트렌지스터
참고 링크
http://www.ktword.co.kr/test/view/view.php?m_temp1=4498
트렌지스터의 역할
트렌지스터는 스위치의 역할을 하기도 하고 증폭기의 역할을 하기도 한다. (electrically controlled switches or as amplifier controls.)
트렌지스터는 다이오드 2개를 붙여놓은 모양이다.
단순히 다이오드 2개를 붙여서 신기한 역할을 하게 만든다.
트렌지스터 원리
트렌지스터도 다른 회로들과 같은 공식이 통한다. 예를 들어 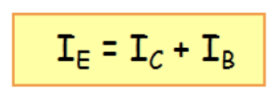
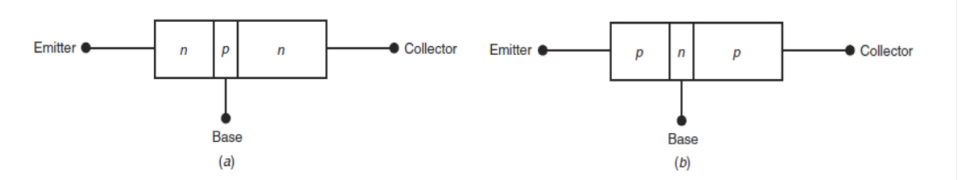
다음과 같이 에미터 전류는 콜렉터와 베이스 전류의 합이다.
트렌지스터는 pnp냐 npn이냐에 따라서 베이스 전류가 변하는데
npn일 경우에는 uses a small input current and positive voltage at its base.
pnp일 경우에는 uses a small output base current
and negative base voltage.
이러한 베이스 전류로 큰 에미터나 콜렉터 전류를 제어하게 된다.
도핑
트렌지스터는 다이오드와 같게 도핑을 하는데 E, B, C는 각각 도핑하는 법이 다르다.
Emitter
Emitter의 경우에 heavily doped.
그리고 이것의 역할은 to emit or inject current carriers into the base region.
For npn transistors, the n-type emitter injects free electrons into the base.
For pnp transistors, the p –type emitter injects holes into the base.
Base
The base is very thin and lightly doped. ( 도핑 조금 함)
Most of the current carriers injected into the base region cross over into the collector side and do not flow out the base lead.
Collector
The collector region is moderately doped.
It is also the largest region within the transistor.
Its function is to collect or attract current carriers injected into the base region. (콜렉터는 베이스에 주입된 운반자를 모은다)
The collector region is moderately doped.
It is also the largest region within the transistor.
Its function is to collect or attract current carriers injected into the base region.
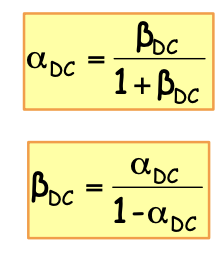
전류 이득
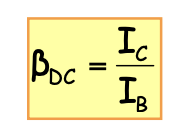
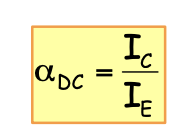
영역
트렌지스터는 동작영역이 있고 이 영역에 따라 응용이 조금 다르다.
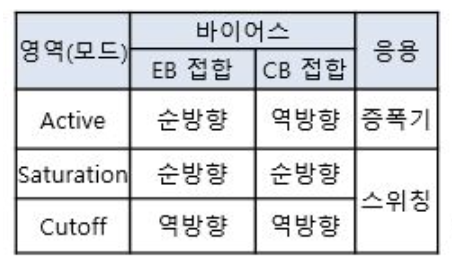
다음과 같이 활성 영역에서는 증폭기의 역할을 수행한다. 또 포화와 컷오프 영역에서는 스위칭의 역할을 수행한다.
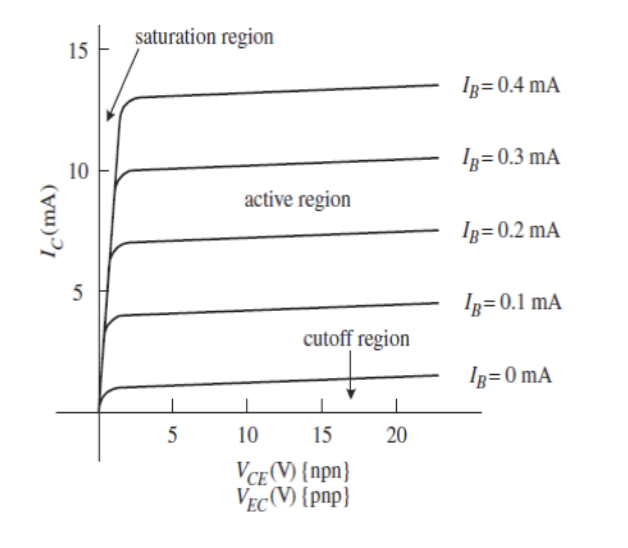
그래프로 나타낸 것이다. 솔직히 그래프가 왜 저렇게 나왔는지 이해가 안된다.
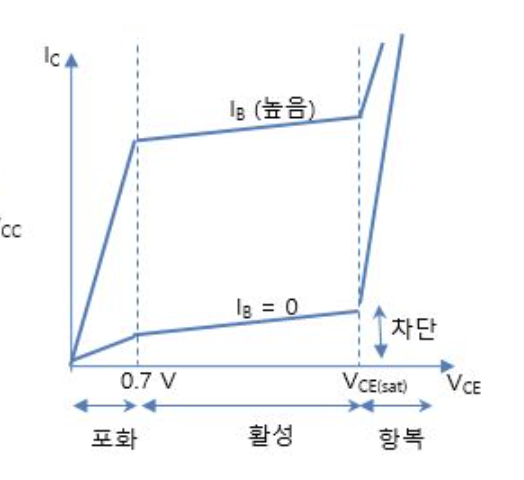
BJT 포화 영역
컬렉터 전류 IC가 최대한 흐름
. 활성영역과는 달리, IB를 증가시켜도, IC가 더이상 증가 안함
. 즉, IC = βIB 관계가 성립하지 않음 ☞ BJT 전류 관계 참조
- 내부적으로, 전하캐리어가 베이스 영역에 만 모여 포화되어, 더이상 전류 흐름에 기여 못함
- 닫힌(closed) 스위치 역할
용도
- 주로, 닫혀진(closed) 스위치에 사용되는 형태
- 만일, 트랜지스터를 스위칭에 사용시 => ON 상태
BJT 차단 영역 (Cutoff)
ㅇ 바이어스 조건
- 2개 접합이, 모두 역 바이어스
ㅇ 용도
- 주로, 열린(open) 스위치에 사용되는 형태
- 만일, 트랜지스터를 스위칭에 사용시 => OFF 상태
ㅇ 특성
- IB,IC = 0
- 매우 적은 역방향 누설전류 ICE0가 존재 IC=ICE0≒0
- 차단점(cutoff point)
. 회로에서 허용 가능한 최대 컬렉터-이미터 전압(VCE(cutoff))
. VCE 축과 교차하는 점
