7576번 (2D 버전)
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7576
- 입력을 받으면서, 1의 위치를 모두 큐에 넣는다. (FIFO)
- 큐에서 1의 위치를 꺼내어 상하좌우에 0이 있는지 탐색한다.
- 0을 발견하면, 2차원 배열의 해당 위치에 0을 발견할 때까지 걸린 시간을 저장한다.
- 발견한 0은 1로 물들었으므로 큐에 1의 위치를 push 한다.
- 큐가 빌 때까지 모든 1에 대해 탐색을 진행했는데
- 0이 남아있으면, -1 출력
- 0이 모두 없어졌으면, 2차원 배열에 저장된 값 중에 최댓값 출력 (모든 0을 1로 물들이는 데 걸린 시간)
- 이때 한 가지 주의할 점이 처음으로 0을 발견했을 때 그 위치에 저장되는 시간이 2이기 때문에, 최댓값에서 1을 빼줘야 정답이 된다.
- 처음부터 모든 토마토가 익어서 1인 경우에는 배열의 값이 바뀌지 않은 상태에서 마지막에 -1을 하므로 정답인 0이 출력된다.
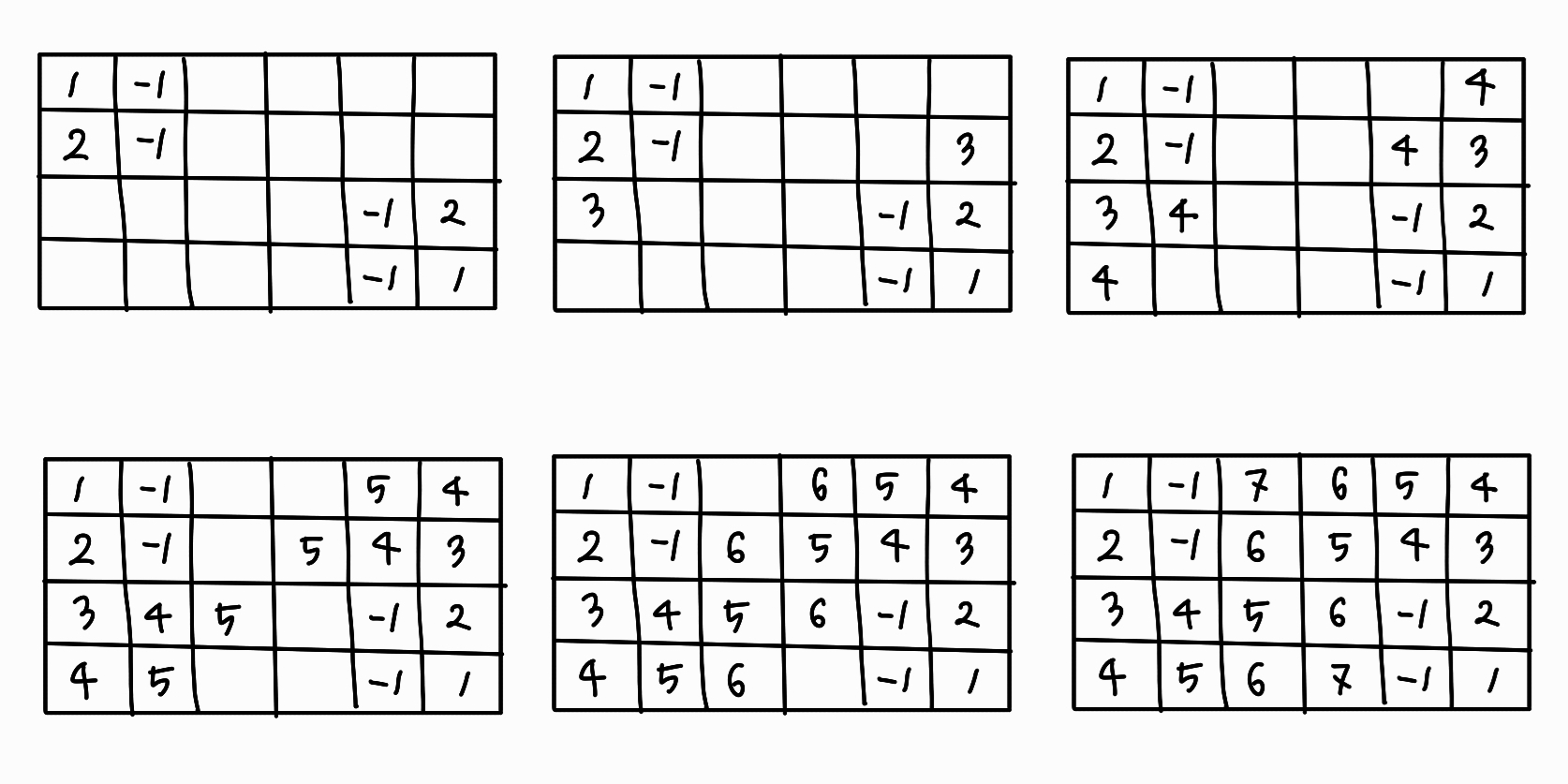
1의 위치를 큐에 저장하고 그 주변에 0이 있는지 탐색하는 것까지는 구현했는데, 큐에 time을 pair로 같이 묶어서 저장하거나 따로 time 변수를 만들어서 증가시키는 식으로 구현하니까 문제가 발생했다. 위의 그림처럼 1이 여러 개 있으면 그 주변의 0은 동시에 물들어야 한다. 그런데 큐에 1의 위치와 시간을 묶어서 같이 저장하고, 그 시간에 +1을 하는 식으로 구현하면 어떤 1의 위치에서 이미 time + 1을 했는데 다른 1의 위치에서 또 time + 1을 하게 된다. 따라서, 2차원 배열 자체에 graph[nx][ny] = graph[x][y] + 1 이런 식으로 걸린 시간을 업데이트 해나가야 한다. 마지막에 1을 빼주는 것도 잊지 말기!
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1001;
int m, n;
int graph[MAX][MAX];
queue<pair<int, int>> q; // 1의 좌표
int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
void bfs() {
while(!q.empty()){
// 1의 위치를 하나씩 꺼내서
int x = q.front().first;
int y = q.front().second;
q.pop();
// 상하좌우에 0이 있는지 탐색한다.
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) continue;
// 0을 발견할 때까지 걸린 시간을 해당 위치에 저장
if(graph[nx][ny] == 0){
graph[nx][ny] = graph[x][y] + 1;
// 0에서 1로 물든 토마토의 위치를 큐에 저장
q.push({nx, ny});
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> m >> n; // n x m
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
cin >> graph[i][j];
// 1의 위치 저장
if(graph[i][j] == 1){
q.push({i, j});
}
}
}
bfs();
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
if(graph[i][j] == 0){
cout << "-1\n";
return 0;
}
if(ans < graph[i][j]){
ans = graph[i][j];
}
}
}
// 최댓값에서 1을 빼면 정답
cout << ans - 1;
return 0;
}
7569번 (3D 버전)
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7569
2차원 버전의 문제와 푸는 원리는 동일하며, 위아래 방향까지 탐색해야 한다는 것만 다르다!
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
const int MAX = 101;
int m, n, h; // 열, 행, 높이
int graph[MAX][MAX][MAX]; // 높이(z), 행(x), 열(y)
queue<pair<int, pii>> q; // 1의 좌표 {z, {x, y}}
int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0};
int dz[] = {0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 1};
void bfs() {
while(!q.empty()){
// 1을 하나씩 꺼내서
int z = q.front().first;
int x = q.front().second.first;
int y = q.front().second.second;
q.pop();
// 상하좌우, 위아래에 0이 있는지 탐색한다.
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++){
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
int nz = z + dz[i];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m || nz < 0 || nz >= h) continue;
// 0을 발견할 때까지 걸린 시간을 해당 위치에 저장
if(graph[nz][nx][ny] == 0){
graph[nz][nx][ny] = graph[z][x][y] + 1;
// 0에서 1로 물든 토마토의 위치를 큐에 저장
q.push({nz, {nx, ny}});
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> m >> n >> h;
for(int i = 0; i < h; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
for(int k = 0; k < m; k++){
cin >> graph[i][j][k];
if(graph[i][j][k] == 1){
q.push({i, {j, k}});
}
}
}
}
bfs();
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < h; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
for(int k = 0; k < m; k++){
if(graph[i][j][k] == 0){
cout << "-1\n";
return 0;
}
if(ans < graph[i][j][k]){
ans = graph[i][j][k];
}
}
}
}
cout << ans - 1;
return 0;
}
2차원 버전에서는 MAX가 1000이어서 O(n^2) → 약 10^6
3차원 버전에서는 MAX가 100이어서 O(n^3) → 약 10^6
두 문제 모두 시간제한이 1초 (약 1억번의 연산) 인데, 입력 크기가 제한되어 있어서 각각 이중 for문, 삼중 for문으로 풀어도 시간초과가 발생하지 않는다.

