JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)
[구성도 사진]
JDBC 연결
1. JDBC Driver loading 작업 → 사용하려는 Database에 맞는 driver class를 등록한다.
방법 1 ) Class라는 Class를 이용한다.
방법 2 ) Driver Manager Class를 이용한다.
/* Class라는 Class 이용하기 */
package lecture0721;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. JDBC Driver Loading
// MySQL 8.0부터는 아래의 class를 이용해요!
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공!");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e1) {
System.out.println(e1);
}
}
}2. DBMS와 연결 ( 실제로 데이터 베이스 연결 )
- 성공하면 "Connection" instance가 생성 → 부하가 많이 걸린다.
- 다 사용한 후 반드시 자원을 해제해야 한다. ( close )
- Database에 session이 종료될 수 있도록 처리를 해야한다.
- DBMS와 연결하기 위해 JDBC URL이 필요하다.
- id, pw를 이용해서 connection 객체를 생성한다.
package lecture0721;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con = null;
try {
// 1. JDBC Driver Loading
// MySQL 8.0부터는 아래의 class를 이용해요!
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공!");
// 2. 데이터베이스 연결
String jdbcURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sqldb?characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false";
con = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcURL, "root", "test1234");
System.out.println("데이터 베이스 연결 성공!");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e1) {
System.out.println(e1);
} catch (SQLException e2) {
System.out.println(e2);
} finally {
try {
if (con != null) con.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
}
3. Statement를 생성
Statement의 종류
- 일반 statement 객체 - sql구문 실행
- 실행할 때 만들어둔 SQL문장을 이용함
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
- 실행할 때 만들어둔 SQL문장을 이용함
- preparedStatement ( 1번의 개량형 ) - sql 구문 실행
- 일반적으로 많이 사용한다
- 내가 사용할 sql을 들고 있다
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); - 속도가 상대적으로 더 빠르다
- callable Statement
- stored procedure를 호출할 때 사용
4. Query 실행
Statement를 이용해서 SQL Query를 DBMS에 전달해서 실행시킨다.
- excute( ) → 다 되요
- executeQuery( ) → SELECT → ResultSet
- executeUpdate( ) → INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
→ int (결과값) - 영향을 받은 row의 수 반환
5. 결과처리(Result set)
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();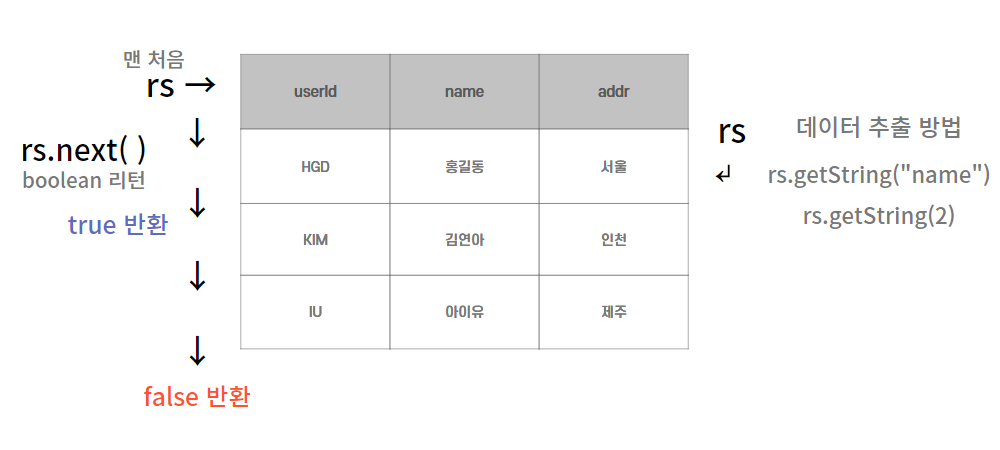
- rs는 실제 데이터를 들고 있지 않고, 포인터의 역할을 한다.
- 실행이 되면 java program에 아래와 같은 결과 레코드 집합이 전달된다.
- rs는 처음에 데이터의 맨 위쪽을 포인팅한다.
- 그 아래 데이터를 가리키기 위해서는 rs를 내려야하는데, 해당 메서드가 rs.next( )다.
(return 값은 boolean, 내려갈 수 있으면 true) - 기본 ResultSet은 위로 올릴 순 없다.
package lecture0721;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con = null;
Statement stmt = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 1. JDBC Driver Loading
// MySQL 8.0부터는 아래의 class를 이용해요!
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공!");
// 2. 데이터베이스 연결
String jdbcURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sqldb?characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false";
con = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcURL, "root", "test1234");
System.out.println("데이터 베이스 연결 성공!");
String sql = "SELECT * FROM usertbl";
// 3. Statement 생성
stmt = con.createStatement();
// PreparedStatement 생성
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
// 4. 실행
// rs1 = stmt.executeQuery(sql); // 일반 statement와 짝을 이룸
// rs2 = pstmt.executeQuery(); // preparedStatement와 짝을 이룸 (sql문 올리지 않음)
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
// 5. 결과처리
while (rs.next()) {
String id = rs.getString(1);
String name = rs.getString(2);
String addr = rs.getString(4);
System.out.println(id + ", " + name + ", " + addr);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e1) {
System.out.println(e1);
} catch (SQLException e2) {
System.out.println(e2);
} finally {
// 6. 사용한 자원을 해제해요!
try {
if (rs != null) rs.close();
// if (stmt != null) stmt.close();
if (pstmt != null) pstmt.close();
if (con != null) con.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
}
특정 값에 해당되는 값 지우기
기본적으로 AutoCommit으로 되어 있기 때문에 데이터의 직접적인 손실을 막기 위해 transaction을 걸어두는게 좋다.
package lecture0721;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class MainDelete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
// 1. JDBC Driver Loading
// MySQL 8.0부터는 아래의 class를 이용해요!
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공!");
// 2. 데이터베이스 연결
String jdbcURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sqldb?characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false";
con = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcURL, "root", "test1234");
System.out.println("데이터 베이스 연결 성공!");
con.setAutoCommit(false); // transaction의 시작
// PreparedStatement는 IN Parameter를 사용할 수 있어요. (여러개 사용 가능, 값이 매핑되는 곳에만 사용 가능)
String sql = "DELETE FROM buytbl WHERE userID = ?";
// 3. Statement 생성
// PreparedStatement 생성
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, "BBK"); // (물음표 순서(DBMS표준 : 1부터 시작), 넣을 값)
// 4. 실행
// rs1 = stmt.executeQuery(sql); // 일반 statement와 짝을 이룸
// rs2 = pstmt.executeQuery(); // preparedStatement와 짝을 이룸 (sql문 올리지 않음)
int result = pstmt.executeUpdate();
// 5. 결과처리
System.out.println("총" + result + "개 행이 삭제되었습니다.");
con.rollback(); // transaction이 종료
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e1) {
System.out.println(e1);
} catch (SQLException e2) {
System.out.println(e2);
} finally {
// 6. 사용한 자원을 해제해요!
try {
if (pstmt != null) pstmt.close();
if (con != null) con.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
}
Connection Pool💧
동시에 많은 사용자에 대해 Database 처리를 제공하려면?🙄
- 그냥 connection을 공유하면 안되나요?
transaction의 영향을 받을 수 있기 때문에 공유하는 것은 안 된다.
이를 해결하기 위해 Pooling 기법을 기본으로 사용한다.
Pooling 기법
- 자주 사용하는 객체를 pool에 모아두었다가 대여하고 반납하는 형태의 기법으로, 자원의 효율적인 사용을 위한 것이다.
- 장점
- 속도를 향상시킬 수 있다.
- 자원에 대한 효율성을 높일 수 있다.
- connection 수를 제어할 수 있다.
Connection pool을 사용하기 위해선 직접 구현이 아니라 이미 만들어진 것을 가져다가 사용한다.
우리는 무료 버전의 Connection Pool인 Apache commons에 있는 DBCP를 사용할 것이다.
/* source/db.properties */
DRIVER_CLASS=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
JDBC_URL=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sqldb?characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
DB_USER=root
DB_PASSWORD=test1234
/* MainDBCP */
package lecture0721;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource;
public class MainDBCP {
private static BasicDataSource basicDS;
static {
try {
basicDS = new BasicDataSource();
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("resources/db.properties");
properties.load(is); // 가지고 온 파일을 properties 객체로 받아드림
basicDS.setDriverClassName(properties.getProperty("DRIVER_CLASS"));
basicDS.setUrl(properties.getProperty("JDBC_URL"));
basicDS.setUsername(properties.getProperty("DB_USER"));
basicDS.setPassword(properties.getProperty("DB_PASSWORD"));
// 어떻게 설정해야 하나요?
basicDS.setInitialSize(10);
basicDS.setMaxTotal(10);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
public static DataSource getDataSource() {
return basicDS;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con = null;
DataSource ds = getDataSource();
try {
con = ds.getConnection();
con.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "DELETE FROM buytbl";
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
int result = pstmt.executeUpdate();
con.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
JDBC 예제 코드
다음 페이지에 layered architecture로 분리한 코드 있어요!
package lecture0721;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.TextArea;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.layout.BorderPane;
import javafx.scene.layout.FlowPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class BookSearch extends Application{
TextArea textarea;
Button connBtn;
Button connBtn2;
TextField textfield;
ResultSet rs;
PreparedStatement pstmt;
Connection con = null;
private static BasicDataSource basicDS;
static {
try {
basicDS = new BasicDataSource();
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("resources/db.properties");
properties.load(is); // 가지고 온 파일을 properties 객체로 받아드림
basicDS.setDriverClassName(properties.getProperty("DRIVER_CLASS"));
basicDS.setUrl(properties.getProperty("JDBC_URL"));
basicDS.setUsername(properties.getProperty("DB_USER"));
basicDS.setPassword(properties.getProperty("DB_PASSWORD"));
// 어떻게 설정해야 하나요?
basicDS.setInitialSize(10);
basicDS.setMaxTotal(10);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
public static DataSource getDataSource() {
return basicDS;
}
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
// 화면 구성
BorderPane root = new BorderPane();
root.setPrefSize(700, 500); // window 크기
textarea = new TextArea();
root.setCenter(textarea); // 화면 center에 textarea를 붙여요!
textfield = new TextField();
textfield.setPrefSize(350, 40);
connBtn = new Button("키워드 검색");
connBtn.setPrefSize(150, 40); // 버튼의 크기
connBtn.setOnAction(e ->{
try {
textarea.clear();
String msg = textfield.getText();
DataSource ds = getDataSource();
try {
con = ds.getConnection();
con.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "SELECT * FROM book WHERE btitle LIKE '%"+msg+"%'";
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
con.commit();
while (rs.next()) {
String bisbn = rs.getString(1);
String btitle = rs.getString(2);
String bauthor = rs.getString(6);
textarea.appendText(btitle + ", " + bauthor + ", " + bisbn+"\n");
System.out.println(btitle + ", " + bauthor + ", " + bisbn);
}
} catch (SQLException e1) {
System.out.println(e1);
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
} finally {
// 6. 사용한 자원을 해제해요!
try {
if (rs != null) rs.close();
if (pstmt != null) pstmt.close();
if (con != null) con.close();
} catch (Exception e3) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
});
connBtn2 = new Button("ISBM으로 삭제");
connBtn2.setPrefSize(150, 40); // 버튼의 크기
connBtn2.setOnAction(e ->{
try {
String msg = textfield.getText();
DataSource ds = getDataSource();
try {
con = ds.getConnection();
con.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "DELETE FROM BOOK where bisbn = '"+msg+"'";
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
int result = pstmt.executeUpdate();
con.commit();
if (result >= 1) {
textarea.appendText("삭제완료!\n");
}
} catch (SQLException e1) {
System.out.println(e1);
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
} finally {
// 6. 사용한 자원을 해제해요!
try {
if (rs != null) rs.close();
if (pstmt != null) pstmt.close();
if (con != null) con.close();
} catch (Exception e3) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
});
FlowPane flowPane = new FlowPane();
flowPane.setPadding(new Insets(10, 10, 10, 10)); // 여백을 줘요!
flowPane.setPrefSize(700, 40);
flowPane.setHgap(10);
flowPane.getChildren().add(connBtn); // 버튼 부착
flowPane.getChildren().add(textfield); // 입력상자 부착
flowPane.getChildren().add(connBtn2);
root.setBottom(flowPane);
// 화면에 띄우기 위한 코드
Scene scene = new Scene(root);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(); // 화면에 창을 띄우는 준비 작업 완료!
}
}

