
회원가입시 선착순 100명에게 커피 쿠폰을 제공하는 이벤트가 있다고 가정 해보겠습니다.
이 경우에 일시적으로 1000명의 인원이 동시에 참여 버튼을 눌렀다면?
이 경우에 어떻게 선착순 100명을 지정하고 나머지 900명의 인원에게 "선착순 마감"이라는 메세지를 전해줄수 있을까요?
이러한 궁금증에서 시작했습니다.
1000개의 요청을 동시에 Jmeter를 활용하여 request하고 Java 코드 레벨에서 Test 해보겠습니다.
이전 포스팅
JAVA 멀티 스레드 환경에서 공유 자원에 대한 궁금증을 해결해보자
이전 포스팅에서 JVM을 공부하며, 공유자원의 중요성을 느꼈고, 예제와 test를 통해서 학습을 진행해보려 합니다.
공유 자원 테스트
- Controller
package com.example.threadsafetest;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController()
@RequestMapping("hello")
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping()
public Integer hello() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
helloService.plusNumber();
}
return helloService.getNumber();
}
}
- Service
getNumber
해당 클래스의 count 변수를 get 한다.
plusNumber
해당 클래스의 count 변수를 ++ 해준다.
package com.example.threadsafetest;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class HelloService {
private int number = 0;
public void plusNumber() {
number++;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
}
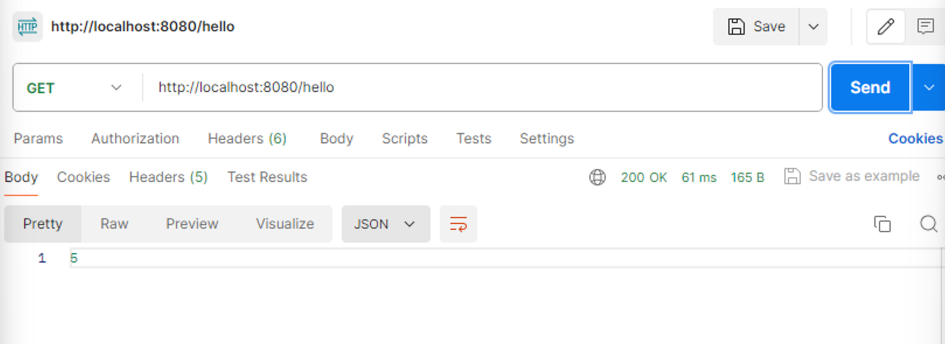
1번째 호출
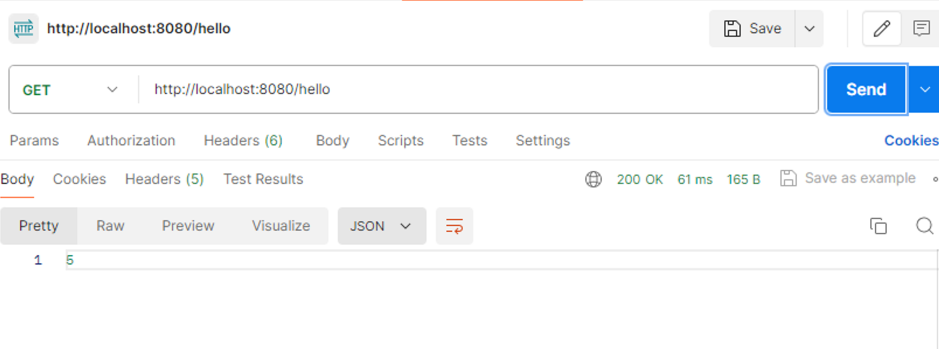
2번째 호출
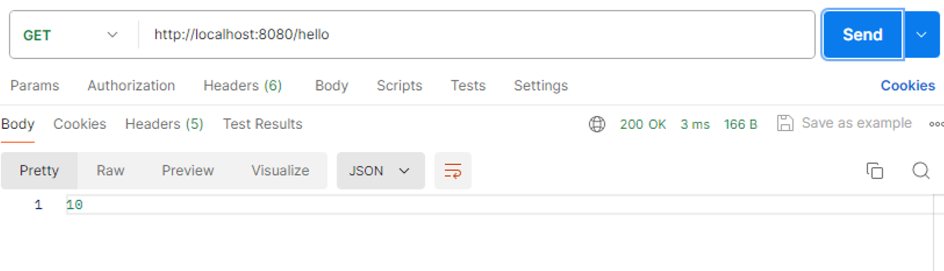
5번째 호출
Spring load시에
HelloService 객체가 로드되고 해당 객체는 컨텍스트에 존재한다.
따라서 HelloService는 모든 스레드에서 공유 자원으로 사용하고 해당 객체의 클래스 변수의 값 또한 공유된다.
따라서 number 라는 변수는 계속해서 증가한다.
@Scope("prototype")
그러면 스프링의 기본 방식인 싱글톤을 사용하지 않는다면 어떨까?
@Scope("prototype")Controller와 Service에 해당 어노테이션을 추가했다.
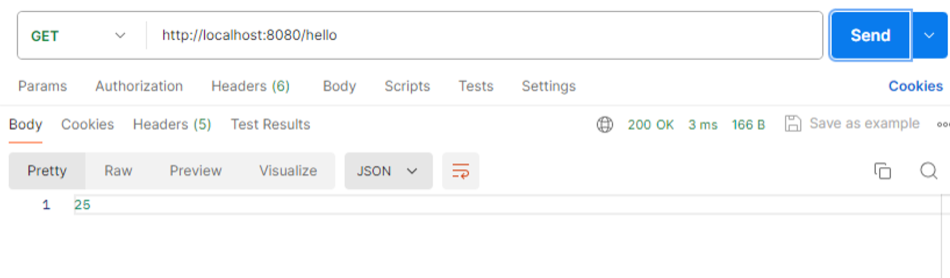
이후 API요청을 보내게 되면
5라는 숫자가 지속해서 출력된다.
왜 그럴까?
prototype은 요청마다 객체를 새로 제공해주는 설정으로 요청이 들어올때마다 새로운 Controller, Service 객체가 생성된다.
Q. 그럼 Controller, Service 양쪽다 설정이 필요한가 ? -> Yes
- @Scope("prototype") Controller 에만
Service는 싱글톤으로 설정되기에 Controller 객체들은 같은 Service 객체를 사용한다.
따라서 -> 요청하면 같은 객체를 랜더링해준다.
- @Scope("prototype") Service 에만
이게 조금 헷갈렸다 ! (생각해보니 당연했다..)
컨텍스트에 싱글톤으로 생성된 Controller는 이미 하나의 Service를 가지고있고 따라서 Controller는 하나의 Service만 바라보게 된다(Service가 prototype으로 선언 되어 있어도 !)
request 1000개
그렇다면 다시 양쪽에 싱글톤으로 처리한뒤 JMeter를 활용해 1000개의 요청을 병렬로 처리해보자
-
IP, Port, URL 설정
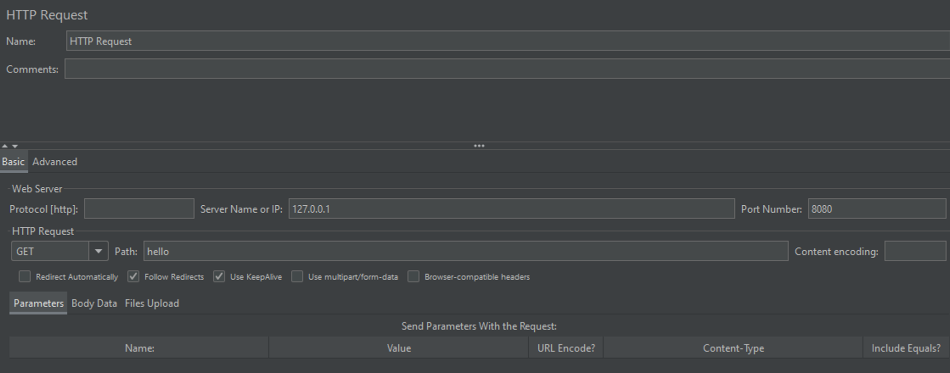
-
스레드 갯수, 시간, 반복 설정
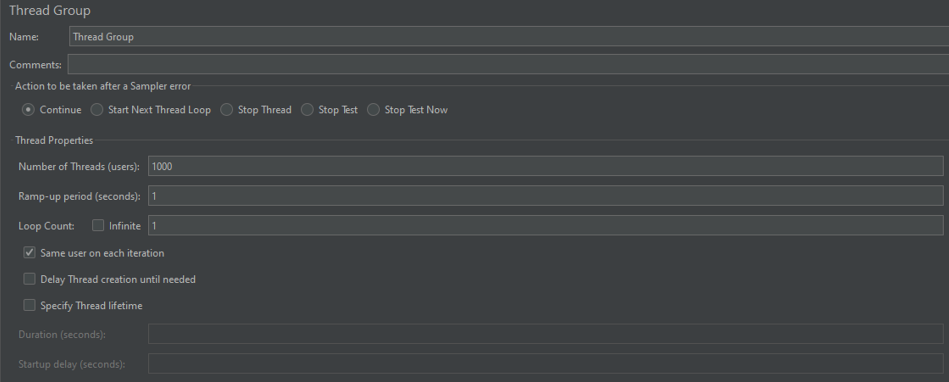
-
요청 성공
-
1000번째 응답
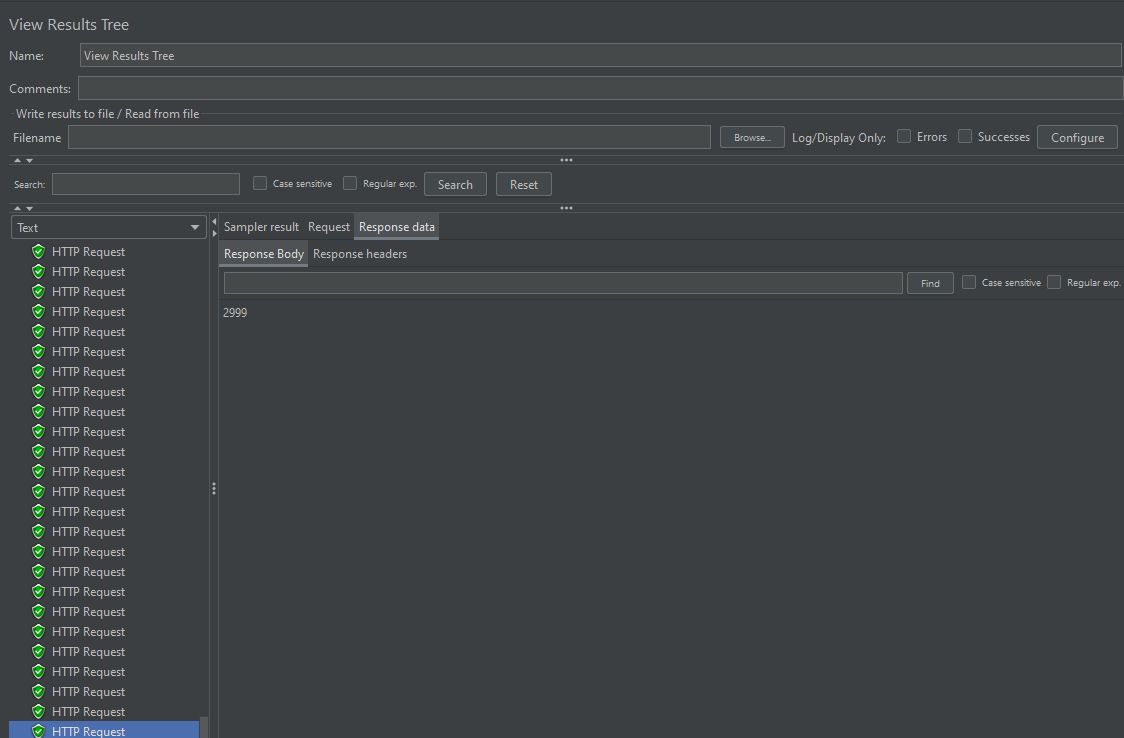
응답 결과를 보면 1000 * 5 = 5000을 기대했지만, 결과는 2999이다
헉 ~!~!~!~!~!
이게 바로 멀티 스레드 환경에서 발생하는 동시성 문제이다.
병렬로 요청하게 되면 동시에 Plus 요청을 하게 되고 -> 이는 많은 양의 요청을 무시하는 결과를 가져온다.
synchronized
그러면 어떻게 동시성을 보장 받을수 있을까?
방법은 간단하다 !
병렬로 요청이 동시에 들어오더라도 코드 레벨에서 메소드의 접근을 하나씩만 차례로 받아 드린다면? 이런 문제를 해결할수 있다.
Java에서 그런 역할을 해주는게 바로 "synchronized"
package com.example.threadsafetest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
//@Scope("prototype")
public class HelloService {
private int number = 0;
public synchronized void plusNumber() {
number++;
}
public synchronized int getNumber() {
return number;
}
}
plusNumber & getNumber 에 synchronized 기능을 추가하여 동시성을 보장시킬수 있다 !
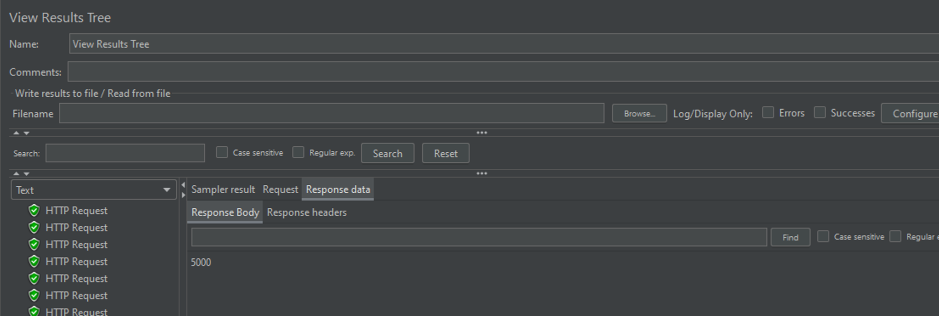
1000번째 요청이 정상적으로 기대한 5000이 나오는것을 알수있다.
변수가 여러개라면 ?
그렇지만 만약에 number 라는 변수말고 다른 변수에도 랜덤하게 접근한다면?
인기있는 축구 경기(토트넘 VS 뮌헨) 많은 관중들이 각자 원하는 자리를 선착순으로 선택한다 !
이때 만약 자리에 상관없이 동시성 처리를 한다면 10000명의 사람이 순서에 따라서 기다려야 한다 !
그치만 만약 각 자리(100좌석 가정)에 동시성이 걸린다면? 그렇다면 평균적으로 각 자리에 100명의 사람만 기다리면 되는 결과가 만들어진다.
이렇게 자리별(버킷 or 인덱스)로 Lock을 걸어주는 컬렉션이 바로 !
"ConcurrentHashMap"
일반 HashMap 은 동기화 처리가 안되있기 때문에 스레드 세이프하지 않다.
HashTable 은 모두 synchronized 되어있기 때문에 성능적으로 느리다 !
ConcurrentHashMap 은 선택적으로 동기화 처리가 되어있기 때문에 성능적으로 개선이 된다.
package com.example.threadsafetest;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController()
@RequestMapping("hello")
//@Scope("prototype")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class HelloController {
final private HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping()
public Integer hello() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
helloService.plusNumber();
}
return helloService.getNumber();
}
}
기존의 synchronized를 제거하고
plusNumber, getNumber 메소드에서 ConcurrentHashMap에 접근해서 Plus, Get 해주고 있다.
이 과정에서 각 버킷에만 Lock이 걸려 동작한다
package com.example.threadsafetest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
@Service
//@Scope("prototype")
public class HelloService {
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer> concurrentHashMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 초기 값 설정
public HelloService() {
concurrentHashMap.put("number", 0);
}
public void plusNumber() {
concurrentHashMap.computeIfPresent("number", (Key, oldValue) -> oldValue + 1);
}
public int getNumber() {
return concurrentHashMap.get("number");
}
}
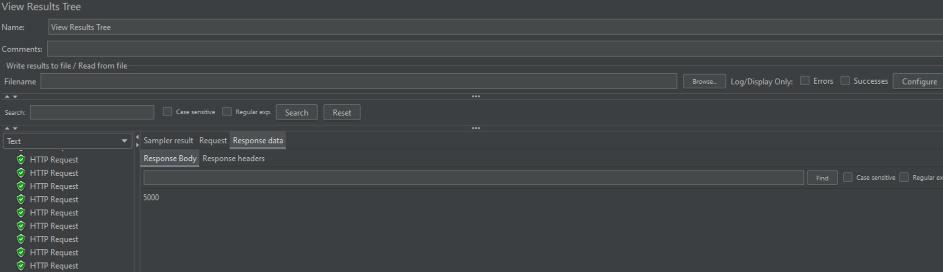
결과값으로 5000을 받아볼수 있다.
- 결론
IT 시대에서 고트래픽에 대비하지 않는다면 그 서비스는 위험..ㅎㅏ다.....
실서비스 경험과 고트래픽 경험이 적어서 동시성에 대한 고민을 해볼수 있는 기회가 없었다.
Java의 내부 원리를 학습하다 동시성까지 오게되었고 덕분에 동시성처리까지 해볼 수 있었다.
스레드끼리 공유할 수 있는 자원에 대해서 동시성 처리와 + 성능 개선이 중요하다!
+++
추가
Q. 또 하나의 궁금증이 생겼다...
DB에 연동됬을때는 어떻게 처리하고?
또 서버의 갯수가 하나가 아니라면?..
다음 포스팅에서 학습해보겠다.
