그리디
이 순간에 현재에서 최선의 선택을 함 --> 전체의 최적해가 됨.
1. 씨름선수

🚩 내 코드
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 씨름선수 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
ArrayList<Person> al = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int h = scanner.nextInt();
int w = scanner.nextInt();
al.add(new Person(h,w));
}
Collections.sort(al);
int answer=0;
int max =Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(Person p : al){
if(p.w > max){
max = p.w;
answer++;
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
public static class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
int h;
int w;
Person(int h, int w){
this.h = h;
this.w = w;
}
// 키로 내림차순 정렬
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return o.h-this.h;
}
}
}
💡 푼 방식
일단은 사람이라는 객체를 만든 후 키,몸무게를 필드로 갖게 한다.
그리고 사람을 키로 정렬해놓고, 몸무게 비교를한다. -> o(n)
첨부터 2중 for문 돌면 시간 초과됨.. -> o(n^2)
내림 정렬 후 첫번째 사람은 일단 키가 제일 크기때문에 뽑힌다.
이제 첫번째 사람의 몸무게(=max)를 기준으로 비교해나가면 된다.
max보다 큰거 나오면 +1하고 그 값을 max로 업뎃.
📚 알게 된 내용
객체 비교하는거
// 키로 내림차순 정렬
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return o.h-this.h;
}## 2. 회의실 배정

🚩 내 코드
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 회의실배정 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
ArrayList<Meeting> al = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int s = scanner.nextInt();
int e = scanner.nextInt();
al.add(new Meeting(s,e));
}
Collections.sort(al);
int answer = 0;
int end = 0;
for(Meeting m : al){
if(m.s >= end){ // 이전에 끝난시간보다 같거나 늦게 시작해야함
answer++;
end = m.e;
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
public static class Meeting implements Comparable<Meeting>{
int s;
int e;
Meeting(int s, int e){
this.s = s;
this.e = e;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Meeting o) {
if(this.e == o.e){
return this.s-o.s;
}else{
return this.e - o.e;
}
}
}
}
💡 푼 방식
기준을 회의가 빨리 끝나는 것으로 해야한다.
먼저 시작하는것을 기준으로 한다면,, 빨리 끝나지만 엄청 늦게 끝나는 경우가 있어서 안된다.
📚 알게 된 내용
3. 결혼식
🚩 내 코드
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 결혼식 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
ArrayList<Person> al = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int s = scanner.nextInt();
al.add(new Person(s,'s'));
int e = scanner.nextInt();
al.add(new Person(e,'e'));
}
int cnt=0;
int answer = 0;
Collections.sort(al);
for(Person p : al){
if(p.state == 's'){
cnt++;
}else{
cnt--;
}
if(cnt>answer){
answer=cnt;
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
private static class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
int time;
char state;
Person(int time, char state){
this.time = time;
this.state = state;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
if(this.time == o.time){
return this.state - o.state;
}else{
return this.time - o.time;
}
}
}
}💡 푼 방식
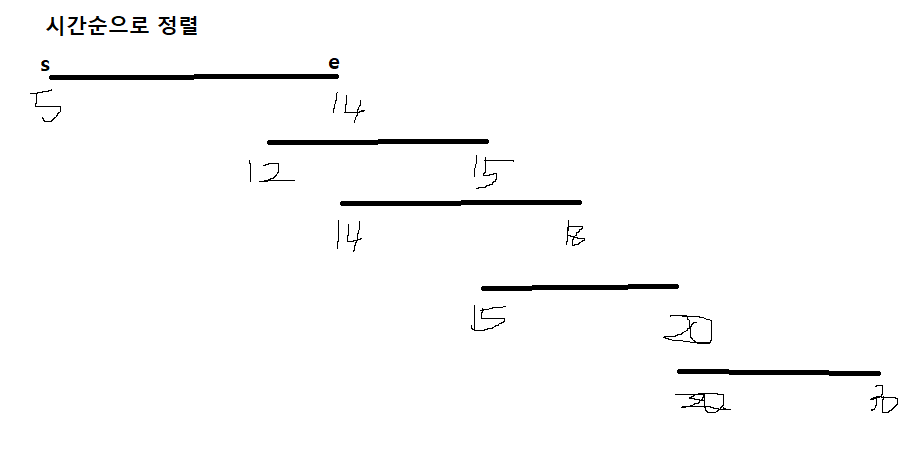
이렇게 시간순으로 정렬해서,
cnt에는 현재있는 사람수, answer에는 지금껏 최고수를 해보도록했다.
answer는 cnt보다 클 때만 바꿔주도록..
그러기 위해서는 e 끝점에서 사람이 먼저 빠지는걸 체크해줘야한다. (s에서 사람 들어오는걸 먼저하면 answer가 갱신될 수도 있으니까.)
따라서 Person이라는 객체에 시간과 상태(s,e)를 넣어주고
시간을 오름차순으로 정렬 -> 시간이 같다면 상태를 오름차순으로 정렬하면 된다.
4. 최대 수입 스케줄

🚩 내 코드
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 결혼식 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
ArrayList<Person> al = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int s = scanner.nextInt();
al.add(new Person(s,'s'));
int e = scanner.nextInt();
al.add(new Person(e,'e'));
}
int cnt=0;
int answer = 0;
Collections.sort(al);
for(Person p : al){
if(p.state == 's'){
cnt++;
}else{
cnt--;
}
if(cnt>answer){
answer=cnt;
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
private static class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
int time;
char state;
Person(int time, char state){
this.time = time;
this.state = state;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
if(this.time == o.time){
return this.state - o.state;
}else{
return this.time - o.time;
}
}
}
}💡 푼 방식

이렇게 시간순으로 정렬해서,
cnt에는 현재있는 사람수, answer에는 지금껏 최고수를 해보도록했다.
answer는 cnt보다 클 때만 바꿔주도록..
그러기 위해서는 e 끝점에서 사람이 먼저 빠지는걸 체크해줘야한다. (s에서 사람 들어오는걸 먼저하면 answer가 갱신될 수도 있으니까.)
따라서 Person이라는 객체에 시간과 상태(s,e)를 넣어주고
시간을 오름차순으로 정렬 -> 시간이 같다면 상태를 오름차순으로 정렬하면 된다.
4. 최대 수입 스케줄
🚩 내 코드
public class 최대수입스케줄 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// 큰 값을 우선순위
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
ArrayList<Schedule> al = new ArrayList<>();
int max = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int m = scanner.nextInt();
int d = scanner.nextInt();
al.add(new Schedule(m,d));
if (d> max){
max=d;
}
}
int answer = 0;
// 날짜가 큰 것부터 정렬됨.
Collections.sort(al);
int j=0;
for(int i=max; i>=1; i--){
for(;j<n;j++){
if(al.get(j).d<i) break;
queue.offer(al.get(j).m);
}
if(!queue.isEmpty()) answer+=queue.poll();
}
}
public static class Schedule implements Comparable<Schedule>{
int d;
int m;
Schedule(int d, int m){
this.d = d;
this.m = m;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Schedule o) {
return o.d - this.d;
}
}
}
💡 푼 방식
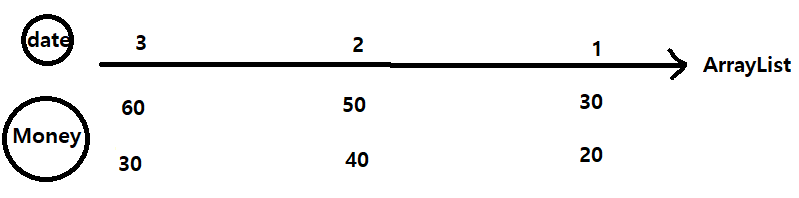
날짜가 클 수록, 선택지가 많아지므로 날짜 내림차순으로 강의를 정렬한다.
(강의는 날짜와 시간이라는 필드를 가짐)
그리고 돈이 많은 것부터 queue에 넣어준다.
