💁 메소드(Method)란,
어떤 특정 작업을 수행하기 위한 명령문(코드)의 집합
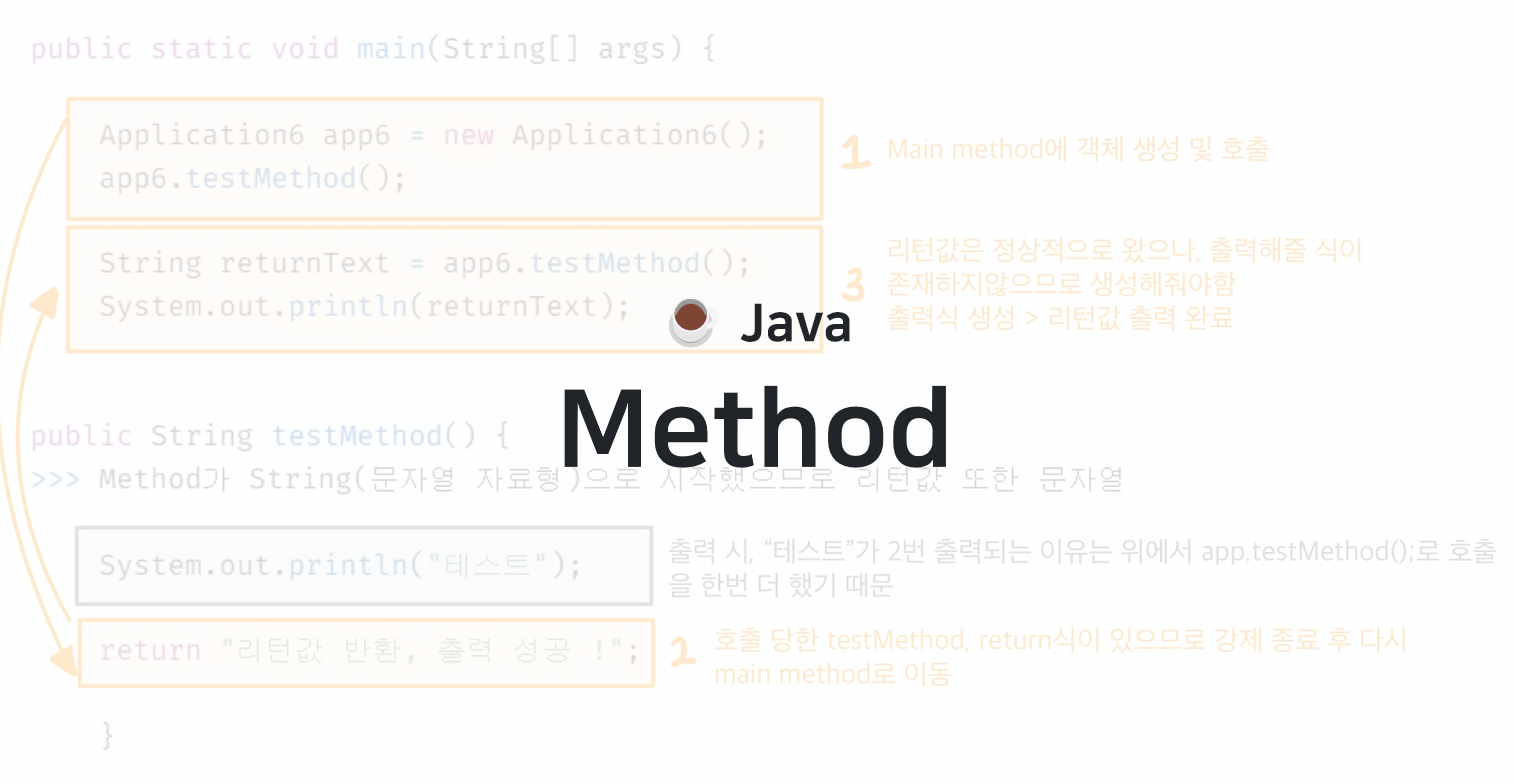
👀 Method 호출 흐름
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main 시작 ! ! !"); >>> [1]
Application2 app2 = new Application2();
app2.methodA(); >>> methodA 호출
app2.methodB(); >>> methodB 호출
System.out.println("main 종료..."); >>> [6]
}
public void methodA() {
System.out.println("methodA 호출..."); >>> [2]
System.out.println("methodA 종료..."); >>> [3]
}
public void methodB() {
System.out.println("methodB 호출..."); >>> [4]
System.out.println("methodB 종료..."); >>> [5]
}
>>> main method에서 호출한 methodA, methodB가 모두 실행되고 종료되면
>>> 다시 main method로 돌아가 최종 종료
👀 전달인자(Argument)와 매개변수(Parameter)를 이용한 Method 호출
다른 메소드간 서로 공유해야하는 값이 존재하는 경우, 메소드 호출 시 사용하는 괄호를 이용해서 값을 전달할 수 있음
💁 이때 전달하는 값을전달인자(Argument), 메소드 선언 부괄호 안에 전달 인자를 받기 위해 선언하는 변수를매개변수(Parameter)라고 함
1) 전달 인자로 값 전달 테스트
public static void main(String[] args) {
Application3 app3 = new Application3();
>>> 객체 생성
>>> 호출하려는 메소드의 매개변수 선언부에 미리 선언해둔 자료형과 갯수, 순서가
>>> 일치하게 값을 넣어 호출해야함
app3.testMethod(26);
>>> 26이 전달인자2) 변수에 저장한 값 전달 테스트
public static void main(String[] args) {
Application3 app3 = new Application3();
>>> 객체 생성
// 1. 변수에 저장된 값을 이용하여 값을 전달할 수 있음
int age = 25;
app3.testMethod(age);
// 2. 자동 형변환을 이용하여 값 전달을 할 수 있음
byte byteAge = 24;
app3.testMethod(byteAge);
// 3. 강제 형변환을 이용하여 값 전달을 할 수 있음
long longAge = 23;
app3.testMethod((int)longAge);
>>> 데이터 손실 주의
// 4. 연산 결과를 이용해서 값 전달을 할 수 있음
app3.testMethod(age * 2);
}public void testMethod(int age) {
>>> age가 매개변수
System.out.println("효연이의 나이는 " + age + "살 입니당");
}👀 Method에 Java docs 기능 사용
/**
* <pre>
* Class : Application4
* Comment : 여러 개의 전달인자와 매개변수를 이용한 메소드 호출
* History
* 2002/12/22 (우별림) 처음 작성함
* 2022/12/22 (조효연) 수정함
* </pre>
* @author 조효연
* @version 1.0.0
*/
>>> jave docs (아래 Application4에 커서를 대면 위에 작성한 java docs 확인할 수 있음)
>>> 메소드의 목적, 기능, 매개변수에 무엇이 전달되어야하는지 등의 내용이 포함
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 각각의 전달인자를 변수로 전달 */
String name = "조효연";
int age = 26;
char gender = 'F';
Application4 app4 = new Application4();
app4.testMethod(name, age, gender);
}
} 📌 Ref.
* 전달인자를 변수로 전달할 때, 순서가 다르게 전달되면 호출되지 못함
ex) app4.testMethod(age, name, gender); >>> 값의 순서가 다름/**
* </pre>
* 이름과 나이와 성별을 전달받아 한 번에 출력해주는 기능을 제공합니다.
* </pre>
* @param name 출력할 이름을 전달해주세요.
* @param age 출력할 나이를 전달해주세요.
* @param gender 출력할 성별을 전달해주세요. 성별은 변경되지 않을 것을 보장합니다. >>> final을 붙여 상수 사용
* */
>>> jave docs (아래 testMethod와 각각의 매개변수에 커서를 대면 위에 작성한 java docs 확인할 수 있음)
>>> 메소드의 목적, 기능, 매개변수에 무엇이 전달되어야하는지 등의 내용이 포함
public void testMethod(String name, int age, final char gender) { >>> 상수 사용
System.out.println("제 이름은 " + name + "이고, 나이는 " + age + "세 이며, 성별은 " + gender + "입니다.");
}
}📌 Ref.
* 매개변수도 일종의 지역변수이며 final 키워드를 사용할 수 있음
* final 매개변수는 상수 네이밍 규칙을 선택적으로 따름
(대문자로 작성해도 되고 소문자로 작성해도 됨)👀 Method 리턴값 테스트
- 반환 값이 있는 메소드를 호출만 하면 아무런 내용이 출력되지않는데, 이는 출력하는 명령어가 존재하지않기 때문
- 반환 값이 있는 메소드를 호출할 때는 반환 값을 변수에 담거나, 동작하고자 하는 메소드 안에서 호출

📌 Ref.
* public 뒤에는 return으로 가지고 갈 타입(자료형)을 명시
아무 값도 리턴하지않을경우 void, 값을 반환하는 경우 반환 값의 자료형을 작성해야함👀 매개변수, 리턴값이 존재하는 Method를 이용하여 계산기 만들기
public static void main(String[] args) {
Application7 app7 = new Application7();
>>> 객체 생성
int first = 100;
int second = 10;
>>> 프린트와 동시에 아래의 메소드를 골라서 호출
System.out.println("두 수를 더하면? : " + app7.plusTwoNumbers(first, second));
System.out.println("두 수를 빼면? : " + app7.minusTwoNumbers(first, second));
System.out.println("두 수를 곱하면? : " + app7.mutipleTwoNumbers(first, second));
System.out.println("두 수를 나누면? : " + app7.divideTwoNumbers(first, second));
}
// 더하기 method
public int plusTwoNumbers(int first, int second) {
return (first + second);
}
// 빼기 method
public int minusTwoNumbers(int first, int second) {
return (first - second);
}
// 곱하기 method
public int mutipleTwoNumbers(int first, int second) {
return (first * second);
}
// 나누기 method
public int divideTwoNumbers(int first, int second) {
return (first / second);
}👀 Static method 호출
클래스명.메소드명();
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("20과 30의 합 : " + Application8.sumTwoNumbers(20, 30));
>>> 클래스명(Application8).메소드명(sumTwoNumbers)(인자(20, 30));
>>> 동일한 클래스 내에 작성된 static method는 클래스명 생략이 가능
System.out.println("20과 30의 합 : " + sumTwoNumbers(20,30));
}
public static int sumTwoNumbers(int first, int second) {
return first + second;
} 📌 Ref.
* static method는 메모리상에 올라가는 위치가 다름
* static method는 non-static method와 달리 객체를 만들지않기 때문에 호출 방법이 더 간단👀 다른 클래스에 작성한 Method 호출
◼ Application9 Class
public class Application9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int first = 100;
int second = 150;
// non-static 메소드 호출
Calculator calc = new Calculator();
int min = calc.minNumberOf(first, second);
>>> 반환값을 담을 변수 생성 (int min)
System.out.println("두 수 중 최소값은 " + min + "이다.");
// static 메소드 호출 (객체 생성 필요 X)
int max = Calculator.maxNumberOf(first, second);
>>> 반환값을 담을 변수 생성 (int max)
>>> 다른 클래스에서 작성된 static 메소드를 호출할 때는 클래스명을 반드시 기술
System.out.println("두 수 중 최대값은 " + max + "이다.");
}
}◼ Calculator Class
public class Calculator {
// 매개변수로 전달받은 두 수를 비교하여 더 작은 값을 가진 정수를 반환하는 method
// (같은 값을 가지는 조건에 대해서는 처리하지않음)
public int minNumberOf(int first, int second) {
return first > second ? second : first;
}
// 매개변수로 전달받은 두 수를 비교하여 더 큰 값을 가진 정수를 반환하는 method
// (같은 값을 가지는 조건에 대해서는 처리하지않음)
public static int maxNumberOf(int first, int second) {
return first > second ? first : second;
}
}