📝 3주차
- PBR(BRDF + Light)
- Remapping roughness
- Gamma correction
- Normal mapping(min-map)
1. Physically-based Rendering
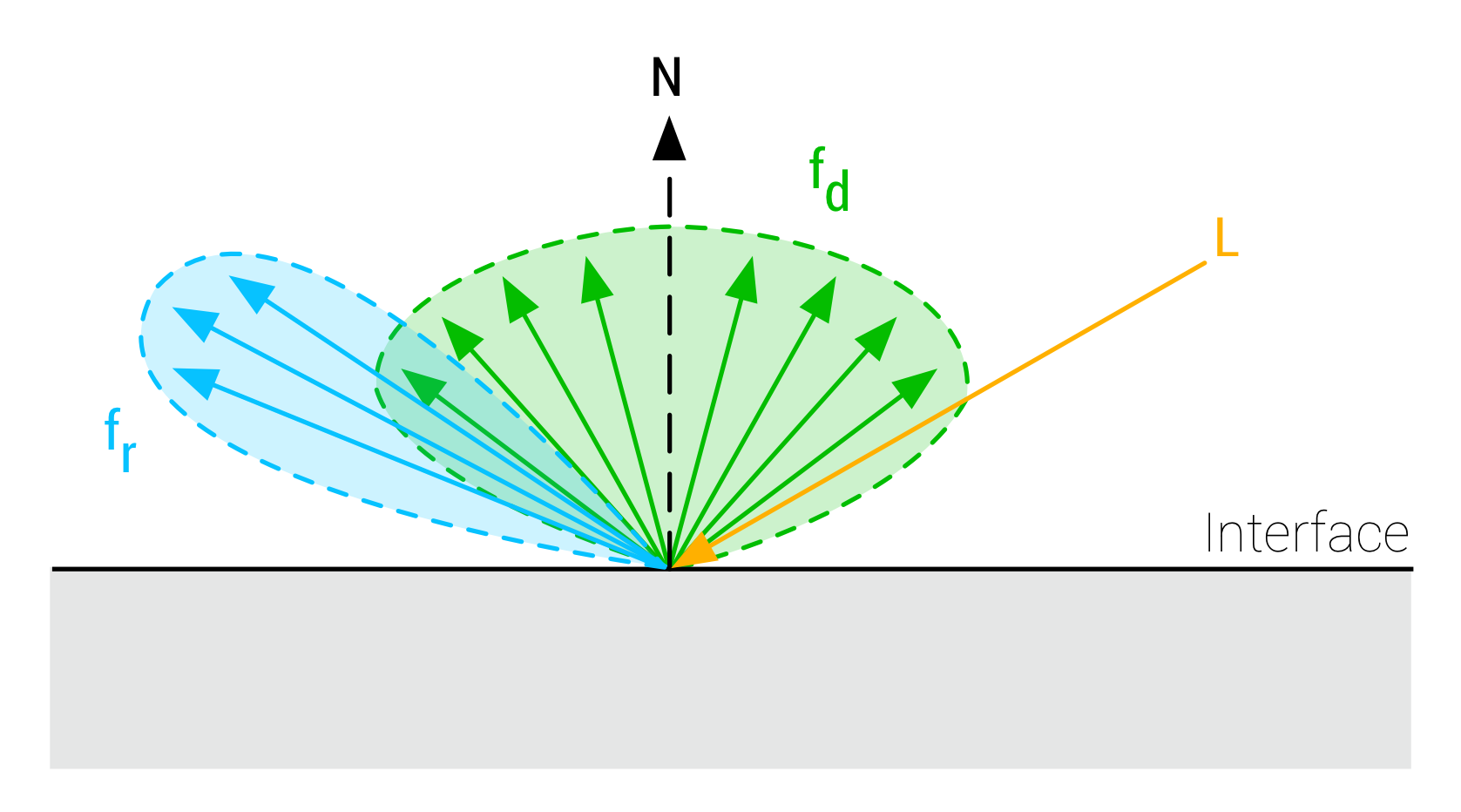
BRDF
- Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function
- Incident light가 어떤 방향으로 반사가 되는가
- diffuse reflectance fd
- specular reflectance fr
- f(v,l)=fd(v,l)+fr(v,l)
- 실제로는 일부 incient light는 표면을 투과하여 분산되고, 다시 표면을 나와 diffuse reflectance를 형성
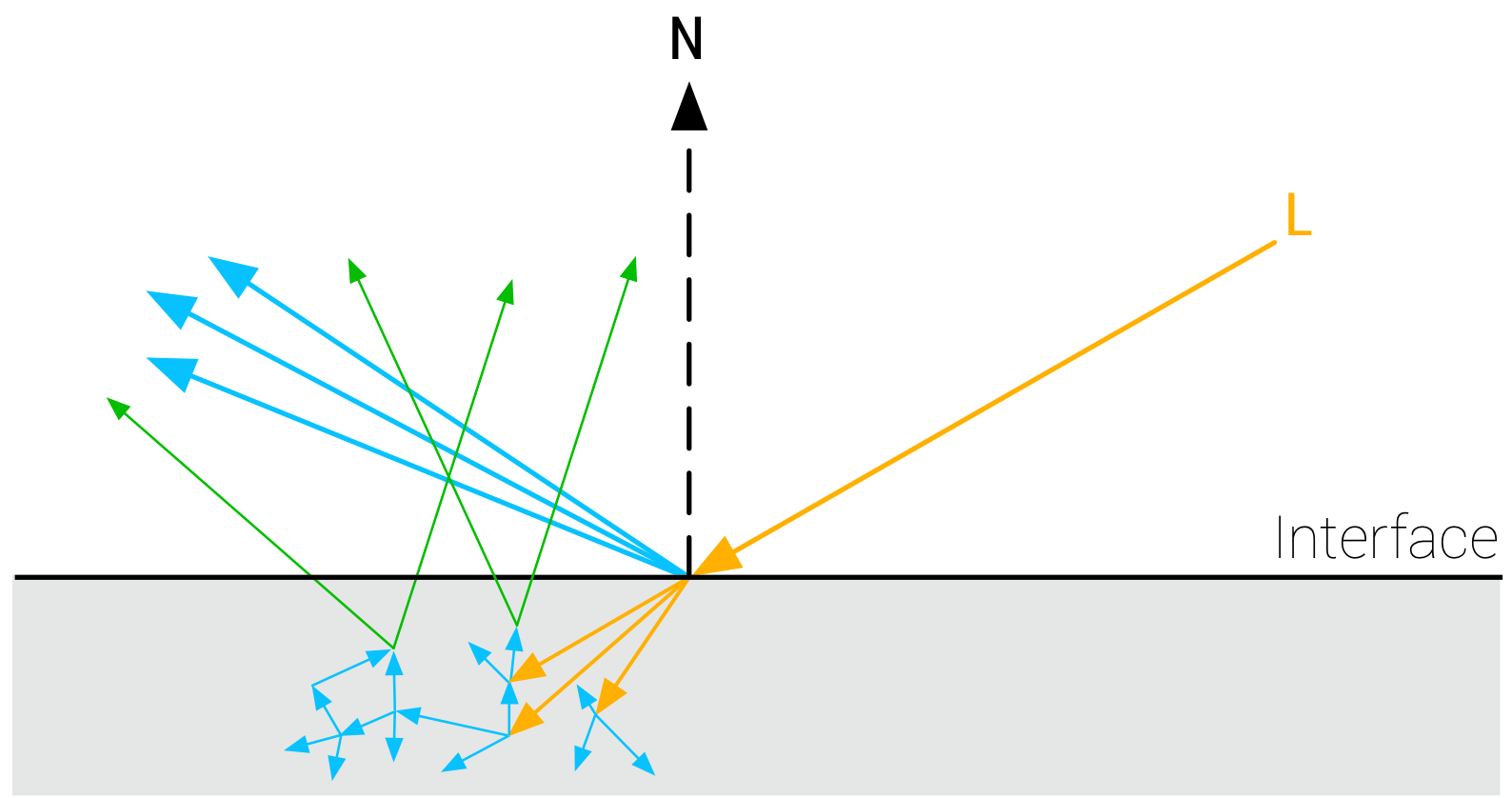
- specular reflectance + diffuse reflectance energy < incident energy
- no subsurface scattering
- no diffuse component
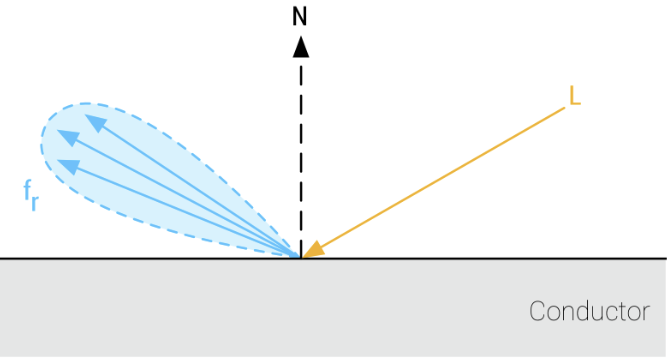
- subsurface scattering
- have specular and diffuse components
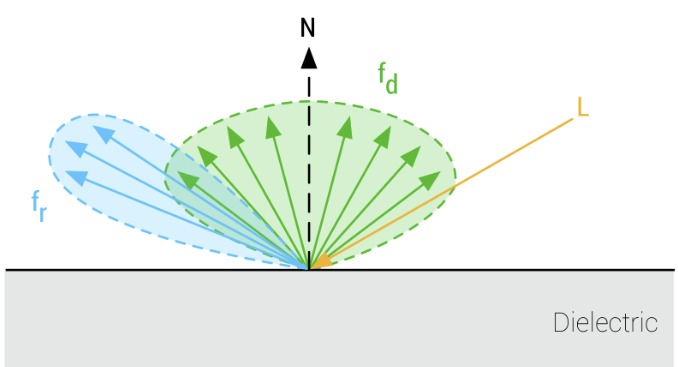
Specular BRDF
- fr(v,l)=4(n⋅v)(n⋅l)D(h,α)G(v,l,α)F(v,h,f0)
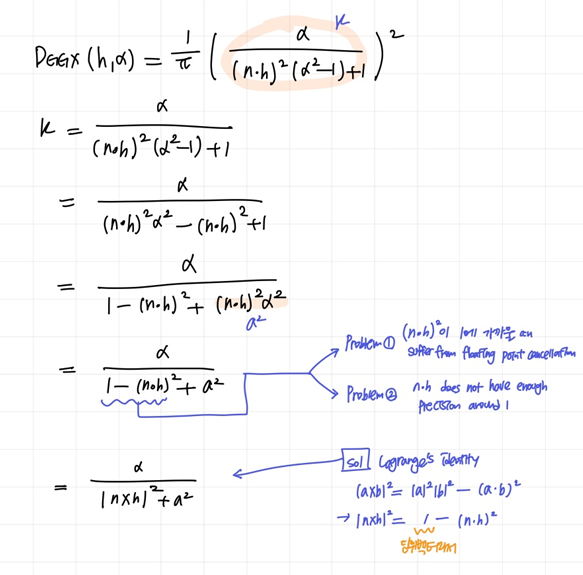
1. Normal distribution function (specular D)
- long-tailed normal distribution functions이 실제 표면에 적절 -> GGX 모델 사용
- DGGX(h,α)=π((n⋅h)2(α2−1)+1)2α2
#define MEDIUMP_FLT_MAX 65504.0
#define saturateMediump(x) min(x, MEDIUMP_FLT_MAX)
float D_GGX(float roughness, float NoH, const vec3 n, const vec3 h) {
vec3 NxH = cross(n, h);
float a = NoH * roughness;
float k = roughness / (dot(NxH, NxH) + a * a);
float d = k * k * (1.0 / PI);
return saturateMediump(d);
}
2. Geometric shadowing (specular G)
- V(v,l,α)=4(n⋅v)(n⋅l)G(v,l,α)
- V(v,l,α)=n⋅l(n⋅v)2(1−α2)+α2+n⋅v(n⋅l)2(1−α2)+α20.5
float V_SmithGGXCorrelated(float NoV, float NoL, float roughness) {
float a2 = roughness * roughness;
float GGXV = NoL * sqrt(NoV * NoV * (1.0 - a2) + a2);
float GGXL = NoV * sqrt(NoL * NoL * (1.0 - a2) + a2);
return 0.5 / (GGXV + GGXL);
}
3. Fresnel (specular F)
- 반사되는 빛의 양은 보는 방향(각도)과 IOR(index of refraction; 굴절률)에 따라 다르다
- 표면과 수직인 각도일수록 적은 반사, 이때 굴절률은 f0
- 표면과 평행한 각도일수록 많은 반사, 이때 굴절률은 f90
- FSchlick(v,h,f0,f90)=f0+(f90−f0)(1−v⋅h)5
vec3 F_Schlick(float u, vec3 f0, float f90) {
return f0 + (vec3(f90) - f0) * pow(1.0 - u, 5.0);
}
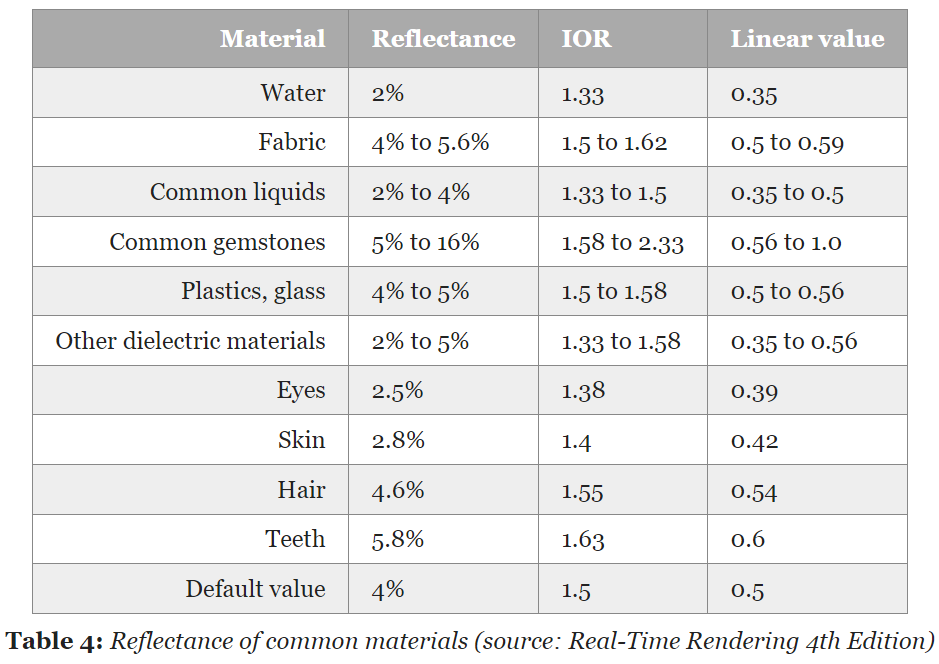
Fresnel Reflectance value
f0
- specular reflectance at normal incidence angle
- non-metallic에선 색이 없고, metallic에선 색이 있음
f90
- fresnel reflectance at grazing angle
- All materials have a Fresnel reflectance of 100% at grazing angles (f90=1.0)
- acceptable Fresnel reflectance(f0) values for various types of materials (no real world material has a value under 2%)
f0 = vec3(0.028);
f90 = 1;
Diffuse BRDF
- f0과 f90의 interpolating
- 실제 material은 non-metallic과 metallic 둘 다 grazing angles에서 무색의 specular reflectance를 나타냄
- 실제 material은 fresnel reflectance는 90도에서 1
vec3 f0 = 0.16 * reflectance * reflectance * (1.0 - metallic) + baseColor * metallic;
- simple diffuse Lambertian BRDF
- assume uniform diffuse response over the microfacets hemisphere
- σ: diffuse reflectance
- fd(v,l)=πσ

- higher quality Disney diffuse BRDF
- roughness 고려
- grazing angle의 retro-reflection 생성 (아래 우측 구의 left edge)
- fd(v,l)=πσFSchlick(n,l,1,f90)FSchlick(n,v,1,f90)

✔️ main.cpp
- light 위치, 색상 추가
- fragment shader에 전달
. . .
vec3 lightPosition = vec3(3, 3, 10);
vec3 lightColor = vec3(500)
. . .
void render(GLFWwindow* window)
{
. . .
GLuint lightPositionLocation = glGetUniformLocation(program.programID, "lightPosition");
glUniform3fv(lightPositionLocation, 1, value_ptr(lightPosition));
GLuint lightColorLocation = glGetUniformLocation(program.programID, "lightColor");
glUniform3fv(lightColorLocation, 1, value_ptr(lightColor));
. . .
}
✔️ shader.frag
- dot product한 결과는
clamp를 사용하여 [0, 1] 범위로 지정
- specular BRDF와 diffuse BRDF 계산
. . .
float V_SmithGGXCorrelated(float NoV, float NoL, float roughness) {
float a2 = roughness * roughness;
float GGXL = NoV * sqrt((-NoL * a2 + NoL) * NoL + a2);
float GGXV = NoL * sqrt((-NoV * a2 + NoV) * NoV + a2);
return 0.5 / (GGXV + GGXL);
}
float D_GGX(float NoH, float roughness) {
float a2 = roughness * roughness;
float f = (NoH * a2 - NoH) * NoH + 1.0;
return a2 / (PI * f * f);
}
vec3 F_Schlick(float u, vec3 f0) {
return f0 + (vec3(1.0) - f0) * pow(1.0 - u, 5.0);
}
float Fd_Lambert(){
return 1.0 / PI;
}
void main(void)
{
vec3 L = lightPosition - worldPosition;
vec3 l = normalize(L);
vec3 n = normalize(normal);
vec3 v = normalize(cameraPosition - worldPosition);
vec3 h = normalize(l+v);
float NoV = abs(dot(n, v)) + 1e-5;
float NoL = clamp(dot(n, l), 0.0, 1.0);
float NoH = clamp(dot(n, h), 0.0, 1.0);
float LoH = clamp(dot(l, h), 0.0, 1.0);
vec3 f0 = vec3(0.028);
float roughness = texture(roughTex, texCoords).r;
float D = D_GGX(NoH, NoH * roughness);
float V = V_SmithGGXCorrelated(NoV, NoL, roughness);
vec3 F = F_Schlick(LoH, f0);
vec3 Fr = (D * V) * F;
vec4 diffColor = texture(diffTex, texCoords);
vec3 Fd = diffColor.rgb * Fd_Lambert();
out_Color.xyz = Fd + Fr);
}
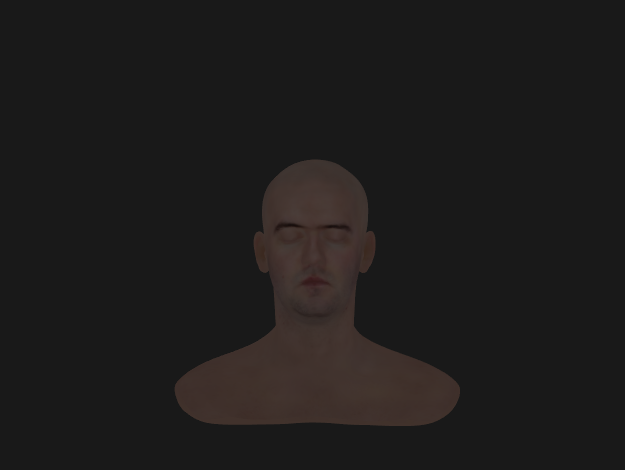

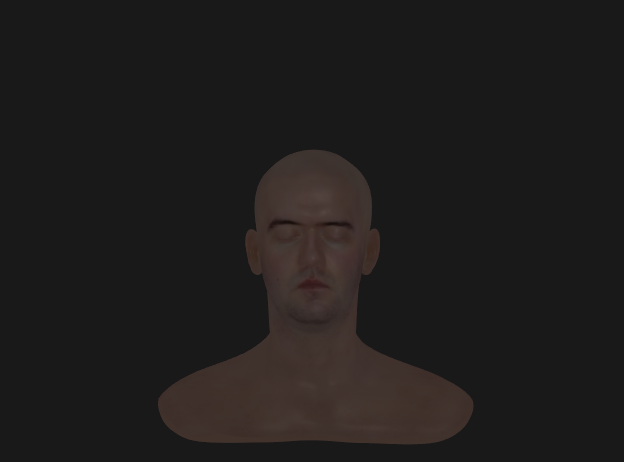
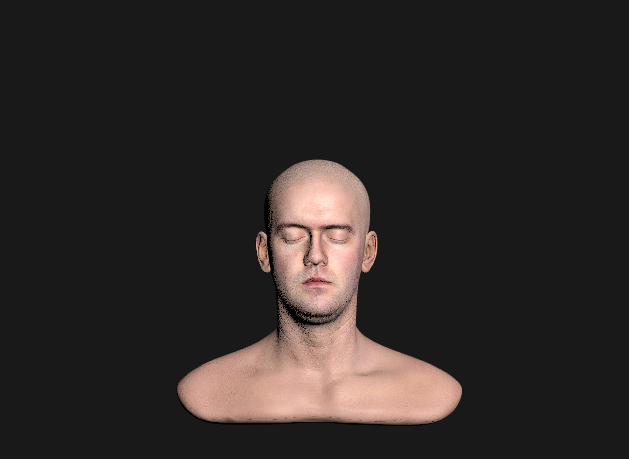
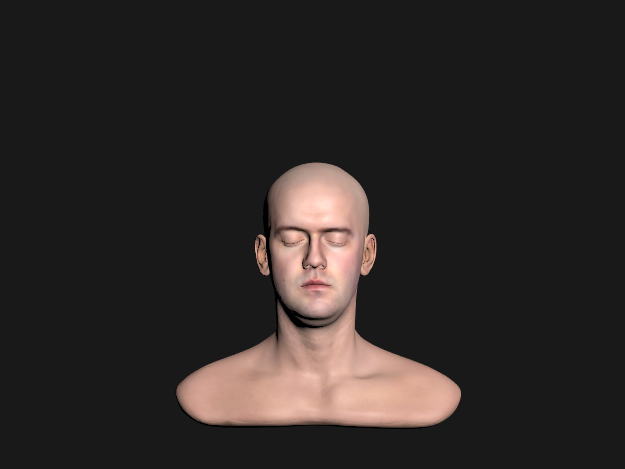
Roughness remapping
- 유저가 설정한 roughness값(또는 roughness Texture)을 그대로 사용하면 rough범위가 좁아 활용 범위가 적어짐
- real world같은 rough범위를 만들기 위해 유저가 설정한 roughness 값을 제곱한 알파 값을 사용 (실제로 보통 알파라고 칭함)
- α=perceptualRoughness2
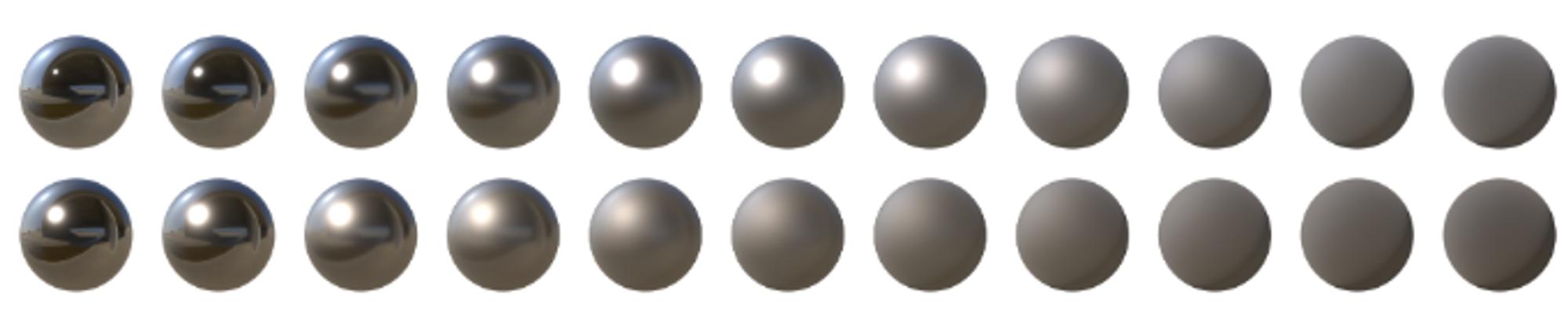 (위-알파값 사용, 아래-roughness값만 사용)
(위-알파값 사용, 아래-roughness값만 사용)
✔️ shader.frag
...
vec3 f0 = vec3(0.028);
float roughness = texture(roughTex, texCoords).r;
roughness *= roughness;
...

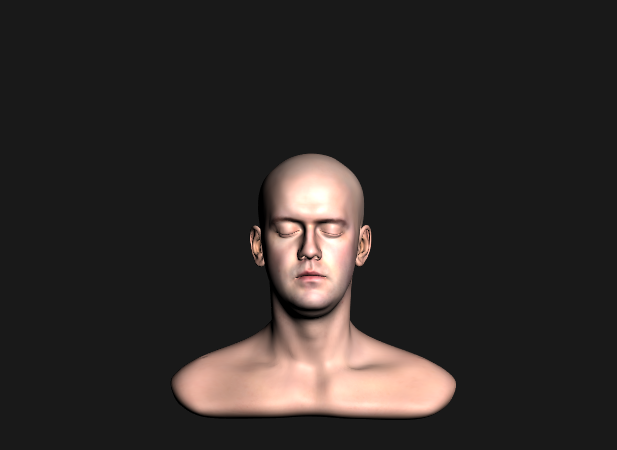
light 추가
- PRB 식에서 밑줄친 Li(x,ωi)(ωi,n)부분을 추가
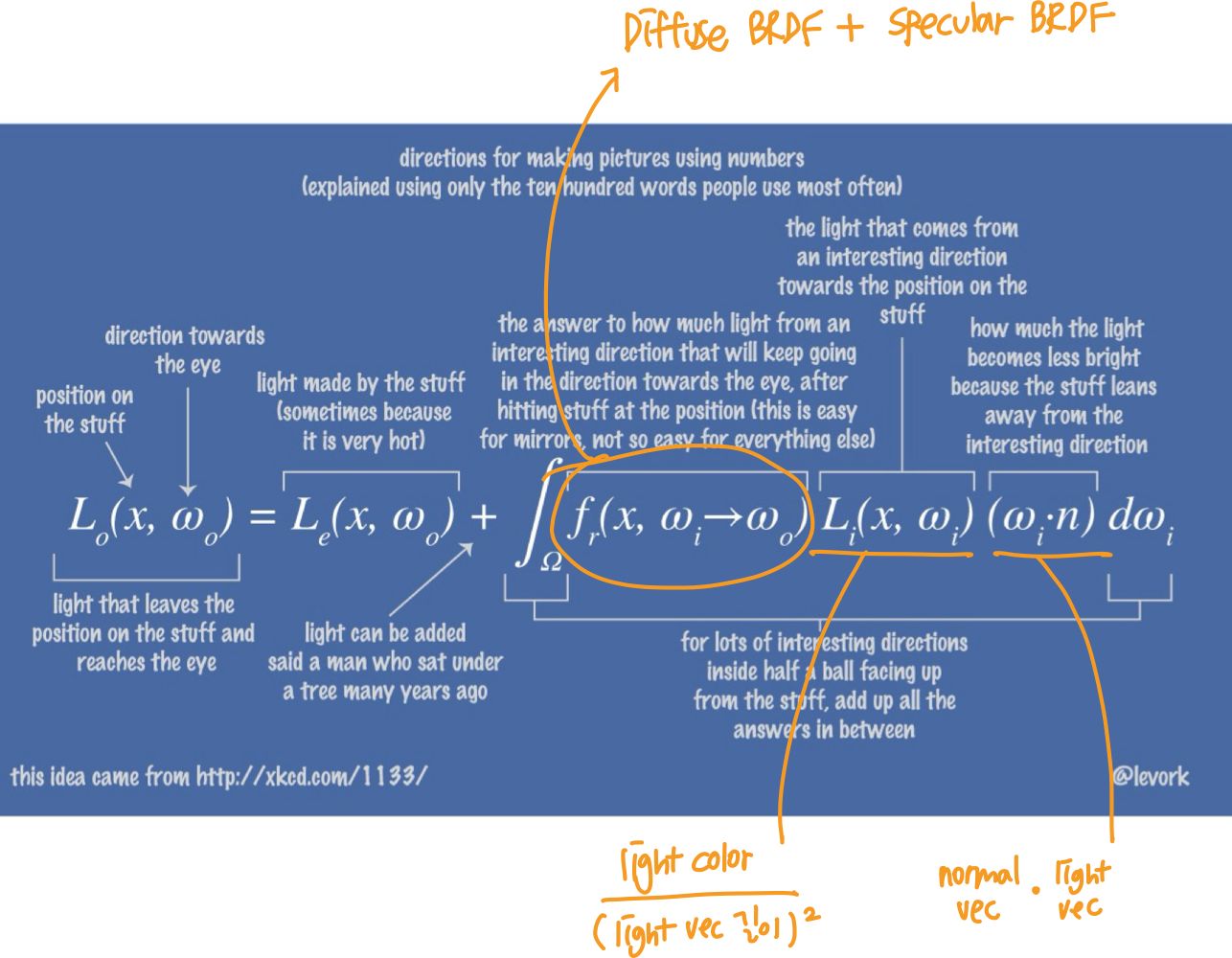
✔️ shader.frag
...
vec3 c = (Fd + Fr) * (lightColor/dot(L, L)) * NoL;
out_Color.xyz = c;

2. Gamma Correction
- 모니터는 비선형, 렌더러는 선형
- 이미지는 SRGB이고, 렌더러는 linear space
to linear space
- 이미지(ex-diffuse texture)를 렌더러로 가져와서 계산할 때, 이미지를 γ=2.2로 Gamma correction해서 linear space로 변형 (두 가지 방법 존재)
ⅰ. shader code에서 받은 텍스쳐 값에 직접 gamma correction
vec4 diffColor = texture(diffTex, texCoords);
diffColor.rgb = pow(diffColor.rgb, vec3(2.2));
vec3 Fd = diffColor.rgb * Fd_Lambert();
ⅱ. 이미지 읽어올 때 GL_SRGB8_ALPHA8로 읽어오기
int w, h, n;
void* buf = stbi_load("LPS_lambertian.jpg", &w, &h, &n, 4);
glGenTextures(1, &diffTex);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, diffTex);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_SRGB8_ALPHA8, w, h, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, buf);
stbi_image_free(buf);
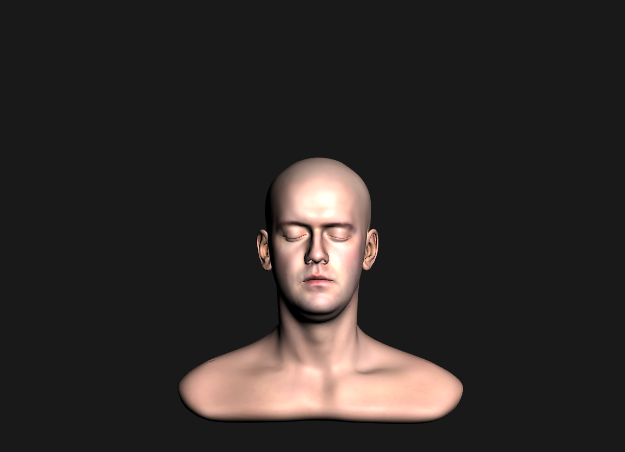
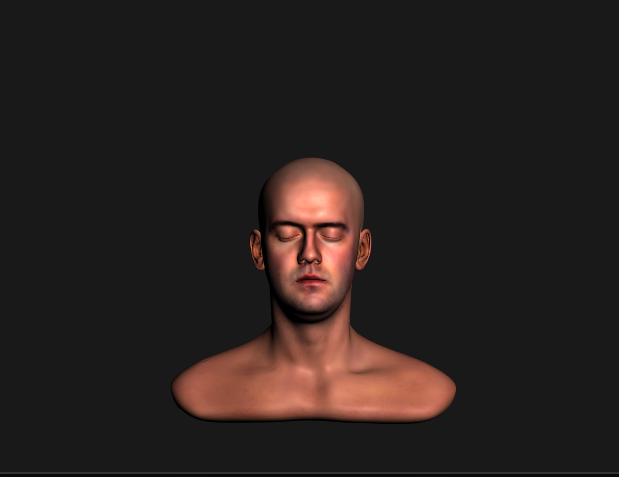


- dielectric material(피부 등)은 색 없이 빛을 반사하므로 PBR skin shader는 white specular color를 가짐
-> 근데 Gamma correction을 하지 않으면 전반적으로 노란 specular color를 갖게 됨!
to SRGB
3. Normal mapping
✔️shader.frag
- Normal map 텍스쳐로부터 읽어온 normal의 범위를 [-1~1]로 확장
- 읽어온 normal에 TBN행렬을 곱하여 변환
. . .
mat3 getTBN(vec3 N){
vec3 Q1 = dFdx(worldPosition), Q2 = dFdy(worldPosition);
vec2 st1 = dFdx(texCoords), st2 = dFdy(texCoords);
float D = st1.s*st2.t - st1.t*st2.s;
return mat3(normalize((Q1*st2.t - Q2*st1.t)*D),
normalize((-Q1*st2.s + Q2*st1.s)*D),
N);
}
void main(void)
{
vec3 L = lightPosition - worldPosition;
vec3 l = normalize(L);
vec3 n = normalize(normal);
vec3 v = normalize(cameraPosition - worldPosition);
vec3 h = normalize(l+v);
mat3 TBN = getTBN(n);
vec3 normVec = texture(normTex,texCoords).rgb*2-1;
n = normalize(TBN * normVec);
. . .

Mip-Map
- 모델이 작아질 때 패턴이 깨지는 문제를 보완하기 위해 mip-mapping으로 미리 평균 구하기
- 텍스쳐 크기를 줄여가며 미리 texel 평균을 구해두고, 모델이 작아졌을 때 미리 구한 작은 텍스쳐의 평균을 사용해 mapping
✔️main.cpp
GLuint loadTextureMap(const char* filename)
{
int w, h, n;
GLuint texID;
void* buf = stbi_load(filename, &w, &h, &n, 4);
glGenTextures(1, &texID);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texID);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, w, h, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, buf);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
stbi_image_free(buf);
return texID;
}
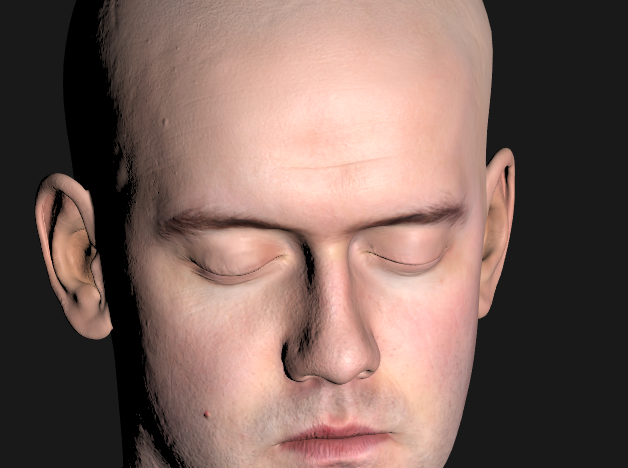


🔎 구현 과정에서...
fresnel reflectance value
- F_schlick 식에서는 f0을 vec3로 받는데, 금속 물질은 vec3으로 나타나있는데 피부같은 비금속의 f0은 스칼라로 나타나있어 어떻게 사용하는지 몰랐음
→ 그냥 vec3(0.028, 0.028, 0.028) 사용는 것임
gamma correction
- 계산 다 하고, 최종 색상 값에만 gamma correction을 하여 렌더링했는데, 모델의 색상이 회색빛이 도는 문제
-> diffuse texture에 gamma correction을 하지 않아 생긴 문제
- SRGB와 linear space를 이해하고, gamma correction의 모호했던 개념을 정확히 짚고 넘어갈 수 있었음
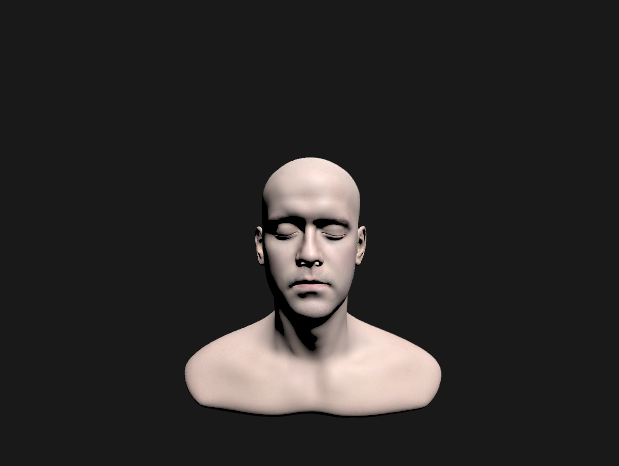
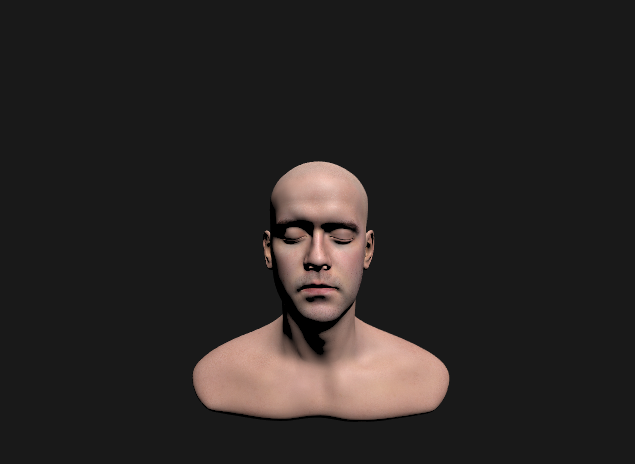


light 추가
- (specualr BRDF + diffuseBRDF)에 light 추가하고 너무 밝아지는거 보완하기 위해 gamma correction했는데 요상하게 나온당
→ dot product하고 clamp안해서;;ㅎㅎ
vec3 c = (Fd + Fr) * (lightColor/dot(L, L)) * dot(n, l);
vec3 c = (Fd + Fr) * (lightColor/dot(L, L)) * NoL;
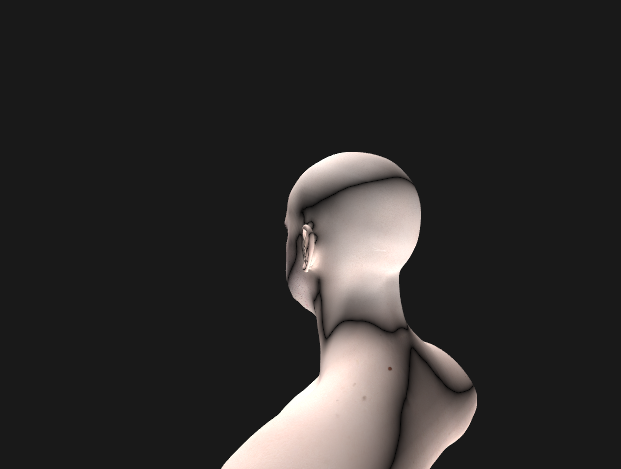
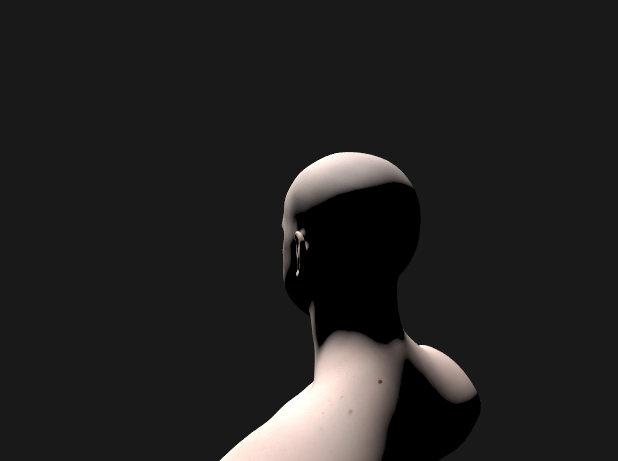


❗벡터 곱할때 *가 아니라 dot product!! 바보






 (위-알파값 사용, 아래-roughness값만 사용)
(위-알파값 사용, 아래-roughness값만 사용)
















