1. 딥러닝의 기본 개념
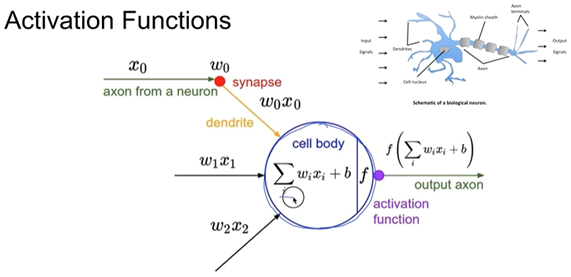 입력값 x가 들어와서 weight을 만나 합해지고 bias를 더해주면서 activation function이 만들어지는데
입력값 x가 들어와서 weight을 만나 합해지고 bias를 더해주면서 activation function이 만들어지는데
이 때 출력값이 임의의수 이상이면 1을 출력, 임의의 수 이하이면 0을 출력
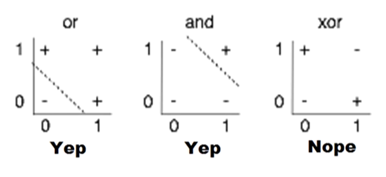
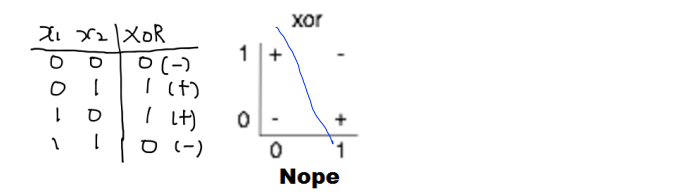
2. XOR
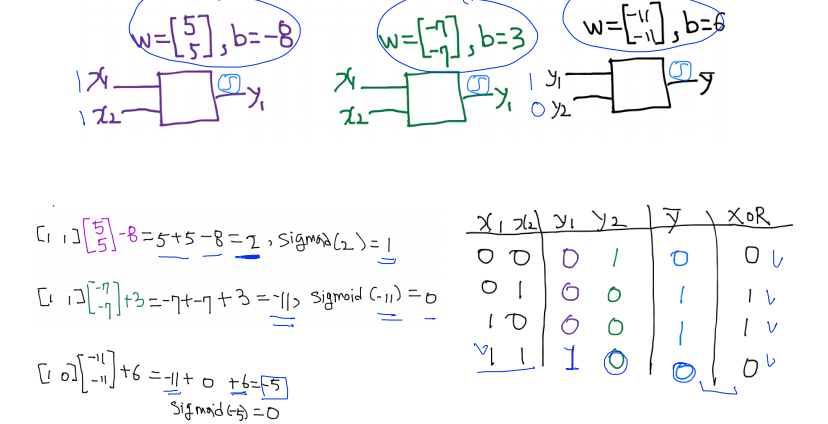 y1 = s(-8) = 0, y2 = s(3) = 1, ŷ = s(-5) = 0 ======> XOR 성립
y1 = s(-8) = 0, y2 = s(3) = 1, ŷ = s(-5) = 0 ======> XOR 성립
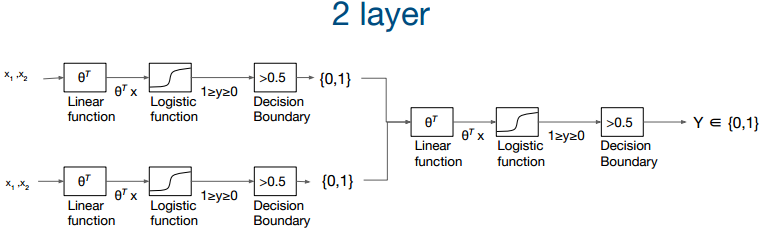
X의 w,b 합친 것을 unit, perceptron이라 부른다.
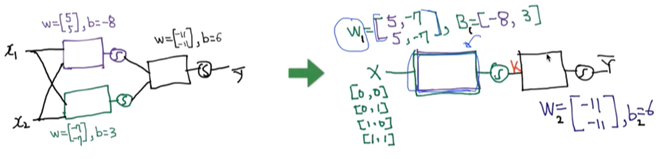 하나의 neural network라 부른다.
하나의 neural network라 부른다.
각각의 연산을 하나로 합하면서 vector → matrix 형태로 바꾸었다.
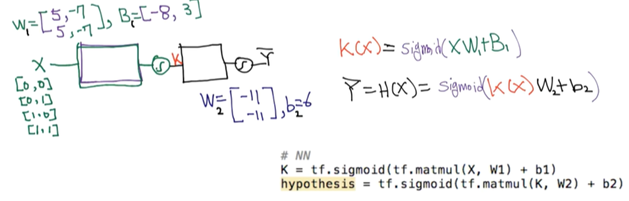
3. 딥넷트웍 학습 시키기
w,b를 자동으로 어떻게 학습시킬 수 있을까?
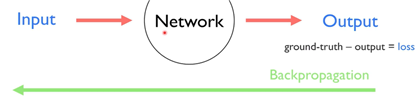
- Back propagation(chain rule)
f=wx+b, g=wx, f=g+b일 때
w가 f에 미치는 영향, x가 f에 미치는 영향, b가 f에 미치는 영햐을 알기 위해 미분을 한다.
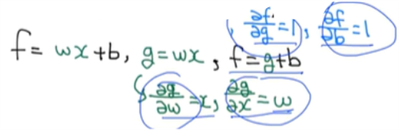
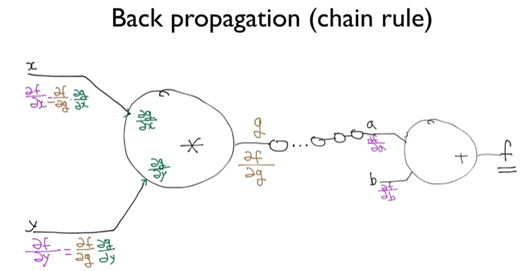
 뒤에서 부터 앞으로 차근차근 미분한다.
뒤에서 부터 앞으로 차근차근 미분한다.
오차를 loss라고 하는데 loss를 미분한 것을 backpropagation 하면서 network를 학습시킨다.
chain rule
f는 g+b라서 g를 먼저 미분 * w를 기준으로 다시 미분
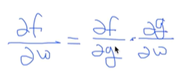
4. Neural Net(NN) for XOR
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import tensorflow as tf
tf.random.set_seed(777) # for reproducibility
x_data = [[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 0],
[1, 1]]
y_data = [[0],
[1],
[1],
[0]]
plt.scatter(x_data[0][0],x_data[0][1], c='red' , marker='^')
plt.scatter(x_data[3][0],x_data[3][1], c='red' , marker='^')
plt.scatter(x_data[1][0],x_data[1][1], c='blue' , marker='^')
plt.scatter(x_data[2][0],x_data[2][1], c='blue' , marker='^')
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_data, y_data)).batch(len(x_data))
def preprocess_data(features, labels):
features = tf.cast(features, tf.float32)
labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.float32)
return features, labels
#NN를 통해 XOR 해결
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal((2,1)), name='weight1')
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal((1,)), name = 'bias1')
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal((2, 1)), name='weight2')
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal((1,)), name='bias2')
W3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal((2, 1)), name='weight3')
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal((1,)), name='bias3')
def neural_net(features):
layer1 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(features, W1) + b1)
layer2 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(features, W2) + b2)
layer3 = tf.concat([layer1, layer2],-1)
layer3 = tf.reshape(layer3, shape = [-1,2])
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(layer3, W3) + b3)
return hypothesis
def loss_fn(hypothesis, labels):
cost = -tf.reduce_mean(labels * tf.math.log(hypothesis) + (1 - labels) * tf.math.log(1 - hypothesis))
return cost
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
def accuracy_fn(hypothesis, labels):
predicted = tf.cast(hypothesis > 0.5, dtype=tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(predicted, labels), dtype=tf.float32))
return accuracy
def grad(hypothesis, features, labels):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
loss_value = loss_fn(neural_net(features),labels)
return tape.gradient(loss_value, [W1, W2, W3, b1, b2, b3])
EPOCHS = 50000
for step in range(EPOCHS):
for features, labels in dataset:
features, labels = preprocess_data(features, labels)
grads = grad(neural_net(features), features, labels)
optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=zip(grads,[W1, W2, W3, b1, b2, b3]))
if step % 5000 == 0:
print("Iter: {}, Loss: {:.4f}".format(step, loss_fn(neural_net(features),labels)))
x_data, y_data = preprocess_data(x_data, y_data)
test_acc = accuracy_fn(neural_net(x_data),y_data)
print("Testset Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(test_acc))
5. ReLU
f(x) = max(0,x) : x값이 0보다 크면 x로 추출, 0보다 작으면 0으로 추출
vanishing gradient : gradient가 소실, 즉 0에 가까워져서 전달받을 네트워가크 없는 상태

