friend란
접근 제한자를 무력화하여 외부에서 클래스의 멤버 함수처럼 사용 할 수 있도록 하는 키워드이다.
friend의 필요성
프로그램을 작성하다보면 클래스 멤버 함수로는 적합하지 않지만, 클래스의 private와 protected 멤버에 접근해야 하는 특별한 경우, 이 함수를 외부 함수로 작성하고 프렌드로 선언한다.
선언할 수 있는 경우
- 클래스 외부에 작성된 함수
- 다른 클래스의 멤버 함수
- 클래스 자체 프렌드 선언
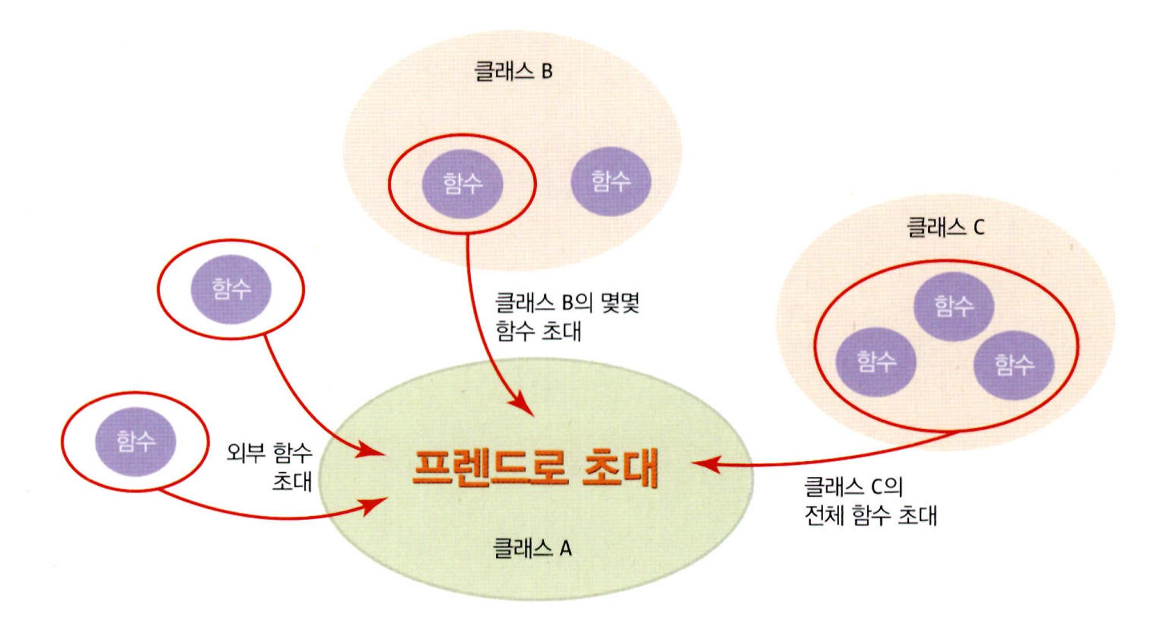
friend 함수
클래스 외부에 작성된 함수를 클래스 내에 프렌드로 선언하는 것으로, 클래스 외부에 구현된 함수를 friend 키워드로 클래스 내의 아무 곳에나 선안하면 된다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Example {
private:
int num;
public:
Example(int _num);
void printNum();
// frined 선언. 해당 함수 삭제시 컴파일 오류 발생
friend Example sum(const Example& a, const Example& b);
};
Example::Example(int _num) {
num = _num;
}
Example sum(const Example& a, const Example& b) {
Example temp(a.num + b.num);
return temp;
}
void Example::printNum() {
cout << num << endl;
}
int main() {
Example a(10);
Example b(20);
Example c = sum(a, b);
c.printNum();
return 0;
}위 코드에서 sum() 함수는 전역 함수이며 Example 클래스의 멤버 함수가 아니기에 원래는 Example 클래스의 private 멤버 변수에 접근이 불가능하다. 그러나 friend로 선언하여 private 멤버 변수에 접근하도록 만든 것이다.
다음 예제는 서로 다른 클래스에서 하나의 클래스의 멤버 함수만 friend함수로 선언한 모습이다.
class A {
int x;
public:
void Print();
friend void B::access(const A& x); // friend 멤버 함수 선언
};
class B {
int y;
public:
// friend void Print();
void access(const A& x);
};이로 인해 클래스 B의 멤버 함수인 access는 클래스 A의 private 멤버 변수에 접근할 수 있다. 하지만 클래스 A의 멤버 함수인 Print는 클래스 B의 private 멤버 변수에 접근할 수 없다.
만약 Print 멤버 함수 역시 클래스 B의 멤버 변수 y에 접근하고 싶다면, 클래스 B안에 frined 함수로 선언해 주면 된다.
추가로, 프렌드 함수는 const 한정자 사용이 불가능하다.
// Error 발생
friend Example sum(const Example& a, const Example& b) const;왜냐하면 const 한정자는 클래스의 멤버 함수가 객체의 상태를 변경하지 않음을 보장하기 위해 사용되기 때문인데, friend 함수는 멤버 함수가 아니기 때문이다.
friend 함수의 특징
- 일반 함수이거나 다른 클래스의 멤버이지만 내 클래스의 모든 멤버에 접근 가능
- 일반 함수처럼 호출됨
- 상속되지 않음
- this 포인터를 갖지 않음(멤버 함수가 아니기에)
- 캡슐화에 위배될 수 있으므로 남용 금지
- const 한정자 사용 불가능
friend class
클래스 자체를 friend로 선언하면, 해당 클래스의 모든 멤버에 접근이 가능해진다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect;
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
class RectManager {
public:
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
void copy(Rect &dest, Rect &src);
};
class Rect {
int width, height;
public:
Rect(int width, int height) {
this->width = width;
this->height = height;
}
friend RectManager; // 클래스를 friend로 선언. RectManager의 모든 멤버 접근 가능.
};
bool RectManager::equals(Rect r, Rect s) {
if (r.width == s.width && r.height == s.height)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void RectManager::copy(Rect &dest, Rect &src) {
dest.width = src.width;
dest.height = src.height;
}
int main() {
Rect a(3, 4), b(4, 5);
RectManager man;
man.copy(b,a);
if (man.equals(a, b))
cout << "equal" << endl;
else
cout << "not equal\n";
return 0;
}참고로 프렌드 키워드의 선언은 private, protected, public 어떠한 위치나 가능하다.
한 쪽으로만 접근이 가능한 경우
class A {
int x;
public:
friend class B;
};
class B {
int y;
}이 경우 B는 A의 private한 멤버 변수에 접근할 수 있지만, A는 B의 private한 멤버 변수 y에 접근할 수 없다.
양 쪽으로 접근이 가능한 경우
class A {
int x;
public:
friend class B;
};
class B {
int y;
public:
friend class A;
};쌍방으로 friend를 설정하면, 각자의 클래스 멤버 변수에 접근할 수 있다.
출처
명품 C++ Programming - 황기태
https://wn42.tistory.com/111
