Achievement Goal
Before You Learn
Asynchronous & Promise 에서의 비동기 요청에 대한 이해와, 코드 작성법
DOM을 이용해 동적으로 HTML element를 화면에 표시하는 방법
Achievement Goals
클라이언트, 서버, API 가 무엇인지 정의 내릴 수 있다.
웹 개발과 관련한 클라이언트-서버 아키텍처를 이해할 수 있다.
클라이언트와 서버가 서로 통신하기 위해 사용하는 HTTP 프로토콜에 대해 이해할 수 있다.
HTTP 메소드의 종류를 이해할 수 있다.
HTTP 메시지가 어떤 구성으로 이루어져 있는지 이해할 수 있다.
서버에서 정의한 API 문서를 통해, 서버가 제공하는 리소스를 이용할 수 있다.
API 테스팅 툴 Postman을 이용할 수 있다.
API를 활용해서 UI를 만들 수 있다.
AJAX가 무엇이고, 왜 필요한지를 이해할 수 있다.
AJAX 통신을 가능하게 하는 fetch API를 이용할 수 있다.
Browser Security Model
CORS가 왜 필요한지 이해할 수 있다.
XSS가 어떤 원리를 통한 공격 방법인지 이해할 수 있다.
XSS를 어떻게 방지하는 지 이해할 수 있다.
Fetch API, XMLHTTPRequest replacement
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vj7W8pI-L6w&t=361s
HTTP Cookies Crash Course
쿠키 진짜 너무 어려워...
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sovAIX4doOE&t=288s
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Crash Course - HTTP 1.0, 1.1, HTTP/2, HTTP/3
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0OrmKCB0UrQ
2.1 Server-side with Node.js - Working with Data and APIs in JavaScript
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wxbQP1LMZsw&t=950s
8.2: HTTP Server with Express - Programming with Text
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6oiabY1xpBo
코딩트레인이 가장 설명을 잘해주지 않은가싶다.
https://shiffman.net/a2z/node-api/
basic routes
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.listen(port, listening);
function listening() {
console.log(`Example app listening at http://localhost:${port}`);
}
app.use(express.static("website"));
app.get("/search/:flower/:num", sendFlower);
=> 여기가 라우터다 이 디렉토리를 통하여서 어떻게 표시하게 될것인지
결정이 된다.
=> callback함수를 작성해주는데
function sendFlower(request, response) {
var data = request.params;
var num = data.num;
var reply = "";
for (var i = 0; i < num; i++) {
reply += "I love " + data.flower + " too";
}
response.send(reply);
}
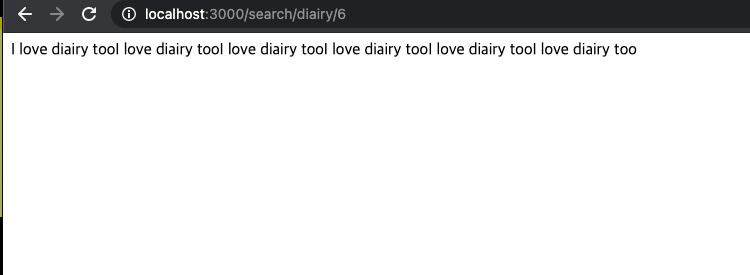
서버 사이드를 써야하는 이유를 썼다
Why use server-side programming?
In session four’s notes on node and twitter bots I covered the basics of working with node, npm, and building an API with “RESTian” routes.
This page picks up on that thread and looks at a few scenarios where running server side code to work with text has advantages over running everything on the client.
One of the main reasons you might go down this road is if you have a large dataset that takes a significant amount of time to process. For example, let’s say you want to build a word counting app and you have one million documents to process. This would be unrealistic to do on the client-side, but reasonable on the server.
const words = {
rainbow: 5,
unicorn: 3,
doom: -3,
};
app.get("/all", sendAll);
function sendAll(request, response) {
response.send(words);
}

신기하게 출력이 된다.
Sprint
im-sprint-chatterbox-client
https://velog.io/@naseriansuzie/imcourseTIL12
https://velog.io/@rlcjf0014/TIL-13-Chatterbox-Client-Review
https://velog.io/@jangwonyoon/Immersive12-chatterbox-client
Singleton_pattern
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Singleton_pattern
In software engineering, the singleton pattern is a software design pattern that restricts the instantiation of a class to one "single" instance. This is useful when exactly one object is needed to coordinate actions across the system. The term comes from the mathematical concept of a singleton.
Critics consider the singleton to be an anti-pattern in that it is frequently used in scenarios where it is not beneficial, introduces unnecessary restrictions in situations where a sole instance of a class is not actually required, and introduces global state into an application.
https://www.daleseo.com/js-window-fetch/
fetch(Get)은 쉽게 했는데
send(Post)는 어렵다.
// Example POST method implementation:
postData('http://example.com/answer', {answer: 42})
.then(data => console.log(JSON.stringify(data))) // JSON-string from `response.json()` call
.catch(error => console.error(error));
function postData(url = '', data = {}) {
// Default options are marked with *
return fetch(url, {
method: 'POST', // *GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.
mode: 'cors', // no-cors, cors, *same-origin
cache: 'no-cache', // *default, no-cache, reload, force-cache, only-if-cached
credentials: 'same-origin', // include, *same-origin, omit
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
// 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
},
redirect: 'follow', // manual, *follow, error
referrer: 'no-referrer', // no-referrer, *client
body: JSON.stringify(data), // body data type must match "Content-Type" header
})
.then(response => response.json()); // parses JSON response into native JavaScript objects
}
https://velog.io/@underlier12/Servlet-JSP-06-Post-Request-52k5rj94zu
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kw5tC5nQMRY&t=125s
Create An API: CORS, SPA / Client-Side Routing Explanation
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xq34NS4S59o&t=392s
POST
ExpressJS Tutorial #3 - POST Requests
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1cjdlfB11Ss
const cors = require("cors");
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
app.use(cors());
app.use(express.json());
app.get("/api/animal/:name", (req, res) => {
if (req.params.name === "meowsalot") {
res.json({
name: "Meowsalot",
species: "cat",
photo: "https://learnwebcode.github.io/json-example/images/cat-1.jpg",
bio:
"This cat is great and very vocal. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Quis asperiores, sunt consectetur a amet dolorem rem animi tempore molestias nesciunt fuga, sequi alias voluptatum totam reprehenderit assumenda deleniti distinctio? Cumque.",
});
} else if (req.params.name === "barksalot") {
res.json({
name: "Barksalot",
species: "dog",
photo: "https://learnwebcode.github.io/json-example/images/dog-1.jpg",
bio:
"This dog is very communicative. Deleniti, tempora quis commodi qui inventore ratione rem porro doloribus et obcaecati cumque quibusdam voluptatibus iure nisi aut minima consequuntur, officiis esse? Lorem ipsum, dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit.",
});
} else if (req.params.name === "purrsloud") {
res.json({
name: "Purrsloud",
species: "cat",
photo: "https://learnwebcode.github.io/json-example/images/cat-2.jpg",
bio:
"Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Quis asperiores, sunt consectetur a amet dolorem rem animi tempore molestias nesciunt fuga, sequi alias voluptatum totam reprehenderit assumenda deleniti distinctio? Cumque. Lorem ipsum.",
});
} else {
res.json("Animal not found.");
}
});
app.get("/fake-search", (req, res) => {
console.log(req.query);
res.json("Thank you for your request.");
});
app.post("/api/secret", (req, res) => {
if (req.body.username === "johndoe" && req.body.password === "qwerty") {
res.json("You have secret access for us to tell you that 2 + 2 is 4.");
} else {
res.json("That is incorrect.");
}
});
//app.delete()
//app.put()
app.listen(3000);여기서 cors를 공부해보았다.
cors를 이해는 잘안되었지만 express를 통해서 쓰는법을 알게되었다.
SPA
Cookies, Sessions, JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and More 🍪🔐
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uXDnS5PcjCA
Cross Origin Resource Sharing (Explained by Example)
