포인터(pointer)란?
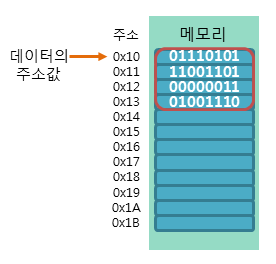
주소값: 해당 데이터가 저장된 메모리의 시작 주소
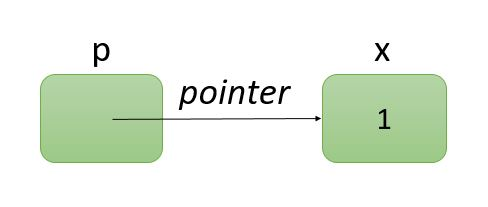
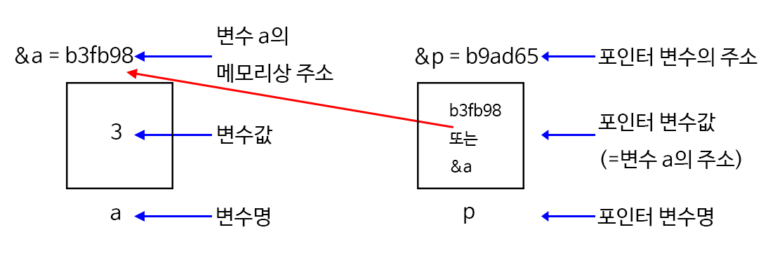
포인터(pointer)란 메모리의 주소값을 저장하는 변수
포인터의 선언
int n = 100; // 변수의 선언
int *ptr = &n; // 포인터의 선언주소 연산자(&)
: 변수의 이름 앞에서 사용 -> 해당 변수의 주소값 반환. ampersand
참조 연산자(*)
: 포인터의 이름이나 주소 앞에 사용하여, 포인터에 가리키는 주소에 저장된 값 반환 ,asterisk
포인터의 참조
int x = 7; // 변수의 선언
int *ptr = &x; // 포인터의 선언
int *pptr = &ptr; // 포인터의 참조 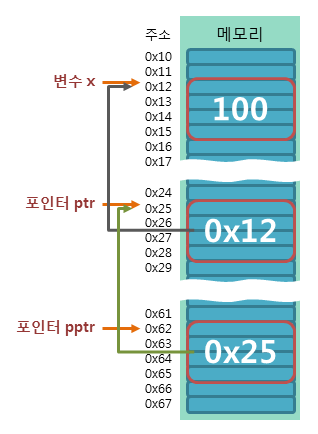
int main() {
int *p;
int a = 2;
p = &a;
printf("%d\n", p);
printf("%d\n", *p);
}
#include <stdio.h> void fun(int *ptr) { *ptr = 30; } int main() { int y = 20; fun(&y); printf("%d", y); return 0; }결과는 30이 된다.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int arri[] = {1, 2, 3};
int *ptri = arri;
char arrc[] = {1, 2, 3};
char *ptrc = arrc;
printf("sizeof arri[] = %d ", sizeof(arri));
printf("sizeof ptri = %d ", sizeof(ptri));
printf("sizeof arrc[] = %d ", sizeof(arrc));
printf("sizeof ptrc = %d ", sizeof(ptrc));
return 0;
} int 요소 1개 - 4byte 3개
char 요소 1개 - 1 byte 3개
=> 출력 결과 12 4 3 4
포인터의 크기는 주소를 저장하기 위해 사용되는 메모리의 크기에 따라 달라지지만, 일반적으로 4바이트 또는 8바이트

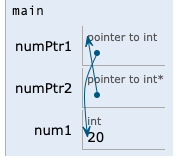
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int *numPtr1;
int **numPtr2;
int num1 = 20;
numPtr1 = &num1;
numPtr2 = &numPtr1;
printf("%d\n", **numPtr2);
return 0;
}
//출력결과는 20이 된다.