Spring Boot Exception
 크게 두 가지의 방식이 존재
크게 두 가지의 방식이 존재
@ControllerAdvice 모든 Controller에서 발생할 수 있는 예외 처리
@ExceptionHandler 특정 Controller의 예외 처리
@ControllerAdvice로 모든 예외를 정의하고 @ExceptionHandler로 예외마다 세부적으로 정의
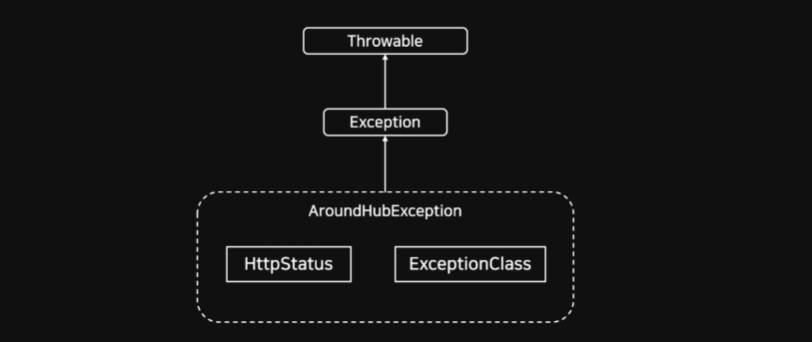
@AroundHubException을 통해 새로운 예외처리 클래스를 만들 수 있음
Exception Class
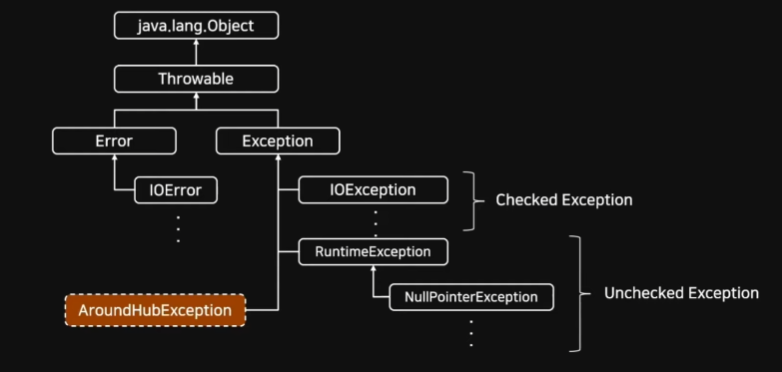
 모든 예외 클래스는 Throwable 클래스를 상속받고 있음
모든 예외 클래스는 Throwable 클래스를 상속받고 있음
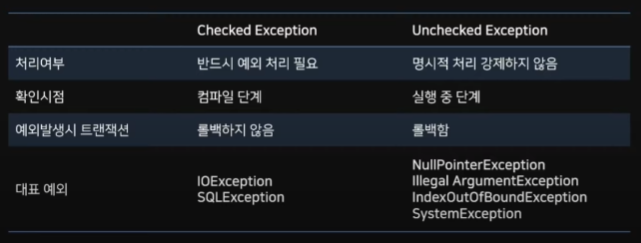
RuntimeException은 Unchecked이며 그 외 Exception은 Checked Exception
@ControllerAdvice
Spring에서 제공하는 Annotaiton
@Controller나 @RestController에서 발생하는 예외를 한 곳에서 관리하고 처리할 수 있게 하는 Anniotation
설정을 통해 범위 지정이 가능, Default 값으로 모든 Controller 예외 처리 가능
예외 발생 시 JSON 형태로 결과 반환을 위해서는 RestControllerAdvice 사용
@ExceptionHandler
예외처리 상황이 발생하면 해당 Handler로 처리하겠다고 명시하는 Annotation
Annotation 뒤에 괄호를 붙여 어떤 ExceptionClass를 처리할지 설정 가능
ex. @ExceptionHandler(OOException.class)
Exception.class는 최상위 클래스로 하위 세부 예외 처리 클래스로 설정한 핸들러가 존재하면 그 핸들러가 우선처리하게 되며, 처리되지 못하는 예외에 대해 ExceptionClass에서 핸들링
@ControllerAdvice로 설정된 클래스 내에서 메소드로 정의할 수 있지만, 각 Controller 내부에서도 설정할 수 있다
Exception 우선순위
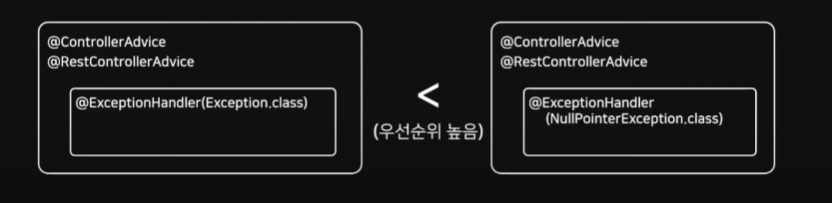
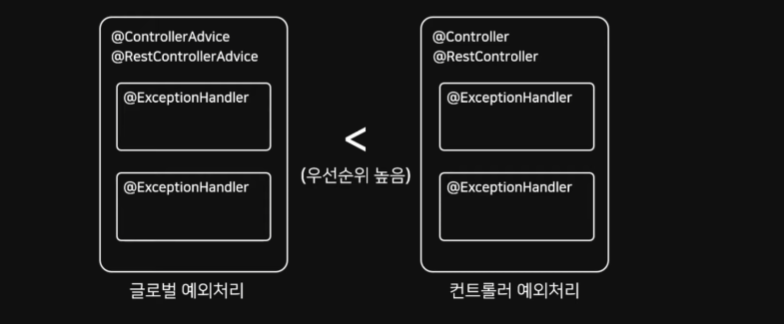 전역설정 (@ControllerAdvice)보다 지역설정 (Controller)로 정의한 Handler가 우선순위 가짐
전역설정 (@ControllerAdvice)보다 지역설정 (Controller)로 정의한 Handler가 우선순위 가짐
/controller/HelloController.java
@RestController
@TypeAnnotation(name = "Hello?", value = "World")
public class HelloController {
@FieldAnnotation(name = "returnValue", value = "Bye World!")
public String returnValue = "Hello World!";
private final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloController.class);
...
@PostMapping("/exception")
public void exceptionTest() throws Exception {
throw new Exception();
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> ExceptionHandler(Exception e) {
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
//responseHeaders.add(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/json");
HttpStatus httpStatus = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
LOGGER.info(e.getMessage());
LOGGER.info("Controller 내 ExceptionHandler 호출");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("error type", httpStatus.getReasonPhrase());
map.put("code", "400");
map.put("message", "에러 발생");
return new ResponseEntity<>(map, responseHeaders, httpStatus);
}
}Custom Exception
error type, error code, message를 응답하여 Client와 에러 내용을 공유
Exception 구조
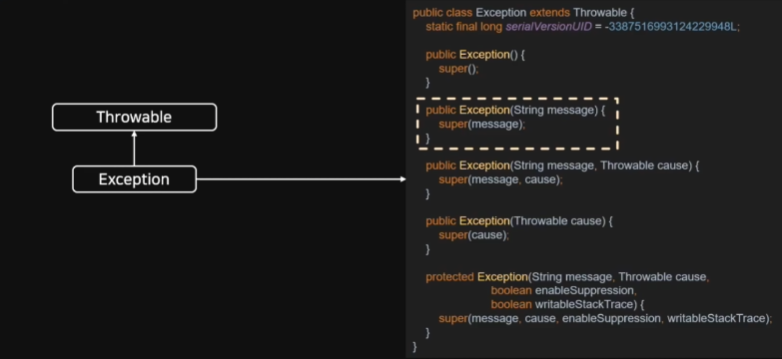 Throwable 부분에서 메세지를 처리하는 로직이 존재한다
Throwable 부분에서 메세지를 처리하는 로직이 존재한다
Throwable 구조
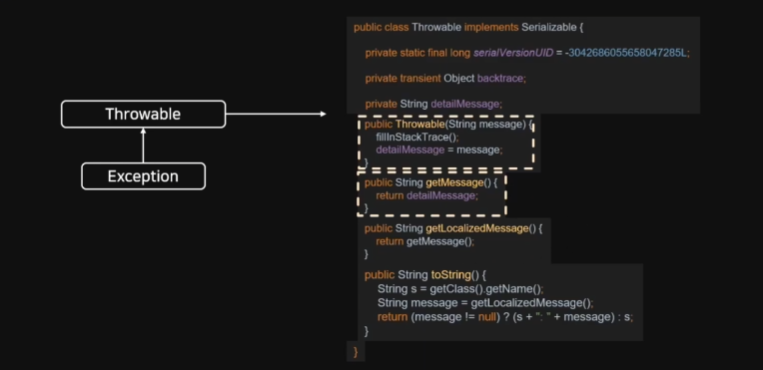
HTTP Status
Enum Class, BAD_REQUEST(300, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Bad Request")
/valid/Constants.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.common;
public class Constants {
public enum ExceptionClass {
PRODUCT("Product"), SIGN("Sign");
private String exceptionClass;
ExceptionClass(String exceptionClass) {
this.exceptionClass = exceptionClass;
}
public String getExceptionClass() {
return exceptionClass;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getExceptionClass() + " Exception. ";
}
}
}/exception/AroundHubException.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.common.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.common.Constants;
public class AroundHubException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4663380430591151694L;
private Constants.ExceptionClass exceptionClass;
private HttpStatus httpStatus;
public AroundHubException(Constants.ExceptionClass exceptionClass, HttpStatus httpStatus,
String message) {
super(exceptionClass.toString() + message);
this.exceptionClass = exceptionClass;
this.httpStatus = httpStatus;
}
public Constants.ExceptionClass getExceptionClass() {
return exceptionClass;
}
public int getHttpStatusCode() {
return httpStatus.value();
}
public String getHttpStatusType() {
return httpStatus.getReasonPhrase();
}
public HttpStatus getHttpStatus() {
return httpStatus;
}
}/exception/AroundHubExceptionHandler.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.common.exception;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
@RestControllerAdvice
public class AroundHubExceptionHandler {
private final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AroundHubExceptionHandler.class);
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> ExceptionHandler(Exception e) {
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
//responseHeaders.add(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/json");
HttpStatus httpStatus = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
LOGGER.error("Advice 내 ExceptionHandler 호출, {}, {}", e.getCause(), e.getMessage());
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("error type", httpStatus.getReasonPhrase());
map.put("code", "400");
map.put("message", "에러 발생");
return new ResponseEntity<>(map, responseHeaders, httpStatus);
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = AroundHubException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> ExceptionHandler(AroundHubException e) {
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("error type", e.getHttpStatusType());
map.put("error code",
Integer.toString(e.getHttpStatusCode())); // Map<String, Object>로 설정하면 toString 불필요
map.put("message", e.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(map, responseHeaders, e.getHttpStatus());
}
}/controller/ProductCopntroller.java
@PostMapping(value = "/product/exception")
public void exceptionTest() throws AroundHubException {
throw new AroundHubException(ExceptionClass.PRODUCT, HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN, "접근이 금지되었습니다.");
}Rest Template
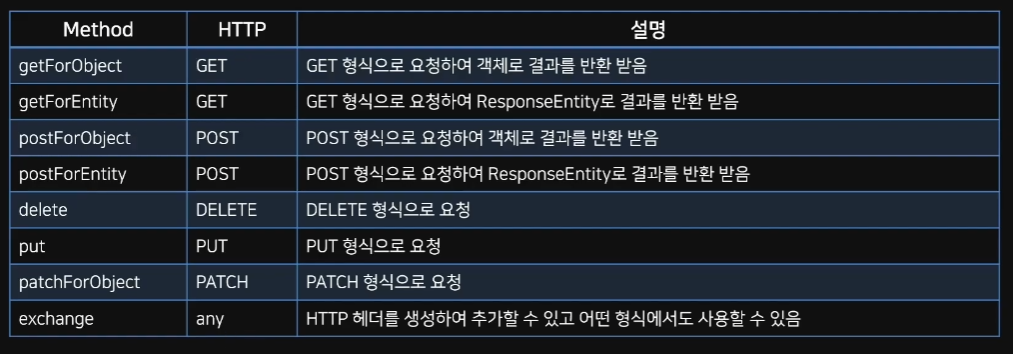 Spring에서 제공하는 HTTP 통신 기능을 쉽게 사용할 수 있게 설계된 템플릿
Spring에서 제공하는 HTTP 통신 기능을 쉽게 사용할 수 있게 설계된 템플릿
HTTP 서버와의 통신을 단순화하고 RESTful 원칙을 고수함
동기 방식으로 처리, 비동기 방식은 AsyncRestTemplate을 사용한다
RestTemplate Class는 REST 서비스를 호출하도록 설계되어 HTTP Protocol의 메소드에 맞게 여러 메소드들을 제공한다
/service/RestTemplateService.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.service;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.dto.MemberDTO;
public interface RestTemplateService {
public String getAroundHub();
public String getName();
public String getName2();
public ResponseEntity<MemberDTO> postDto();
public ResponseEntity<MemberDTO> addHeader();
}/service/RestTemplateServiceImpl.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.service.impl;
import java.net.URI;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.http.RequestEntity;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.dto.MemberDTO;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.service.RestTemplateService;
@Service
public class RestTemplateServiceImpl implements RestTemplateService {
private final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RestTemplateServiceImpl.class);
@Override
public String getAroundHub() {
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder
.fromUriString("http://localhost:9090")
.path("/api/server/around-hub")
.encode()
.build()
.toUri();
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity(uri, String.class);
LOGGER.info("status code : {}", responseEntity.getStatusCode());
LOGGER.info("body : {}", responseEntity.getBody());
return responseEntity.getBody();
}
@Override
public String getName() {
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder
.fromUriString("http://localhost:9090")
.path("/api/server/name")
.queryParam("name", "Flature")
.encode()
.build()
.toUri();
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity(uri, String.class);
LOGGER.info("status code : {}", responseEntity.getStatusCode());
LOGGER.info("body : {}", responseEntity.getBody());
return responseEntity.getBody();
}
@Override
public String getName2() {
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder
.fromUriString("http://localhost:9090")
.path("/api/server/path-variable/{name}")
.encode()
.build()
.expand("Flature") // 복수의 값을 넣어야할 경우 , 를 추가하여 구분
.toUri();
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity(uri, String.class);
LOGGER.info("status code : {}", responseEntity.getStatusCode());
LOGGER.info("body : {}", responseEntity.getBody());
return responseEntity.getBody();
}
@Override
public ResponseEntity<MemberDTO> postDto() {
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder
.fromUriString("http://localhost:9090")
.path("/api/server/member")
.queryParam("name", "Flature")
.queryParam("email", "jjj@jjj.com")
.queryParam("organization", "Around Hub Studio")
.encode()
.build()
.toUri();
MemberDTO memberDTO = new MemberDTO();
memberDTO.setName("flature!!");
memberDTO.setEmail("aaa@aaa.com");
memberDTO.setOrganization("Around Hub Studio!!");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
ResponseEntity<MemberDTO> responseEntity = restTemplate.postForEntity(uri, memberDTO,
MemberDTO.class);
LOGGER.info("status code : {}", responseEntity.getStatusCode());
LOGGER.info("body : {}", responseEntity.getBody());
return responseEntity;
}
@Override
public ResponseEntity<MemberDTO> addHeader() {
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder
.fromUriString("http://localhost:9090")
.path("/api/server/add-header")
.encode()
.build()
.toUri();
MemberDTO memberDTO = new MemberDTO();
memberDTO.setName("flature");
memberDTO.setEmail("jjj@jjj.com");
memberDTO.setOrganization("Around Hub Studio");
RequestEntity<MemberDTO> requestEntity = RequestEntity
.post(uri)
.header("around-header", "Around Hub Studio")
.body(memberDTO);
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
ResponseEntity<MemberDTO> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(requestEntity,
MemberDTO.class);
LOGGER.info("status code : {}", responseEntity.getStatusCode());
LOGGER.info("body : {}", responseEntity.getBody());
return responseEntity;
}
}/controller/RestTemplateController.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.dto.MemberDTO;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.service.RestTemplateService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/rest-template")
public class RestTemplateController {
RestTemplateService restTemplateService;
@Autowired
public RestTemplateController(RestTemplateService restTemplateService) {
this.restTemplateService = restTemplateService;
}
@GetMapping(value = "/around-hub")
public String getAroundHub() {
return restTemplateService.getAroundHub();
}
@GetMapping(value = "/name")
public String getName() {
return restTemplateService.getName();
}
@GetMapping(value = "/name2")
public String getName2() {
return restTemplateService.getName2();
}
@PostMapping(value = "/dto")
public ResponseEntity<MemberDTO> postDto() {
return restTemplateService.postDto();
}
@PostMapping(value = "/add-header")
public ResponseEntity<MemberDTO> addHeader() {
return restTemplateService.addHeader();
}
}Test Code Appliance
TDD
테스트 주도 개발, 테스트를 먼저 설계 및 구축 후 테스트를 통과할 수 있도록 코드 작성
애자인 개발 방식 중에 하나, 방향 일치로 인한 피드백과 진행 방향 충돌 방지
테스트 코드 작성 목적
코드의 안정성을 높일 수 있음, 기능을 추가하거나 변경할 때 Side-Effect 줄일 수 있음, 해당 코드가 작성된 목적을 명확하게 표현할 수 있음
F.I.R.S.T
Fast 테스트 코드의 실행은 빠르게 진행되어야 함
Independent 독립적인 테스트가 가능해야 함
Repeatable 테스트는 매번 같은 결과를 만들어야 함
Self-Validating 테스트는 그 자체로 실행하여 결과를 확인할 수 있어야 함
Timely 단위 테스트는 비즈니스 코드가 완성되지 전에 구성하고 테스트 가능해야 함 (TDD의 원칙을 담고 있음)
통합 테스트
여러 기능을 조합하여 전체 비즈니스 로직이 제대로 동작하는지 확인
@SpringBootTest를 사용하여 진행, 대규모 프로젝트에서 무거운 작업을 수행
단위 테스트
프로젝트에 필요한 모든 기능에 대한 테스트를 각각 진행하는 것
org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test로 일반적으로 Spring Boot에서 의존성을 모두 가질 수 있음
JUnit
Java 진영의 대표적인 Test Framework, Unit Test를 위한 도구 제공
Unit Test 코드의 특정 모듈이 의도된 대로 동작하는지 테스트하는 절차, 모든 함수와 메소드에 대한 각각의 TestCase 작성
Annotation 기반으로 테스트 지원
Assert(단정문)으로 테스트 케이스 기댓값에 대해 수행 결과 확인
JUnit Platform
Test를 실행하기 위한 뼈대
Test를 발견하고 테스트 계획을 생성하는 TestEngine 인터페이스를 가짐
TestEngine을 통해 Test를 발견, 수행, 결과 보고
각종 IDE를 연동하여 보조하는 역할 수행
ex. Platform = TestEngine API + Console Launcher + JUnit 4 Based Runner
JUnit Jupiter
개발자가 테스트 코드를 작성할 때 사용
TestEngine API의 구현체로 JUnit 5를 구현하고 있음
테스트의 실제 구현체는 별도의 모듈 역할 수행, 그 중 하나가 Jupiter-Engine
이 모듈은 Jupiter-API를 사용하여 작성한 테스트 코드를 발견하고 실행
JUnit Vintage
 TestEngine API 구현체, JUnit 3~4 구현
TestEngine API 구현체, JUnit 3~4 구현
기존 JUnit 3~4 버전으로 작성된 테스트 코드 실행, Vintage-Engine 모듈 포함
JUnit LifeCycle Annotation

Bean
Spring 컨테이너에 의해 관리되는 재사용 가능한 소프트웨어 컴포넌트
즉, Spring 컨테이너가 관리하는 자바 객체, 인스턴스화된 객체를 의미
Spring 컨테이너에 등록된 객체를 Spring Bean이라고 함
@SpringBootTest
통합 테스트 용도로 사용, 어노테이션 하위의 모든 Bean을 스캔하여 로드
이후 테스트용 Application Context를 만들어 Bean을 추가, MockBean 교체
@ExtendWith
JUnit4에서 @RunWith로 사용되던 어노테이션이 변경됨
메인으로 실행될 Class 지정, @SpringBootTest에 기본적으로 추가됨
@WebMvcTest (Class명.class)
()에 작성된 클래스만 실제로 로드하여 테스트 진행
매개변수를 지정하지 않으면 Controller와 연관된 Bean이 모두 로드됨
Spring의 모든 Bean을 로드하는 SSpringBootTest대신 Controller와 관련된 코드만 테스트할 경우 사용
@Autowired about Mockbean
Controller의 API를 테스트하는 용도인 MockMvc 객체를 주입받음
perform() 메소드 활용, Controller의 동작을 확인
andExpect(), andDo(), andReturn()과 함께 사용
@MockBean
테스트할 클래스에서 주입 받고 있는 객체에 대해 가짜 객체를 생성
해당 객체는 실제 행위를 하지 않음, given()을 활용해 가짜 객체의 동작 정의
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
spring.test.mockmvc의 설정을 로드하면서 MockMvc의 의존성 자동 주입
MockMvc 클래스는 REST API 테스트를 할 수 있는 Class
@Import
필요한 Class들을 Configuration으로 만들어 사용할 수 있음
Configuration Component Class도 의존성을 설정 가능
Import된 Class는 주입으로 사용 가능
/test/test/TestLifeCycle.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class TestLifeCycle {
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll() {
System.out.println("## BeforeAll Annotation 호출 ##");
System.out.println();
}
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() {
System.out.println("## afterAll Annotation 호출 ##");
System.out.println();
}
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("## beforeEach Annotation 호출 ##");
System.out.println();
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("## afterEach Annotation 호출 ##");
System.out.println();
}
@Test
void test1() {
System.out.println("## test1 시작 ##");
System.out.println();
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Test Case 2!!!")
void test2() {
System.out.println("## test2 시작 ##");
System.out.println();
}
@Test
@Disabled
// Disabled Annotation : 테스트를 실행하지 않게 설정하는 어노테이션
void test3() {
System.out.println("## test3 시작 ##");
System.out.println();
}
}/test/ApplicationTests
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class ApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
}/test/controller/ProductControllerTest.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.controller;
import static org.mockito.BDDMockito.given;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.verify;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.post;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers.print;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.dto.ProductDto;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.service.impl.ProductServiceImpl;
@WebMvcTest(ProductController.class)
//@AutoConfigureWebMvc // 이 어노테이션을 통해 MockMvc를 Builder 없이 주입받을 수 있음
public class ProductControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
// ProductController에서 잡고 있는 Bean 객체에 대해 Mock 형태의 객체를 생성해줌
@MockBean
ProductServiceImpl productService;
// http://localhost:8080/api/v1/product-api/product/{productId}
@Test
@DisplayName("Product 데이터 가져오기 테스트")
void getProductTest() throws Exception {
// given : Mock 객체가 특정 상황에서 해야하는 행위를 정의하는 메소드
given(productService.getProduct("12315")).willReturn(
new ProductDto("15871", "pen", 5000, 2000));
String productId = "12315";
// andExpect : 기대하는 값이 나왔는지 체크해볼 수 있는 메소드
mockMvc.perform(
get("/api/v1/product-api/product/" + productId))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.productId").exists()) // json path의 depth가 깊어지면 .을 추가하여 탐색할 수 있음 (ex : $.productId.productIdName)
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.productName").exists())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.productPrice").exists())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.productStock").exists())
.andDo(print());
// verify : 해당 객체의 메소드가 실행되었는지 체크해줌
verify(productService).getProduct("12315");
}
// http://localhost:8080/api/v1/product-api/product
@Test
@DisplayName("Product 데이터 생성 테스트")
void createProductTest() throws Exception {
//Mock 객체에서 특정 메소드가 실행되는 경우 실제 Return을 줄 수 없기 때문에 아래와 같이 가정 사항을 만들어줌
given(productService.saveProduct("15871", "pen", 5000, 2000)).willReturn(
new ProductDto("15871", "pen", 5000, 2000));
ProductDto productDto = ProductDto.builder().productId("15871").productName("pen")
.productPrice(5000).productStock(2000).build();
Gson gson = new Gson();
String content = gson.toJson(productDto);
// 아래 코드로 json 형태 변경 작업을 대체할 수 있음
// String json = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(productDto);
mockMvc.perform(
post("/api/v1/product-api/product")
.content(content)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.productId").exists())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.productName").exists())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.productPrice").exists())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.productStock").exists())
.andDo(print());
verify(productService).saveProduct("15871", "pen", 5000, 2000);
}
}/test/service/impl/ProductServiceImplTest.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.service.impl;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.verify;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.mockito.Mockito;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.dto.ProductDto;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.entity.Product;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.handler.impl.ProductDataHandlerImpl;
//@SpringBootTest(classes = {ProductDataHandlerImpl.class, ProductServiceImpl.class})
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@Import({ProductDataHandlerImpl.class, ProductServiceImpl.class})
public class ProductServiceImplTest {
@MockBean
ProductDataHandlerImpl productDataHandler;
@Autowired
ProductServiceImpl productService;
@Test
public void getProductTest() {
//given
Mockito.when(productDataHandler.getProductEntity("123"))
.thenReturn(new Product("123", "pen", 2000, 3000));
ProductDto productDto = productService.getProduct("123");
Assertions.assertEquals(productDto.getProductId(), "123");
Assertions.assertEquals(productDto.getProductName(), "pen");
Assertions.assertEquals(productDto.getProductPrice(), 2000);
Assertions.assertEquals(productDto.getProductStock(), 3000);
verify(productDataHandler).getProductEntity("123");
}
@Test
public void saveProductTest() {
//given
Mockito.when(productDataHandler.saveProductEntity("123", "pen", 2000, 3000))
.thenReturn(new Product("123", "pen", 2000, 3000));
ProductDto productDto = productService.saveProduct("123", "pen", 2000, 3000);
Assertions.assertEquals(productDto.getProductId(), "123");
Assertions.assertEquals(productDto.getProductName(), "pen");
Assertions.assertEquals(productDto.getProductPrice(), 2000);
Assertions.assertEquals(productDto.getProductStock(), 3000);
verify(productDataHandler).saveProductEntity("123", "pen", 2000, 3000);
}
}
Test Coverage
Code Coverage
SW의 테스트 수준이 충분한지 표현할 수 있는 지표 중 하나
테스트를 진행했을 때 해당 코드가 실행되었는지를 표현하는 방법
Black Box Test
SW 내부 구조나 작동 원리를 모르는 상태에서 동작을 검사
다양한 값을 입력하여 올바른 출력이 나오는지 테스트, 사용자 관점
White Box Test
SW 내부 구조나 동작을 검사, 개발자 관점의 테스트 방법
Jacoco
가장 보편적으로 사용되는 코드 커버리지 도구
작성된 코드의 테스트 커버리지를 측정하는 도구
Jacoco pom.xml
prepare-agent 테스트중이 앱에 대해 인수를 전달하는 Agent Property 준비
merge 여러 실행 데이터 파일들을 하나로 통합
report 하나의 프로젝트 테스트에 대한 Code Coverage 리포트 생성
check Code Coverage Metric 충돌 여부 확인 명령어
Jacoco Rule
Element Type 코드 커버리지 체크 기준
Counter 코드 커버리지를 측정할 때 사용하는 지표
Value 커버리지 정도를 나타내는 지표
LifeCycle
compile > test > package > install > deployJacoco 플러그인은 Maven LifeCycle에 의해 동작, test phrase 이후 측정 가능
