[235 C++] Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Question.
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) node of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example.
Example 1:
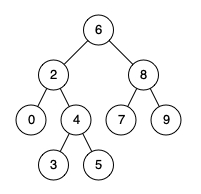
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
Output: 6
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 2 and 8 is 6.
Example 2:
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
Output: 2
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
Example 3:
Input: root = [2,1], p = 2, q = 1
Output: 2Constraints.
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [2, 105].
-109 <= Node.val <= 109
All Node.val are unique.
p != q
p and q will exist in the BST.
Explanation.
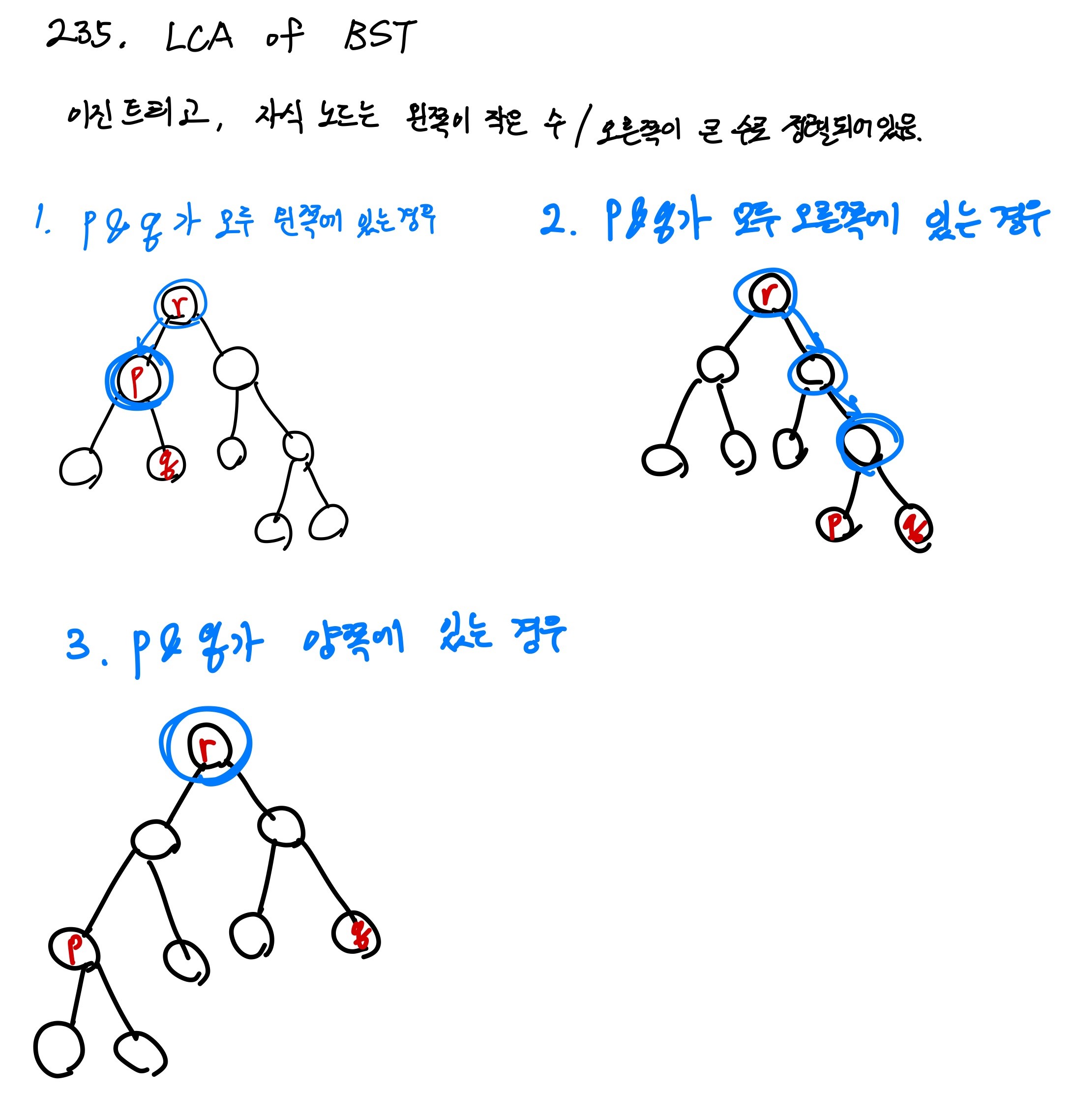
해당 문제는 공통된 조상노드 중 가장 작은 노드를 찾는 문제이다.
문제를 풀기 위해서 p와 q에 맞게 root를 이동하면서 풀었다.
1. p와 q가 모두 현재 노드(root)보다 작은 값들이라면, 왼쪽 자식노드 중에 있기 때문에 root를 왼쪽으로 이동시킨다.
2. p와 q가 모두 현재 노드(root)보다 큰 값들이라면, root를 오른쪽으로 이동시킨다.
3. 1, 2과정을 반복하다가 p와 q가 한 곳에 몰려있지 않다면 현재 root노드를 return한다.
Code.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
while(root){
if(p->val > root->val && q->val > root->val)
root = root->right;
else if(p->val < root->val && q->val < root->val)
root = root->left;
else
return root;
}
return nullptr;
}
};Plus.
처음에는 문제를 어떻게 접근해야할지 막막했다. 트리를 다루는 것에 대해 익숙하지 않다보니 p와 q에 대해서 하나씩 위치를 찾고, 찾으러 가는 와중의 값들을 저장할까 생각해봤지만 시간, 공간 복잡도 측면에서 큰 손실이 있을 것 같았다. 결국 NeetCode로 풀이힌트를 얻었다.
문제 중 node의 왼쪽에는 작은 값, 오른쪽에는 큰 값들이 정렬된다는 점을 빠르게 이해했다면 방법이 떠올랐을 수도 있을 것 같다.
