 /home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/blue/image_b200_121.png: 96x96 blue 1.00, green 0.00, red 0.00, 20.8ms
Speed: 3.4ms preprocess, 20.8ms inference, 0.1ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 96, 96)
Image: /home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/blue/image_b200_121.png
- Predicted Class Index: 0
- Confidence: 1.0000
- Inference Time: 0.0299 s
image 1/1 /home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/blue/image_b200_190.png: 96x96 blue 1.00, green 0.00, red 0.00, 14.4ms
...
Total Inference Time: 20.3878 s
Average Inference Time per Image: 0.0227 s
Inference results saved to: inference_results.txt아주 잘됩니다.
onnx 변환하기
변환은 YOLO 공식 문서를 참고하시면 됩니다.
YOLO onnx 변환
python:
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO11 model
model = YOLO("yolo11n.pt")
# Export the model to ONNX format
model.export(format="onnx") # creates 'yolo11n.onnx'
# Load the exported ONNX model
onnx_model = YOLO("yolo11n.onnx")
# Run inference
results = onnx_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")CLI:
# Export a YOLO11n PyTorch model to ONNX format
yolo export model=yolo11n.pt format=onnx # creates 'yolo11n.onnx'
# Run inference with the exported model
yolo predict model=yolo11n.onnx source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'model에 본인 모델을 입력하시고 format을 지정해주시면 됩니다.
onnx파일로 분류하기
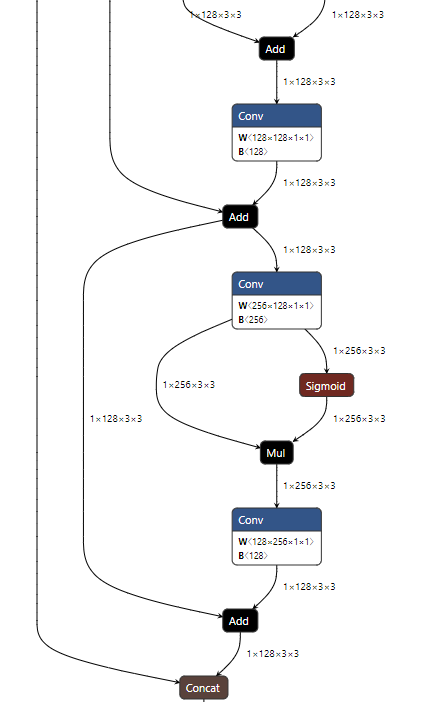
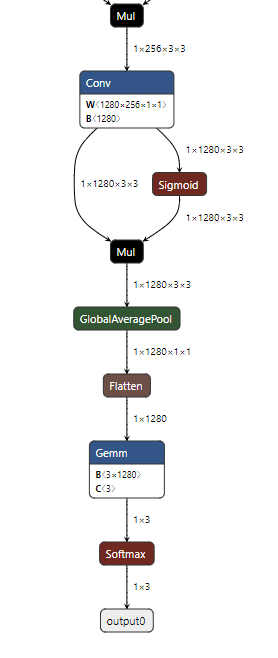
구조가 상당히 복잡한데 일단 구조를 뜯어보죠
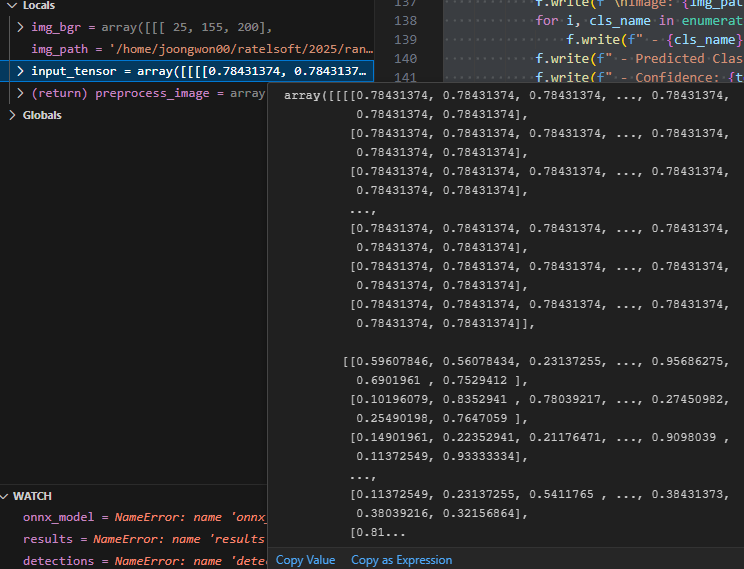
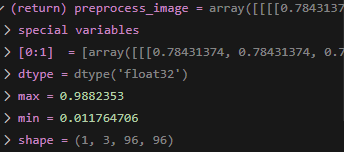
onnx inference를 진행하면
return 값들이 나오는데 max랑 min을 볼 수 있습니다.
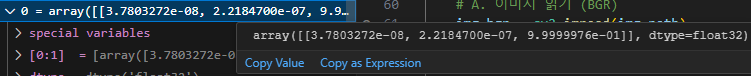
예를들어 해당 array 배열을 보면 혼자 0.999에 수렴하는 값이 하나 있죠
이게 바로 우리가 취해야 하는 값입니다.
코드를 작성해봅시다.
import os
import time
from ultralytics import YOLO
# (A) 학습 완료된 모델 로드
# (위에서 학습된 최적 가중치 위치)
trained_model = YOLO("/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/runs/classify/my_custom_train3/weights/best.pt")
# (B) 추론할 폴더 목록
folders = [
"/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/blue",
"/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/red",
"/home/joongwon00/ratelsoft/2025/random_images/green"
]
# (C) 이미지 확장자 목록
valid_exts = (".jpg", ".jpeg", ".png", ".bmp")
# (D) 결과 로그를 기록할 txt 파일
output_txt_path = "inference_results.txt"
# 총 추론시간 및 이미지 수를 추적하기 위한 변수
total_inference_time = 0.0
total_images = 0
with open(output_txt_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
# (E) 폴더별로 순회하며 추론
for folder_path in folders:
f.write(f"\n=== Inference in folder: {folder_path} ===\n")
print(f"\n=== Inference in folder: {folder_path} ===")
image_files = [img for img in os.listdir(folder_path) if img.lower().endswith(valid_exts)]
for img_file in image_files:
img_path = os.path.join(folder_path, img_file)
start_time = time.time()
# 추론 수행
results = trained_model.predict(img_path)
end_time = time.time()
inference_time = end_time - start_time
total_inference_time += inference_time
total_images += 1
# 결과 해석: 가장 확률 높은 클래스 인덱스/확률
top1_index = results[0].probs.top1
top1_conf = float(results[0].probs.top1conf)
# (F) 화면 출력
print(f"Image: {img_path}")
print(f" - Predicted Class Index: {top1_index}")
print(f" - Confidence: {top1_conf:.4f}")
print(f" - Inference Time: {inference_time:.4f} s")
# (G) TXT 파일에도 기록
f.write(f"\nImage: {img_path}\n")
f.write(f" - Predicted Class Index: {top1_index}\n")
f.write(f" - Confidence: {top1_conf:.4f}\n")
f.write(f" - Inference Time: {inference_time:.4f} s\n")
# (H) 전체 이미지에 대한 총 추론 시간 기록
f.write("\n==================== SUMMARY ====================\n")
print("\n==================== SUMMARY ====================")
if total_images > 0:
average_time = total_inference_time / total_images
summary_str = (
f"Total Images: {total_images}\n"
f"Total Inference Time: {total_inference_time:.4f} s\n"
f"Average Inference Time per Image: {average_time:.4f} s\n"
)
else:
summary_str = "No images were found for inference.\n"
f.write(summary_str)
print(summary_str)
print(f"Inference results saved to: {output_txt_path}")
결과가 잘 나온것을 볼 수 있습니다.

