https://github.com/krafton-ai/Orak 의 repository를 참고했습니다!
src와 scripts 폴더가 특별히 중요해보이는데요, 각각 다음과 같은 구조입니다. supermario를 기준으로만 발췌해봤습니다!
src/
|-- mcp_agent_client
| |-- base_agent.py
| |-- base_client.py
| |-- config_loader.py
| |-- configs
| | |-- super_mario
| | | |-- config.yaml
| |-- json_schemas.py
| |-- llms
| | |-- __init__.py
| | |-- anthropic_utils.py
| | |-- constants.py
| | |-- deepseek_utils.py
| | |-- google_utils.py
| | |-- llm.py
| | |-- openai_utils.py
| | |-- utils.py
| |-- runner
| |-- action_tool_execution.py
| |-- eval.py
| |-- multiagent_eval.py
|-- mcp_agent_servers
| |-- super_mario
| | |-- config.yaml
| | |-- prompts
| | | |-- image
| | | | |-- reflection_planning_agent
| | | | |-- action_inference_system.py
| | | | |-- action_inference_user.py
| | | | |-- self_reflection_system.py
| | | | |-- self_reflection_user.py
| | | | |-- subtask_planning_system.py
| | | | |-- subtask_planning_user.py
| | | |-- text
| | | | |-- planning_agent
| | | | | |-- action_inference_system.py
| | | | | |-- action_inference_user.py
| | | | | |-- subtask_planning_system.py
| | | | | |-- subtask_planning_user.py
| | | | |-- reflection_agent
| | | | | |-- action_inference_system.py
| | | | | |-- action_inference_user.py
| | | | | |-- self_reflection_system.py
| | | | | |-- self_reflection_user.py
| | | | |-- reflection_planning_agent
| | | | | |-- action_inference_system.py
| | | | | |-- action_inference_user.py
| | | | | |-- self_reflection_system.py
| | | | | |-- self_reflection_user.py
| | | | | |-- subtask_planning_system.py
| | | | | |-- subtask_planning_user.py
| | | | |-- zeroshot_agent
| | | | |-- action_inference_system.py
| | | | |-- action_inference_user.py
| | | |-- text_image
| | | `-- reflection_planning_agent
| | | |-- action_inference_system.py
| | | |-- action_inference_user.py
| | | |-- self_reflection_system.py
| | | |-- self_reflection_user.py
| | | |-- subtask_planning_system.py
| | | |-- subtask_planning_user.py
| | |-- server.py
|-- mcp_game_servers
|-- base_env.py
|-- base_server.py
|-- gameio
| |-- gui_utils.py
| |-- io_env.py
| |-- window_capture.py
| |-- window_capture_mac.py
|-- super_mario
| |-- config.yaml
| |-- game
| | |-- __init__.py
| | |-- all_object_patterns.json
| | |-- assets
| | | |-- ...
| | | |-- screenshot
| | | |-- ...
| | |-- bbox_to_tensor.py
| | |-- super_mario_env.py
| | |-- wrappers.py
| |-- server.py
|-- utils
|-- module_creator.py
|-- types
|-- game_io.py
|-- misc.pyscripts/
|-- json_viewer.py
|-- leaderboard
| |-- mcp
| | |-- super_mario.sh
| |-- python
| |-- super_mario.sh
|-- mcp_play_game.py
|-- play_game.py
|-- play_game_multi.pyKrafton의 Orak에서는 LLM 기반 에이전트가 Super Mario 게임을 인식하고 계획을 세워 조작까지 수행하는 파이프라인을 구축을 했습니다. 전체 시스템은 클라이언트 에이전트(mcp_agent_client), 서버 에이전트(mcp_agent_servers), 게임 환경(mcp_game_servers)으로 구성되며, 게임에서 화면 정보를 추출한 뒤 이를 LLM에게 전달하고, 추론된 액션을 다시 게임에 적용하는 방식으로 순환합니다. 클라이언트는 LLM 호출 및 실행을 담당하고, 서버는 다양한 프롬프트와 사고 구조를 제공하며, 게임 서버는 환경 시뮬레이션과 조작을 수행한다. 이러한 구조는 reflection, planning, zeroshot 등 다양한 에이전트 계층을 통해 유연한 게임 플레이가 가능하도록 설계되어 있습니다.
play_game.py, mcp_agent_client/, mcp_agent_servers/, mcp_game_servers/의 순서대로 살펴보도록 하겠습니다!
1. play_game.py
1. 설정(config) 로드
- argparse로 config 파일 경로 입력받음
- config.yaml 불러옴
- CLI 인자로 덮어쓰기 가능
- 로그 저장 경로 생성 및 로깅 설정
2. 러너(BaseRunner) 초기화
- 게임 환경(env) 생성
- LLM 에이전트(agent) 생성
3. 실행
- 러너에 환경 및 에이전트 세팅
- 게임 플레이 실행 → score, step 획득
4. 결과 저장
- score, step 등 정보를 JSON으로 저장
- 로그로 실행 결과 출력주요 구성요소와 역할은 다음과 같습니다.
BaseRunner - 에이전트와 환경 연결 및 플레이 수행
EnvCreator - config 기반으로 게임 환경 생성
BaselineAgent - LLM 기반 에이전트 로딩
OmegaConf - 설정 파일 로딩 및 CLI 병합
logging - 실행 로그 기록 및 저장
2. mcp_agent_client/
mcp_agent_client/
├── base_agent.py # 모든 LLM 에이전트의 추상 클래스 / 기본 동작 정의
├── base_client.py # 서버와의 통신 혹은 클라이언트 실행 기본 구조
├── config_loader.py # config.yaml 로드 및 파싱 유틸
├── json_schemas.py # 입력/출력 데이터 포맷 및 스키마 정의
├── llms/
│ ├── __init__.py # LLM 모듈 초기화
│ ├── anthropic_utils.py # Anthropic Claude 모델 사용 유틸
│ ├── constants.py # 공통 상수 정의
│ ├── deepseek_utils.py # DeepSeek 모델 호출 유틸
│ ├── google_utils.py # Google Gemini 모델 호출 유틸
│ ├── llm.py # LLM 호출 공통 인터페이스 추상화
│ ├── openai_utils.py # OpenAI GPT 모델 유틸
│ └── utils.py # LLM 관련 공통 유틸 함수
├── runner/
│ ├── action_tool_execution.py # 툴 실행 기반 평가를 위한 러너 (예: API 호출)
│ ├── eval.py # 기본 BaseRunner 정의, 메인 실행 로직
│ └── multiagent_eval.py # 멀티에이전트 환경에서의 평가 실행3. mcp_agent_servers/
mcp_agent_servers/
├── agent_types.py # 다양한 에이전트 유형을 정의
├── base_server.py # 서버형 에이전트의 기본 틀
├── memory.py # 에이전트의 기억 시스템
├── memory_utils.py # 메모리 로딩, 정리 등의 유틸 함수
├── setup_openai.py # OpenAI API 키 설정 및 초기화
├── skill_manager.py # 에이전트의 툴/스킬 관리 시스템
├── super_mario/
│ ├── config.yaml # super_mario 환경 설정
│ ├── server.py # super_mario용 서버 실행 코드
│ └── prompts/
│ ├── image/reflection_planning_agent/
│ │ ├── action_inference_system.py
│ │ ├── action_inference_user.py
│ │ ├── self_reflection_system.py
│ │ ├── self_reflection_user.py
│ │ ├── subtask_planning_system.py
│ │ └── subtask_planning_user.py
│ ├── text/{agent_type}/...
│ ├── text_image/{agent_type}/...에이전트의 구성 방식 또는 사고 구조를 구분하는 프롬프트 설계 방식에 따라 아래와 같은 agent_type이 존재합니다.
planning_agentreflection_agentreflection_planning_agentzeroshot_agent
1. planning_agent/
단순한 계획 수립 중심의 agent
subtask_planning_system.py+action_inference_system.py기반- 입력 정보를 받아 단계별 행동 계획을 세우고, 각 단계의 행동을 예측
- self-reflection 없음 (반성 과정 없음)
사용 예시: 명시된 목표가 있고, 비교적 단순한 행동 계획으로 도달할 수 있는 경우
2. reflection_agent/
수행된 행동에 대해 반성(reflection)을 통해 전략을 보완하는 agent
self_reflection_system.py를 포함- 계획보다는 수행 결과에 대한 점검 및 전략 수정에 집중
사용 예시: 실수 가능성이 높거나 행동 수행 후 되짚어야 하는 경우
3. reflection_planning_agent/
계획 + 반성이 결합된 강화형 agent
subtask_planning_system.py,action_inference_system.py,self_reflection_system.py모두 포함- 가장 복합적이고 체계적인 프롬프트 구성
- 계획 → 행동 → 반성 → 조정 → 반복
사용 예시: 난이도가 높고 복잡한 과제를 수행하는 경우 (예: Super Mario)
4. zeroshot_agent/
별도 계획 없이 즉각적 판단만 수행하는 에이전트
action_inference_system.py하나만 있음- Zero-shot prompting 기반: 상황을 보고 바로 행동 결정 (planning_agent와 달리 명시적 계획 없이 즉시 행동을 선택하는 방식.)
- 반성도, 계획도 없음
사용 예시: 간단한 환경에서 빠르게 평가하거나 baseline 비교용
4. mcp_game_servers/
mcp_game_servers/
├── base_env.py # 모든 게임 환경의 추상 베이스 클래스
├── base_server.py # 공통 게임 서버 베이스
├── super_mario/
│ ├── config.yaml
│ ├── server.py # Super Mario 게임 서버 구동
│ └── game/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── bbox_to_tensor.py # BBox 추출 및 텐서 변환 유틸
│ ├── super_mario_env.py # Super Mario 환경 정의
│ ├── wrappers.py # 환경 래핑 (obs 변형 등)
│ └── assets/ # 오브젝트 패턴 정의 JSON & 이미지
└── utils/
├── module_creator.py # config 기반으로 env/module 생성
└── types/
├── game_io.py # 게임 입력/출력 타입 정의
└── misc.py # 기타 타입 유틸5. 시각화
[play_game.py]
│
▼
[mcp_agent_client/]
├─ BaseRunner
├─ llms/ (OpenAI, DeepSeek 등)
└─ runner/eval.py
│
▼
[mcp_agent_servers/]
├─ prompts/
│ ├─ planning_agent/
│ ├─ reflection_agent/
│ ├─ reflection_planning_agent/
│ └─ zeroshot_agent/
└─ server.py
│
▼
[mcp_game_servers/]
├─ super_mario_env.py
├─ wrappers.py
├─ assets/, screenshots/
└─ utils/module_creator.py
│
▼
[게임 상태 관찰: obs, reward, info]
│
▼
[Agent 판단 → Action 선택]
│
└───────────────┐
▼
[환경에 액션 적용 → 다음 상태]
│
└──── feedback loop → (mcp_agent_client/BaseRunner)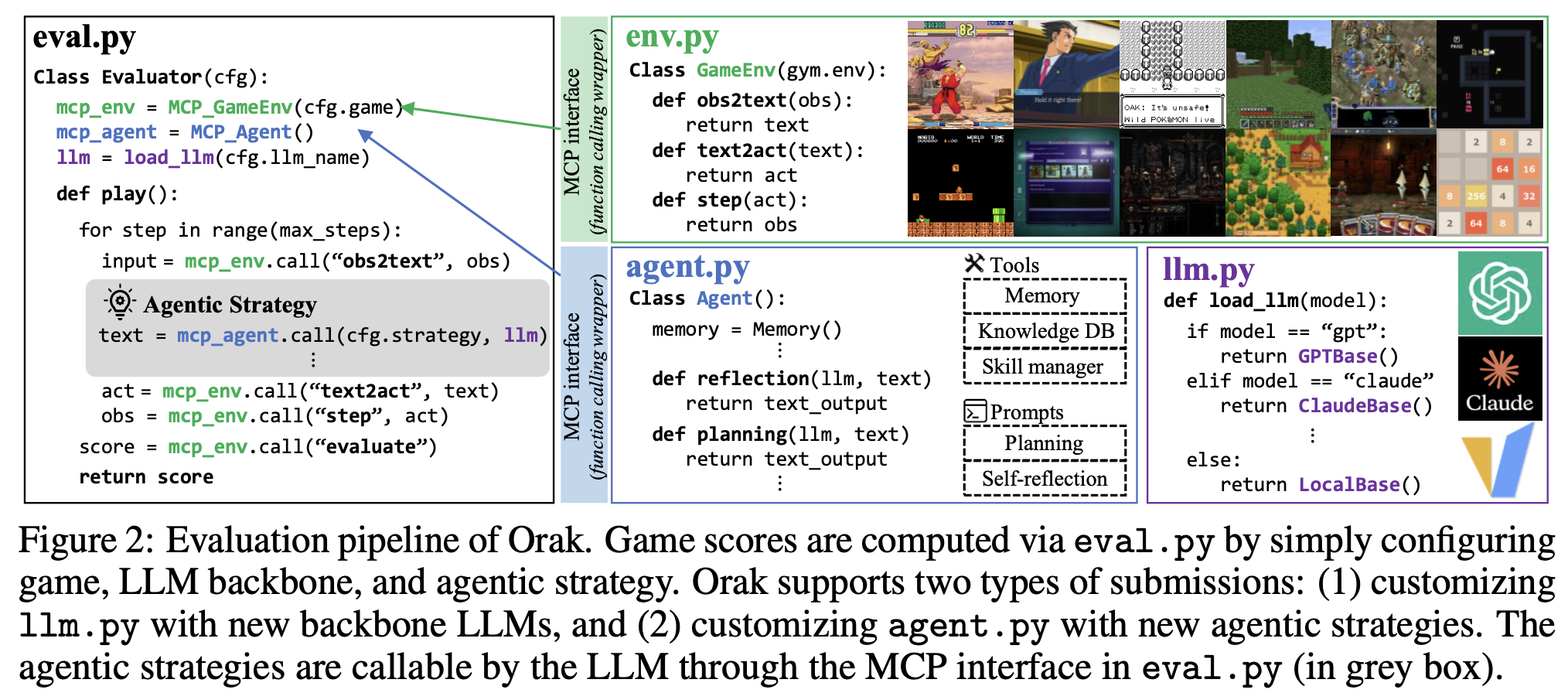
1. [play_game.py]에서 config 로딩 및 실행 시작
2. [BaseRunner]가 [Agent]와 [Env] 구성
3. [Agent]는 프롬프트 및 LLM을 활용해 행동 결정
4. [Env]는 게임 상태 제공 및 액션 수행
5. 결과 (이미지/위치/reward)를 다시 [Agent]에 전달
6. 반복 실행하며 플레이 진행마치며..
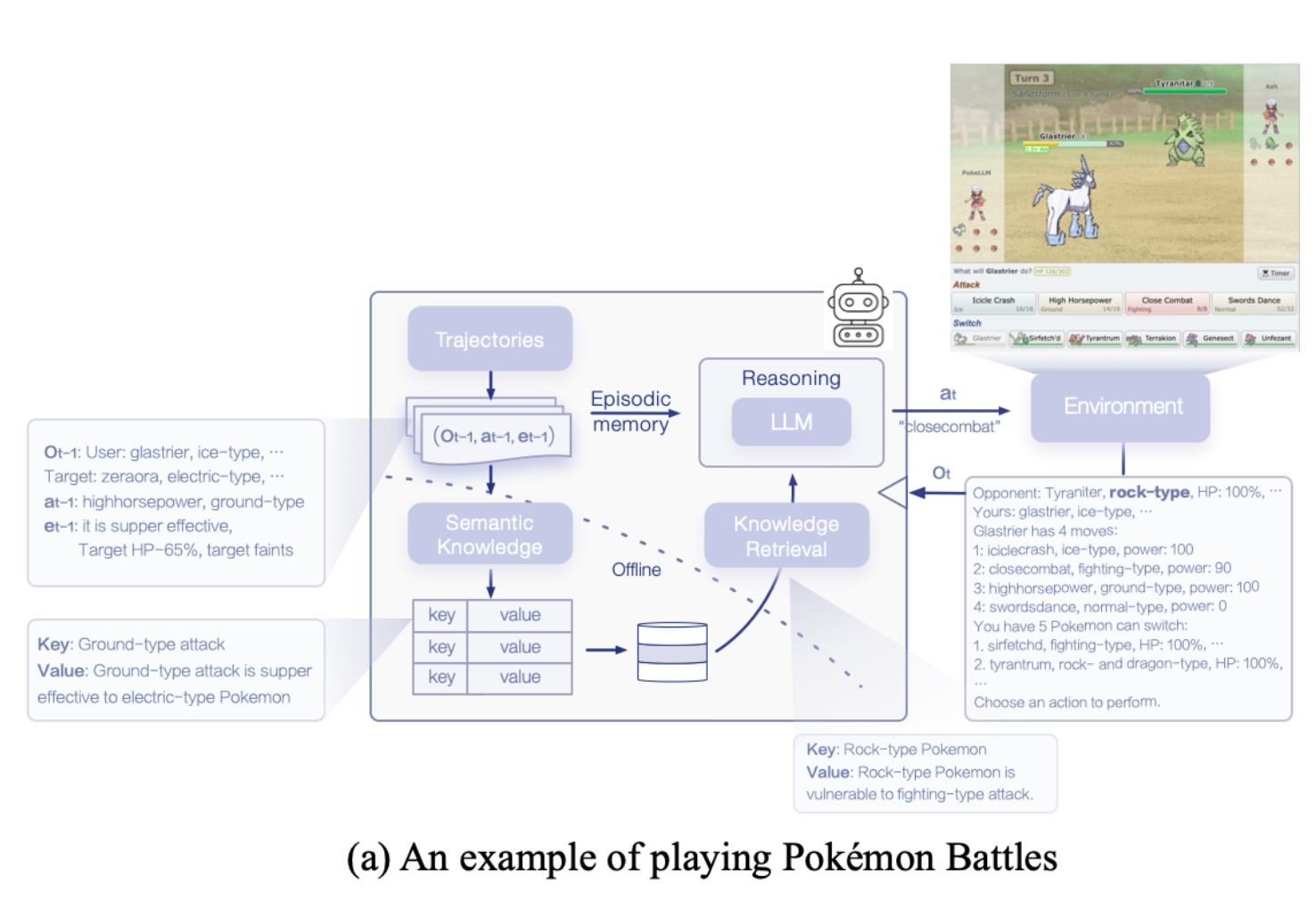
A Survey on Large Language Model Based Game Agents 의 논문을 참고하면 LLM 기반의 game agent는 memory system, reasoning, input/output의 조합으로 위와 같이 작동하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. 디테일한 계층구조는 아래와 같습니다.
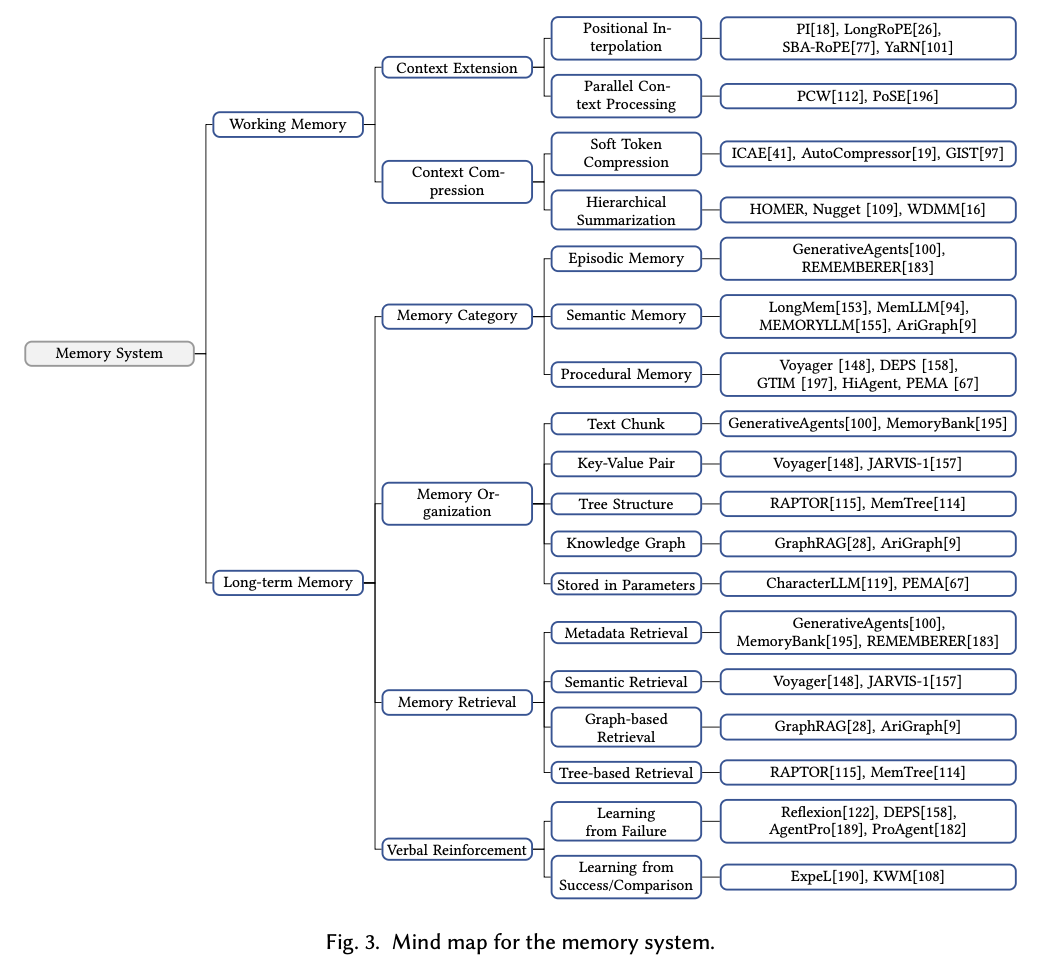
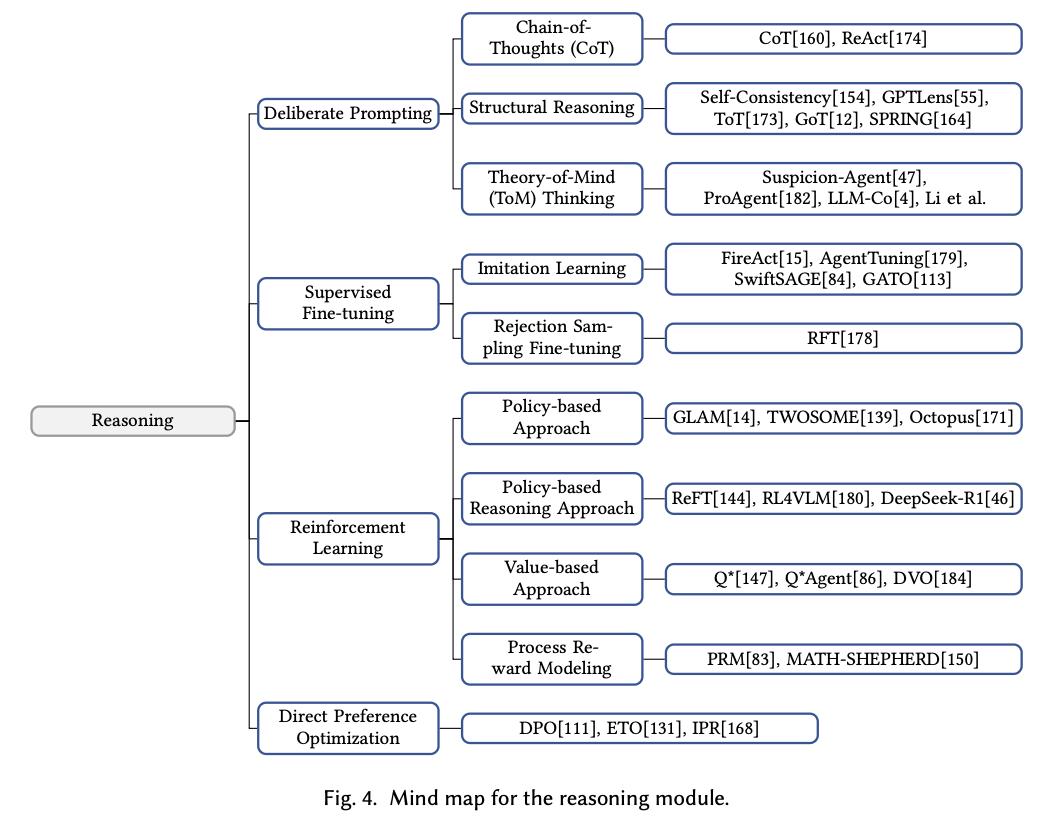
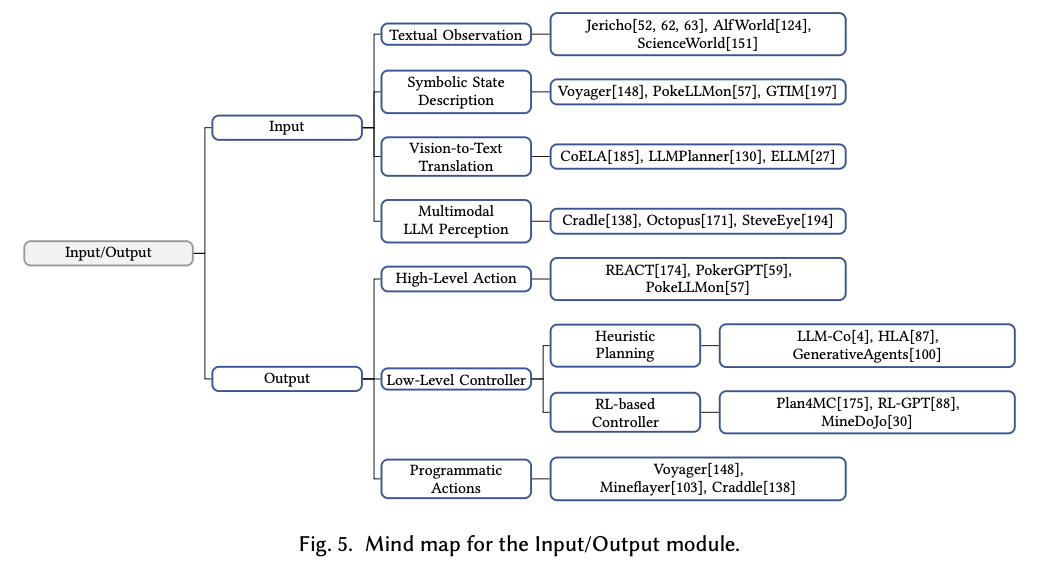 이들의 조합을 통해 최적의 가능성을 탐색해볼 수 있을 것 같습니다.
특히, LLM이 하나의 모듈로 작동하면서 다양한 엔드포인트들과 유연하게 소통하는 프로토콜 구조가 인상적이었습니다.
이들의 조합을 통해 최적의 가능성을 탐색해볼 수 있을 것 같습니다.
특히, LLM이 하나의 모듈로 작동하면서 다양한 엔드포인트들과 유연하게 소통하는 프로토콜 구조가 인상적이었습니다.
현재는 디테일한 코드 구조를 더 깊이 살펴보는 중이며,
- 히스토리 관리 방식, 게임의 내재적 정보가 메모리 뱅크에서 어떻게 유지·활용되는지,
- 프롬프트가 어떤 방식으로 정의되고,
- 각 엔드포인트 간의 정보 교환이 어떤 프로토콜을 통해 이루어지는지
등을 중점적으로 분석해볼 계획입니다.
