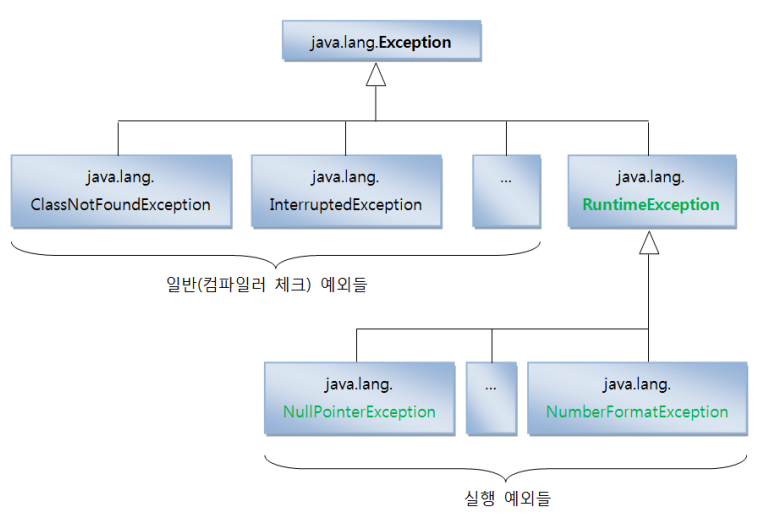
예외와 예외 클래스
오류의 종류
- 에러(Error)
• 하드웨어의 잘못된 동작 또는 고장으로 인한 오류
• 에러가 발생되면 프로그램 종료
• 정상 실행 상태로 돌아갈 수 없음- 예외(Exception)
• 사용자의 잘못된 조작 또는 개발자의 잘못된 코딩으로 인한 오류
• 예외가 발생되면 프로그램 종료
• 예외 처리 추가하면 정상 실행 상태로 돌아갈 수 있음
예외의 종류
- 일반(컴파일 체크) 예외(Exception)
• 예외 처리 코드 없으면 컴파일 오류 발생 - 실행 예외(RuntimeException)
• 예외 처리 코드를 생략하더라도 컴파일이 되는 예외
• 경험 따라 예외 처리 코드 작성 필요
예외 클래스
실행 예외 (RuntimeException)
NullPointerException
String type의 인스턴스가 null일 경우
null 객체에 '.' 를 사용하여 method를 사용할 경우에 발생하는 에러
public class NullPointerException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String data = null;
// println method에서 parameter로 넘어오는 String 인스턴스가 null이면 null로 출력
try {
System.out.println(data);
System.out.println(data.toString());
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("Null Pointer exception error 발생");
}
}
}
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
array에서 접근할 수 없는 index로 array를 사용하면 발생
RuntimeException은 개발자가 본인 능력에 의해서 판단하여 try ~ catch 절을 만들어야만 함
public class ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,2,3};
try {
System.out.println(a[0]);
System.out.println(a[1]);
System.out.println(a[2]);
System.out.println(a[3]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("배열에서 접근할 수 없는 index를 사용했습니다.");
}
}
}
ClassCastException
부모 인스턴스를 자식 인스턴스로 강제 형변환(casting)할 때 발생하는 Exception
class Animal {}
class Dog extends Animal {}
class Cat extends Animal {}
public class ClassCastException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Dog dog = new Dog();
changeDog(dog);
System.out.println("Dog 인스턴스로 강제형변환 되었습니다.");
Cat cat = new Cat();
changeDog(cat);
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
System.out.println("Dog 인스턴스로 변환 불가합니다.");
}
}
public static void changeDog(Animal animal) {
Dog dog = (Dog) animal;
}
}
NumberFormatException
NumberFormatException
1. String 문자열을 정수값등 숫자로 변환할 수 없을 경우에는 발생되는 exception
예 : Integer.parseInt("a100")
public class NumberFormatException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String data1 = "100";
String data2 = "a100";
try {
int val1 = Integer.parseInt(data1);
int val2 = Integer.parseInt(data2);
int result = val1 + val2;
System.out.println(data1 + " + " + data2 + " = " + result);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("문자열을 숫자로 변환할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}Exception multi catch
Exception multi catch 처리 방법
1. catch 순서가 매우 중요
catch에서 최상위 부모 class인 Exception이 맨처음에 나오면 뒤에 나오는 catch문의
Exception block이 처리 안됨
. 이유 : promotion (자동형변환) 발생
2. 최상위 부모 class인 Exception은 multi-catch block의 맨마지막에 넣는 것이 원칙
. 의미 : 앞 부분에 나타난 특정 Exception class들을 처리하고, 맨마지막에 나머지 모든 Exception을 처리
public class Exceptionmulticatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String data1 = null;
String data2 = null;
try {
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 발생
data1 = args[0]; // args[0] = null
data2 = args[1]; // args[1] = null;
int val1 = Integer.parseInt(data1);
int val2 = Integer.parseInt(data2); // "a10"
int result = val1 + val2;
System.out.println(data1 + " + " + data2 + " = " + result);
Class cls = Class.forName("java.lang.String");
// Exception class는 모든 RuntimeException, Compile관련 Exception 모두의 부모
// => promotion 발생됨
// } catch (Exception e) { // 모든 exception 수행되는 문제 발생
//
// }
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("실행 매개 변수의 수가 부족합니다.");
System.out.println("[실행 방법]");
System.out.println("eclipse Run - Run Configuration 메뉴에 들어가서 num1 num2 입력하세요");
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("숫자로 변환할 수 없습니다.");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("compile time 관련 exception 에러 처리");
} catch (Exception e) { // Exception의 최후의 보루
System.out.println("위에 언급한 Exception 이외에 Exception이 발생되었습니다.");
} finally {
// finally : 에러의 유무 상관없이 반드시 실행되게 하는 코드
System.out.println("숫자 덧셈 연산 처리 프로그램이 종료되었습니다.");
}
}
}ThrowException
Throw Exception 처리 방법
1. 원칙 : Exception이 발생한 method에서 try ~ catch를 사용하여 exception 처리하는 것이 원칙
2. Exception이 발생한 method를 호출하는 상위 method에서 처리하도록 하는 방법이 존재
- 하위 메소드에서 throws ClassNotFoundException 같은 Exception을 선언
- 상위 메소드에서는 모든 종류의 exception들을 한 번에 처리할 경우에 사용함
public class ThrowExceptionEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
findClass();
System.out.println("정상 처리됨");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("compile-time Exception 발생");
}
}
// method 선언문에서 throws ClassNotFoundException 의미 :
// => method 내부에서 ClassNotFoundException이 발생되면 method를 호출한 method로 Exception 넘김(throw)
public static void findClass() throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class cls = Class.forName("java.lang.String2");
}
}
사용자 정의 예외 클래스 선언
자바 표준 API에서 제공하지 않는 예외
Account
public class Account { private long balance; // 계좌 잔고 금액
public Account() {
}
public long getBalance() {
return balance;
}
// 입금
public void deposit(int money) {
balance += money;
}
// 출금
public void withdraw(int money) throws BalanceInsufficientException {
if (balance < money) {
throw new BalanceInsufficientException("잔고부족 : " + (money-balance) + " 모자람");
}
balance -= money;
}}
### BalanceInsufficientException
```java
// Exception의 자식 class로 user defined Exception 선언 가능
public class BalanceInsufficientException extends Exception {
public BalanceInsufficientException() {
}
public BalanceInsufficientException(String message) {
super(message); // 부모 클래스인 Exception class의 생성자를 호출
}
}
Main
public class AccountEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account();
// 예금하기
account.deposit(10000);
System.out.println("예금액 : " + account.getBalance());
try {
// 출금하기
account.withdraw(30000);
} catch (BalanceInsufficientException e) {
String message = e.getMessage();
System.out.println(message);
}
}
}