@MappedSuperClass
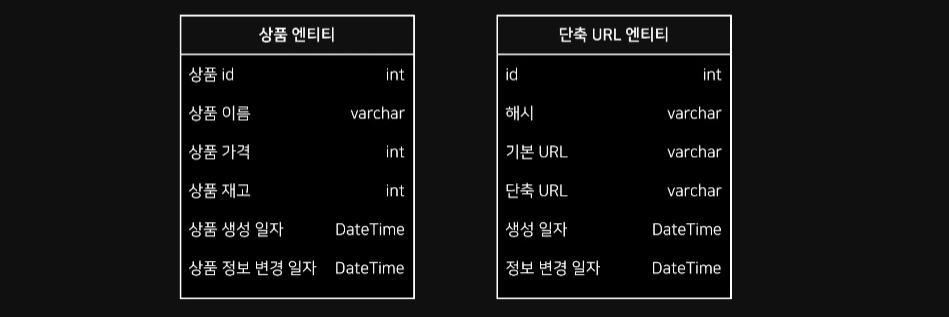 여러 엔티티 객체에서 사용되는 공통 속성이 존재할 경우가 많음
여러 엔티티 객체에서 사용되는 공통 속성이 존재할 경우가 많음
공통적으로 사용되는 속성은 대표적으로 id, createdAt, updatedAt
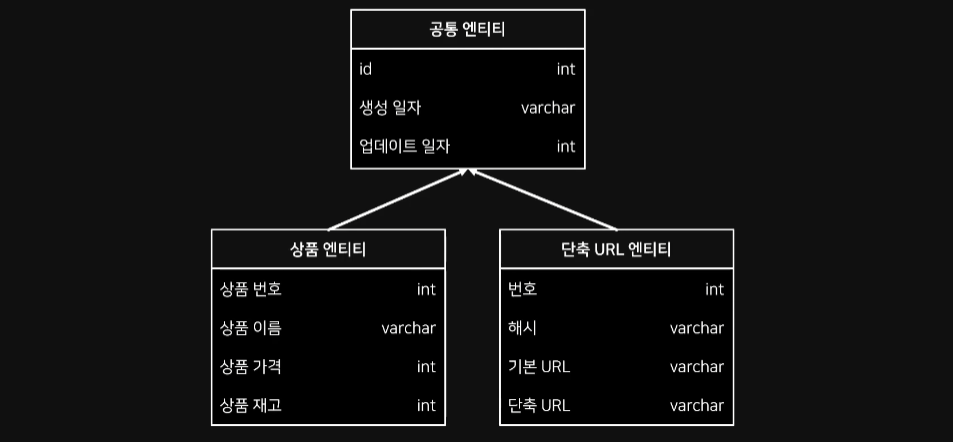 공통되는 속성을 별도의 클래스로 구분하여
공통되는 속성을 별도의 클래스로 구분하여 @MappedSuperClass 선언 후 사용
코드 상 분리되어 있는 것이며, DB 테이블 개념에서는 분리되어 있지 않음
/data/entitiy/BaseEntity.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.entity;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.EntityListeners;
import javax.persistence.MappedSuperclass;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedBy;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedDate;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedBy;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedDate;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.support.AuditingEntityListener;
@Getter
@Setter
@MappedSuperclass
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public class BaseEntity {
@CreatedDate
@Column(updatable = false)
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
/*
@CreatedBy
@Column(updatable = false)
private String createdBy;
*/
@LastModifiedDate
private LocalDateTime updatedAt;
/*
@LastModifiedBy
private String updatedBy;
*/
}JPA Audit
JPA Auditing
각 엔티티별로 누가, 언제 접근했는지 기록하여 감시 체계를 꾸리는 것
Spring Data JPA에서 해당 기능을 사용하기 위해 @EnableJpaAuditing 사용
ex. 데이터 생성 일자, 데이터 생성자, 데이터 변경 일자
@EntitiyListener
Entity 객체를 DB에 적용하기 전/후에 Callback을 요청하는 Annotation
파라미터로 Callback을 요청할 Class를 지정하여 사용
JPA Auditing Annotation
@CreatedDate Entitiy가 저장되는 시점에 자동으로 시간 주입
@CreatedBy 저장되는 시점의 저장 주체 주입
@LastModifiedDate 수정되는 시점에 자동으로 시간 주입
@LastModifiedBy 수정되는 시점의 저장 주체 주입
/data/entitiy/listener/CustomListener.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.entity.listener;
import javax.persistence.PostLoad;
import javax.persistence.PostPersist;
import javax.persistence.PostRemove;
import javax.persistence.PostUpdate;
import javax.persistence.PrePersist;
import javax.persistence.PreRemove;
import javax.persistence.PreUpdate;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.entity.Listener;
public class CustomListener {
private final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CustomListener.class);
@PostLoad
public void postLoad(Listener entity) {
LOGGER.info("[postLoad] called!!");
}
@PrePersist
public void prePersist(Listener entity) {
LOGGER.info("[prePersist] called!!");
}
@PostPersist
public void postPersist(Listener entity) {
LOGGER.info("[postPersist] called!!");
}
@PreUpdate
public void preUpdate(Listener entity) {
LOGGER.info("[preUpdate] called!!");
}
@PostUpdate
public void postUpdate(Listener entity) {
LOGGER.info("[postUpdate] called!!");
}
@PreRemove
public void preRemove(Listener entity) {
LOGGER.info("[preRemove] called!!");
}
@PostRemove
public void postRemove(Listener entity) {
LOGGER.info("[postRemove] called!!");
}
}/service/impl/ListenerServiceImpl.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.entity.Listener;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.repository.ListenerRepository;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.service.ListenerService;
@Service
public class ListenerServiceImpl implements ListenerService {
private ListenerRepository listenerRepository;
@Autowired
public ListenerServiceImpl(ListenerRepository listenerRepository) {
this.listenerRepository = listenerRepository;
}
@Override
public Listener getEntity(Long id) {
return listenerRepository.findById(id).get();
}
@Override
public void saveEntity(Listener listener) {
listenerRepository.save(listener);
}
@Override
public void updateEntity(Listener listener) {
Listener foundListener = listenerRepository.findById(listener.getId()).get();
foundListener.setName(listener.getName());
listenerRepository.save(foundListener);
}
@Override
public void removeEntity(Listener listener) {
listenerRepository.delete(listener);
}
}/data/repository/ListenerRepository.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.entity.Listener;
public interface ListenerRepository extends JpaRepository<Listener, Long> {
}/controller/ListenerController.java
package studio.thinkground.aroundhub.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.data.entity.Listener;
import studio.thinkground.aroundhub.service.ListenerService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/listener")
public class ListenerController {
private ListenerService listenerService;
@Autowired
public ListenerController(ListenerService listenerService){
this.listenerService = listenerService;
}
@GetMapping
public String getListener(Long id){
listenerService.getEntity(id);
return "OK";
}
@PostMapping
public void saveListener(String name){
Listener listener = new Listener();
listener.setName(name);
listenerService.saveEntity(listener);
}
@PutMapping
public void updateListener(Long id, String name){
Listener listener = new Listener();
listener.setId(id);
listener.setName(name);
listenerService.updateEntity(listener);
}
@DeleteMapping
public void deleteListener(Long id){
Listener listener = listenerService.getEntity(id);
listenerService.removeEntity(listener);
}
}Query Method
JPQL
Java Persistent Query Language
테이블이 아닌 Entitiy 객체를 대상으로 사용되는 객체지향 쿼리
JPA는 JPQL을 분석한 후 연동되어 있는 DB에 맞는 SQL로 가공하여 사용
Query Method
Spring Data JPA의 핵심 기능
JpaRepoditory에서 제공하는 기본 메소드 만으로 비즈니스 로직 처리에는 한계 존재
Repository 내 정의되는 메소드 이름만으로 쿼리 생성 가능
Naming Convention (이름에 대한 규칙)하며 규칙에 맞게 이름을 지으면 쿼리 자동 생성
Query Method 문법
주제 (Subject)와 서술어 (Predicate)로 구분됨
find...by와 같은 키워드로 주제를 정하는 by는 서술어의 시작을 나타냄
서술어 영역은 검색 및 정렬 조건을 작성할 수 있음
주제 키워드
find..by, read..by 등 : 조회 기능을 수행하는 키워드
'..'영역은 Entitiy를 표현할 수 있으나, Repository에서 이미 Entitiy를 정의하고 있기 때문에 생략하는 경우가 많음
리턴 타입은 Collenction이나 Streamable에 속하는 타입을 설정할 수 있음
exists..by : 특정 데이터가 존재하는지 확인하는 기능 수행
count..by 조회 Query를 수행항 후 결과 개수를 리턴
delete..by, remove..by 삭제 쿼리 수행, 삭제한 횟수 리턴
...First<number>..., ...Top<number>... : 쿼리ㅏ를 통해 조회되는 결과값의 수를 제한하는 키워드, 단건으로 조회할 경우 number 삭제
조건자 키워드
Is 값의 일치를 위한 키워드, Equals와 동일한 기능 수행
(Is)Not 값의 불일치를 위한 키워드, Is 생략 가능
(Is)Null, (Is)NotNull 해당 Column의 Record 값이 Null인지 아닌지 체크
(Is)True, (Is)False boolean 타입의 Column 값을 확인하는 키워드
And, Or 여러 조건을 묶을 때 사용
(Is)GreaterThan, (Is)LessThan, (Is)Between 숫자나 DateTime Column에서 사용할 수 있는 비교연산 키워드, 경계값 포함x
(Is)StartingWith(==StartsWith), (Is)Containing(==Containing) ...
ProductEntitiy.java
@Entity
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
@ToString
@Table(name = "product")
public class Product extends BaseEntity{
@Id
String id;
String name;
Integer price;
Integer stock;
/*
@Column
String sellerId;
@Column
String sellerPhoneNumber;
*/
public ProductDto toDto(){
return ProductDto.builder()
.productId(id)
.productName(name)
.productPrice(price)
.productStock(stock)
.build();
}
}ProductRepository.java
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, String> {
/* 쿼리 메소드의 주제 키워드 */
// 조회
List<Product> findByName(String name);
List<Product> queryByName(String name);
// 존재 유무
boolean existsByName(String name);
// 쿼리 결과 개수
long countByName(String name);
// 삭제
void deleteByName(String name);
long removeByName(String name);
// 값 개수 제한
List<Product> findFirst5ByName(String name);
List<Product> findTop3ByName(String name);
/* 쿼리 메소드의 조건자 키워드 */
// Is, Equals (생략 가능)
// Logical Keyword : IS , Keyword Expressions : Is, Equals, (or no keyword)
// findByNumber 메소드와 동일하게 동작
Product findByIdIs(String id);
Product findByIdEquals(String id);
// (Is)Not
List<Product> findByIdNot(String id);
List<Product> findByIdIsNot(String id);
// (Is)Null, (Is)NotNull
List<Product> findByStockIsNull();
List<Product> findByStockIsNotNull();
// And, Or
List<Product> findTopByIdAndName(String id, String name);
// (Is)GreaterThan, (Is)LessThan, (Is)Between
List<Product> findByPriceGreaterThan(Integer price);
// (Is)Like, (Is)Containing, (Is)StartingWith, (Is)EndingWith
List<Product> findByNameContaining(String name);
}/test/ProductRepositoryTest.java
@SpringBootTest
class ProductRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
ProductRepository productRepository;
private Product getProduct(String id, int nameNumber, int price, int stock) {
return new Product(id, "상품" + nameNumber, price, stock);
}
@Test
void findTest() {
List<Product> foundAll = productRepository.findAll();
System.out.println("====↓↓ Test Data ↓↓====");
for (Product product : foundAll) {
System.out.println(product.toString());
}
System.out.println("====↑↑ Test Data ↑↑====");
List<Product> foundEntities = productRepository.findByName("상품4");
for (Product product : foundEntities) {
System.out.println(product.toString());
}
List<Product> queryEntities = productRepository.queryByName("상품4");
for (Product product : queryEntities) {
System.out.println(product.toString());
}
}
@Test
void existTest() {
List<Product> foundAll = productRepository.findAll();
System.out.println("====↓↓ Test Data ↓↓====");
for (Product product : foundAll) {
System.out.println(product.toString());
}
System.out.println("====↑↑ Test Data ↑↑====");
System.out.println(productRepository.existsByName("상품4"));
System.out.println(productRepository.existsByName("상품2"));
}
@Test
void countTest() {
List<Product> foundAll = productRepository.findAll();
System.out.println("====↓↓ Test Data ↓↓====");
for (Product product : foundAll) {
System.out.println(product.toString());
}
System.out.println("====↑↑ Test Data ↑↑====");
System.out.println(productRepository.countByName("상품4"));
}
...Query Method Sorting, Paging
Sorting
일반적인 쿼리문을 작성할 때 정렬을 사용하기 위해서 ORDER BY 구문을 사용
@findByNameOrderByStockAsc
쿼리 메소드에서는 메소드의 이름으로 정렬 처리를 설정할 수 있음
@findByNameOrderByStockAscPriceDesc
여러 정렬 기준을 사용하고 싶다면 이어 붙이는 것으로 설정할 수 있음
findByName(String name, Sort sort)
메소드 이름에 정렬 키워드를 넣는 방법이 아닌 Sort 객체를 활용해 정렬 기준 설정
Paging
DB의 Repo들을 개수로 나누어서 페이지로 구분하는 것
페이징 처리를 하면 return 타입으로 Page를 설정하고 매개변수로 Pageable 객체 사용
findByName(String name, Pageable pageable)
findByName("공책", PageRequest.of(0,2)); PageRequest.of 메소드는 아래와 같음

ProductRepository.java
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, String> {
...
/* 정렬과 페이징 */
// Asc : 오름차순, Desc : 내림차순
List<Product> findByNameContainingOrderByStockAsc(String name);
List<Product> findByNameContainingOrderByStockDesc(String name);
// 여러 정렬 기준 사용
List<Product> findByNameContainingOrderByPriceAscStockDesc(String name);
// 매개변수를 활용한 정렬
List<Product> findByNameContaining(String name, Sort sort);
// 페이징 처리하기
List<Product> findByPriceGreaterThan(Integer price, Pageable pageable);
...@Query Annotation
쿼리 메소드를 통해 쿼리를 생성하는 방식은 조건이 많아질 경우 메소드의 이름이 길어져 가독성이 떨어짐
비교적 복잡한 쿼리를 작성하기 위해 사용되는 방식
@Query
Spring Data JPA에서 제공하는 기능으로, JPQL을 사용하여 쿼리 작성
SQL과 문법이 비슷하여 사용하는데 용이, Entitiy 객체를 대상으로 쿼리 수행
직접 쿼리 사용
@Query("SELECT p FROM Product p WHERE p.price > 2000")
List<Product> findByPriceBasis();DB의 Native Query 사용
객체의 필드와 일치하지 않는 객체를 사용하는 것에 대해 주의해야 한다
@Query(value="SELECT * FROM product p WHERE p.price > 2000", nativeQuery=true)
List<Product> findByPriceBasisNativeQuery();파라미터 쿼리 주입
@Query("SELECT p FROM Product p WHERE p.price > ?1")
List<Product> findByPriceWithParameter(Integer price);:parameter 방식으로 주입
@Query("SELECT p FROM Product p WHERE p.price > :pri")
List<Product> findByPriceWithParameterNaming(@Param("pri")Integer price);ProductRepository.java
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, String> {
/* @Query 사용하기 */
@Query("SELECT p FROM Product p WHERE p.price > 2000")
List<Product> findByPriceBasis();
@Query(value = "SELECT * FROM product p WHERE p.price > 2000", nativeQuery = true)
List<Product> findByPriceBasisNativeQuery();
@Query("SELECT p FROM Product p WHERE p.price > ?1")
List<Product> findByPriceWithParameter(Integer price);
@Query("SELECT p FROM Product p WHERE p.price > :price")
List<Product> findByPriceWithParameterNaming(Integer price);
@Query("SELECT p FROM Product p WHERE p.price > :pri")
List<Product> findByPriceWithParameterNaming2(@Param("pri") Integer price);
@Query(value = "SELECT * FROM product WHERE price > :price",
countQuery = "SELECT count(*) FROM product WHERE price > ?1",
nativeQuery = true)
List<Product> findByPriceWithParameterPaging(Integer price, Pageable pageable);
}