Virtual Memory
With one clean mechanism, virtual memory provides three important capabilities
- It uses main memory efficiently by treating it as a cache for an address space stored on disk, keeping only the active areas in main memory and transferring data back and forth between disk and memory as needed.
- It simplifies memory management by providing each process with a uniform address space.
- It protects the address space of each process from corruption by other processes.
- 가상메모리는 메인 메모리를 디스크에 저장된 주소공간에 대한 캐시처럼 사용함으로써 메모리 사용을 효율적으로 한다.
- 각각의 프로세스에 대해 통일된 주소 공간을 제공함으로써 메모리 관리를 단순화 한다.
- 각각의 프로세스들에 대해 주소공간을 보호함으로써, 다른 프로세스에 의해 주소공간이 변질되는 상황을 방어해줍니다. (보안)
9.1 Physical and Virtual Addressing
Physical Addressing
The main memory of a computer system is organized as an array of M contiguous byte-size cells. Each byte has a unique physical address (PA). The first byte has an address of 0, the next byte an address of 1, the next byte an address of 2, and so on. Given this simple organization, the most natural way for a CPU to access memory would be to use physical addresses. We call this approach physical addressing.
메인 메모리는 M 개의 연속된 byte 사이즈의 셀들로 이루어져 있으며, 각각 바이트는 고유한 물리주소 (Physical Address)를 갖고있습니다.
첫 바이트의 주소는 0, 그 다음 바이트 셀의 주소는 1.... 이렇게 쭉 이어집니다. 이와같이 CPU에 접근하는 가장 단순한 방법은 물리주소를 사용하는 것 입니다.
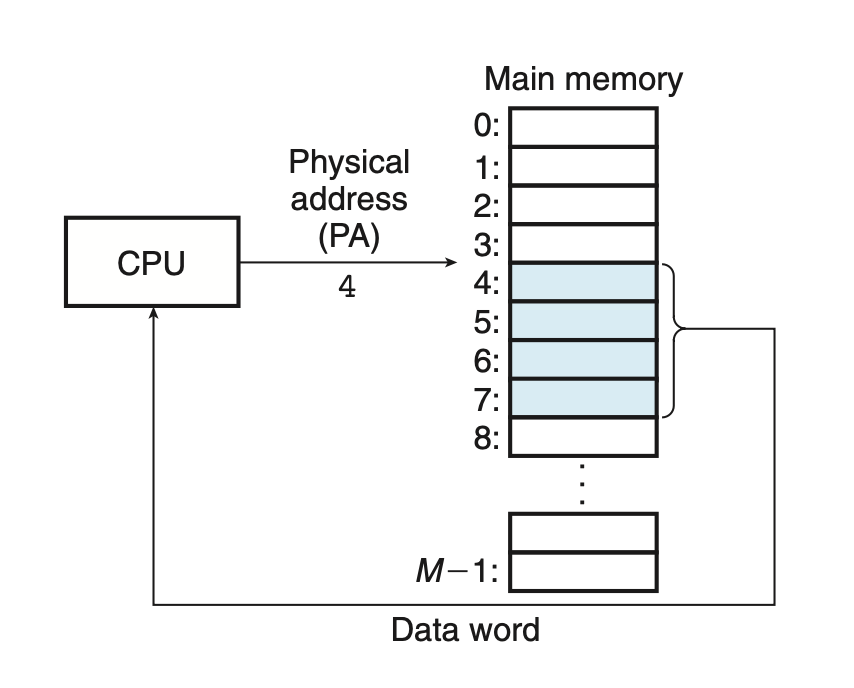
Figure 9.1 shows an example of physical addressing in the context of a load instruction that reads the 4-byte word starting at physical address 4. When the CPU executes the load instruction, it generates an effective physical address and passes it to main memory over the memory bus. The main memory fetches the 4-byte word starting at physical address 4 and returns it to the CPU, which stores it in a register.
위 그림은 물리주소 4에서 시작하는 4바이트 워드를 읽는 로드 인스트럭션의 컨텍스트에서 물리 주소 방식의 예를 보여줍니다.
CPU가 load Instrcution을 실행했을 때, 이는 유효 물리 주소를 생성하고 이것을 메모리 버스를 통해 메인 메모리에 전달합니다. 메인 메모리는 물리주소4에서 시작하는 4바이트 워드를 선입하고, 이것을 CPU에 돌려주고, 다시 이것을 레지스터에 저장합니다.
해석이 너무 난해해서 아래에 다시 정리하였습니다!
1. CPU가 로드 명령어를 실행하면, 해당 명령어는 데이터를 읽어들일 메모리 위치를 가리키는 유효한 물리적 주소를 생성합니다. 이 유효한 주소는 메인 메모리에게 전달됩니다.
2. 그러면 메인 메모리는 해당 물리적 주소에서부터 4바이트의 워드를 읽어와 CPU에게 전달합니다. CPU는 이 데이터를 레지스터에 저장하거나 다른 작업에 활용할 수 있습니다.
Virtual Addressing
With virtual addressing, the CPU accesses main memory by generating a virtual address (VA), which is converted to the appropriate physical address before being sent to main memory.
가상주소기법을 통해서 CPU는 가상주소(Virtual Address)생성하고, 메인 메모리에 접근합니다. 가상 주소는 메모리로 보내지기 전에 적절한 물리 주소로 변환됩니다.
The task of converting a virtual address to a physical one is known as address translation. Like exception handling, address translation requires close cooperation between the CPU hardware and the operating system.
가상 주소를 물리주소로 번역하는 과정은 '주소번역' 이라고 알려져 있습니다. 예외 핸들링 처럼 주소 변역은 CPU 하드웨어와 운영체제의 긴밀한 협업이 필요합니다.
Dedicated hardware on the CPU chip called the memory management unit (MMU) translates virtual addresses on the fly, using a lookup table stored in main memory whose contents are managed by the operating system.
CPU 내부에 Memory Menagement Unit (MMU) 하는 하드웨어는 프로그램 실행 중에 메인 메모리에 저장된 참조 테이블을 사용하여 가상 주소를 번역합니다. 이 테이블은 운영체제가 관리합니다!
9.2 주소 공간
An address space is an ordered set of nonnegative integer addresses
{0,1,2,...}If the integers in the address space are consecutive, then we say that it is a linear address space. To simplify our discussion, we will always assume linear address spaces. In a system with virtual memory, the CPU generates virtual addresses from an address space of N = 2n addresses called the virtual address space:
{0,1,2,...,N −1}가상메모리를 갖는 시스템에서, CPU는 가상 주소공간 이라고 불리는 N=2n 주소의 주소공간에서 가상의 주소를 생성한다.
The size of an address space is characterized by the number of bits that are needed to represent the largest address. For example, a virtual address space with N = 2n addresses is called an n-bit address space. Modern systems typically support either 32-bit or 64-bit virtual address spaces.
주소 공간의 크기는 가장 큰 주소를 표시하는 데 필요한 비트 수로 나타낸다.
예를 들어 N = 2n 주소를 갖는 가상 공간은 n-비트 주소공간 이라고 부른다.
현대 시스템은 32비트 혹은 64비트 가상 주소 공간을 지원한다.
A system also has a physical address space that corresponds to the M bytes of physical memory in the system:
{0,1,2,...,M −1}
M is not required to be a power of 2, but to simplify the discussion, we will assume that M = 2m.
연습문제 1