중첩 클래스: 클래스 멤버로 선언된 클래스
중첩 인터페이스: 클래스 멤버로 선언된 읶터페이스
• UI 컴포넌트 내부 이벤트 처리에 많이 활용
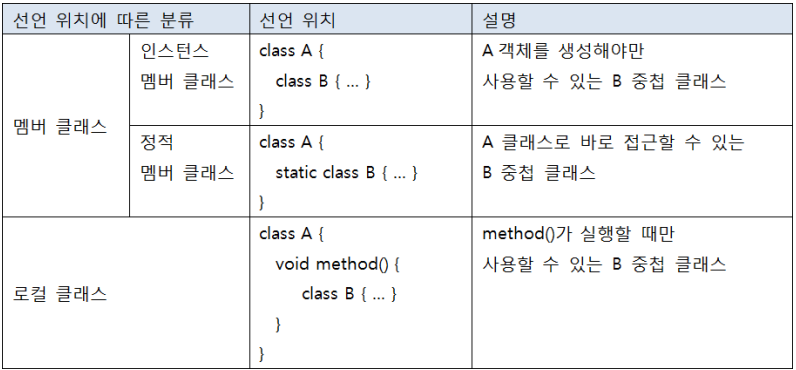
중첩 클래스의 분류
클래스 생성시 바이트 코드 따로 생성
중첩클래스(A)
public class A {
int f1;
static int f2;
public A() {
System.out.println("A 인스턴스 생성");
}
// instance member class
class B {
int field1;
// static int field2; // instance member class에서 static field 선언 불가
public B() {
System.out.println("B instance member class 인스턴스 생성");
}
void method1() {
System.out.println("B class field1 : " + field1);
}
// static void method2() {}
}
// static member class
static class C {
int field1;
static int field2 = 10;
public C() {
System.out.println("C static member class 인스턴스 생성");
}
void method1() {
System.out.println("C method1 class field1 : " + field1);
}
static void method2() {
System.out.println("C method2 class field2 : " + field2);
}
}
// class A의 instance method
void method() {
int f1; // local variable
// static final int f2=0;
// local class (method안에 선언된 class를 의미 :
class D {
int field1;
// static int field2;
public D() {
System.out.println("C static member class 인스턴스 생성");
}
void method1() {
System.out.println("local class field1 : " + field1);
}
// static void method2() {}
}
// method내에서 선언된 local class를 사용할 수 있는 곳은 method내부에서만 가능
// method내부에서 new로 인스턴스 생성해서 사용해야만 함
D d = new D();
d.field1 = 3;
d.method1();
}
}
Main
package p01.nested_class;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
// Instance member class 인스턴스 생성
A.B b = a.new B();
b.field1 = 3;
b.method1();
// static member class 인스턴스 생성
A.C c = new A.C();
c.field1 = 3;
c.method1();
c.field2 = 5;
c.method2();
// local method 실행
a.method();
}
}
중첩 인터페이스(Button)
public class Button {
OnClickListener listener;
// promotion (CallListener나 MessageListener의 자식 인스턴스를 부모 역할을 하는
// OnClickListener Interface로 자동형변환)
public void setListener(OnClickListener listener) {
this.listener = listener;
}
void touch() {
listener.onClick(); // polymorphism
}
interface OnClickListener {
void onClick(); // abstract method
}
}
implements Class(CallLisener,MessageLisener)
public class CallLisener implements Button.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick() {
System.out.println("전화를 겁니다.");
}
}
public class MessageLisener implements Button.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick() {
System.out.println("메세지를 보냅니다.");
}
}
Main
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Button button = new Button();
button.setListener(new CallLisener());
button.touch();
button.setListener(new MessageLisener());
button.touch();
}
}
익명 객체: 이름이 없는 객체
- 익명 객체는 단독 생성 불가
• 클래스 상속하거나 읶터페이스 구현해야만 생성 가능- 사용 위치
• 필드의 초기값, 로컬 변수의 초기값, 매개변수의 매개값으로 주로 대입
• UI 이벤트 처리 객체나, 스레드 객체를 간편하게 생성할 목적으로 주로 활용
Person, Student
public class Person {
void wake() {
System.out.println("7시에 일어납니다.");
}
}
public class Student extends Person {
public void study() {
System.out.println("공부를 합니다.");
}
@Override
void wake() {
System.out.println("9시에 일어납니다.");
study();
}
}
AnonyClass
public class AnonyClass {
// Person의 익명 자식 class의 인스턴스를 만들고, 부모로 promotion을 시킴
Person person = new Person() {
void work() {
System.out.println("출근합니다.");
}
@Override
void wake() {
System.out.println("6시에 일어납니다.");
work();
}
};
public AnonyClass() {
System.out.println("AnonyClass constructor call");
}
void method1() {
// 자식익명객체를 부모인 localVar로 자동형변환 (promotion)
Person localVar = new Person() {
void walk() {
System.out.println("산책합니다.");
}
@Override
void wake() {
System.out.println("8시에 일어납니다");
walk();
}
};
localVar.wake(); // polymorphism 수행
}
// promotion발생 (자식 익명객체를 부모로 자동형변환)
void method2(Person person) {
person.wake(); // polymorphism 수행
}
}
Main
// 부모 class와 자식 class간에도 자식 class를 익명객체로 만들어
//부모 class type으로 자동형변환(promotion)하여 사용
public class AnonyClassEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Student(); // promotion
p.wake(); // polymorphism
Student s = new Student();
AnonyClass ac = new AnonyClass();
ac.person.wake();
ac.method1();
// 자식 익명객체를 method2의 parameter로 넘김
ac.method2(new Person() {
void study() {
System.out.println("공부를 합니다.");
}
@Override
void wake() {
System.out.println("9시에 일어납니다");
study();
}
});
}
}
anonymous Interface
Class(Button)
public class Button {
OnClickListener listener;
public void setListener(OnClickListener listener) {
this.listener = listener;
}
void touch() {
listener.onClick();
}
interface OnClickListener {
void onClick();
}
}
Class(Window)
public class Window {
Button btn1 = new Button();
Button btn2 = new Button();
// 부모인 listener Interface type에 자식 익명객체를 넣음 (promotion)
Button.OnClickListener listener = new Button.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick() {
System.out.println("전화를 겁니다.");
}
};
public Window() {
btn1.setListener(listener);
// setListener에 자식 익명객체를 넘긴 것임 (promotion)
btn2.setListener(new Button.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick() {
System.out.println("메세지를 보냅니다.");
}
});
}
}
Main
public class WindowEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Window window = new Window();
window.btn1.touch();
window.btn2.touch();
}
}
강의를 들은후 느낀점
최근에 느낀점을 적지 않아 지금이라도 적자면 클래스를 지나고 나서는 내가 대학교때 배운 자바는 제대로 된 자바가 아니구나 라는 생각을 했다.
클래스를 지나고 나서부터는 더 이상 종이에 적는 것이 무리라고 생각하여 이렇게 개인 블로그에 간략하게 적는다