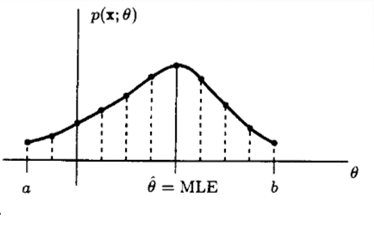
Review of Finding the MVUE
- When the observation and the data are related in a
linear way - And the noise was Gaussian, then the
MVUEwas easy to find :withcovariance matrix, - Using the
CRLB, if you got lucky, you could writewhere would be yourMVUE, which would also be anefficient estimator(meeting the CRLB) - Even if no efficient estimator exists, an
MVUEmay existA systematic way of determining the
MVUEis introduced, if it exists
- We wish to estimate the parameter(s) from the observations
- Step 1
- Determine (if possible) a
sufficient statisticfor the paramter to be estimated - This may be done using the
Neyman-Fisher factorizationtheorem
- Determine (if possible) a
- Step 2
- Determine whether the
sufficient statisticis alsocomplete - This is generally hard to do
- If it is
not complete, we can saynothing moreabout theMVUE - If it is, continue to
Step 3
- Determine whether the
- Step 3
- Find the
MVUEfrom is one of two ways using theRao-Blackwell-Lehmann-Scheffe(RBLS) theorem :- Find a function of the
sufficient statisticthat yields anunbiased estimator, theMVUE - By definition of
completenessof the statistic, this will yield theMVUE
- Find a function of the
- Find any
unbiased estimatorfor- And then determine
- This is usually very difficult to do
- The expectation is taken over the distribution
- Find the
Motivation for MVUE
MVUEoften does not exist or can't be found!Solution : If the PDF is known, then
MLEcan always be used!!
(MLE is one of the most popular practical methods)- Advantages
- It is a "Turn-The-Crank" method
Optimalfor large enough data size
- Disadvantages
Not optimalfor small data size- Can be computationally complex, may require numerical methods
CRLB/RBLS Not Applicable Example
- DC Level in WGN w/ unknown variance
(EitherCRLBtheorem orRBLStheorem is not applicable): unknown level , : WGN withunknown variance
- Firstly, check if
CRLBtheorem can give anefficient estimator:: cannot be factored as , so an efficient estimator cannot be founc, butCRLBis given
- Next, we try to find the
MVUEbased onsufficient statistics - is a single
sufficient statisticfor byNeyman-Fisherfactorization theorem - Assuming that is
complete, find a function of that produces anunbiased estimator - It is not obvious how to choose
- Alternative way is to evaluate , which is quite challenging
Approximately Optimal Estimator
- Cannot find an
MVUE: propose an estimator that is approximatelyoptimal - For finite data records, we can say nothing about its
optimality Better estimatormay exist, but finding them may not be easy
- DC Level in WGN example, continued
- Candidate estimator :
- :
biased, but as - is said to be a consistent estimator, which means that the estimator converges to the parameter in probability as
Asymtatically Unbiased
- To find the mean and variance of as , statiscal linearization can be applied
- when , so the
linearizationworks - Asymptotic variance
CRLBis achieved
Rationale for MLE
- Choose the parameter value that : makes the data you did observe the most likely data to have been observed!!!
- Consider 2 possible parameter values : and
- Ask the following : If were really the true value
What is the probability that I would get the data set I really got?
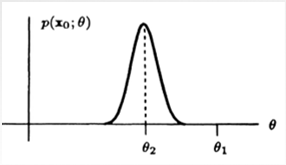
- Let this probability be
- If is small..
- It says you actually got a data set that unlikely to occur!
- Not a good guess for !
- So it is more likely that is the tru value since
- Ask the following : If were really the true value
Maximum Likelihood Estimator(MLE)
-
is the value of that
maximizestheLikelihood Function, -
Note : Equivalently,
maximizesthelog-likelihood function -
General Analytical Procedure to Find the MLE
- Find
log-likelihoodfunction : - Differentiate w.r.t. and set to 0 :
- Solve for value that satisfies the equation
We are still discussing
Classicalestimation( is not a random variable)- Bayesian MLE is that maximizes with a prior probability
- While MAP estimator maximizes
Chap. 11
- Find
MLE Example
- Same example : DC Level in WGN w/
unknown variance
(EitherCRLBtheorem orRBLStheorem is not applicable) - And is the value of that makes it 0
- Replacing by
Finally, we check the second derivative to determine if it is a
maximumor aminimum
Properties of the MLE
- The example
MLEis asymptotically,Unbiased,Efficient(i.e. achievesCRLB) and had a Gaussian PDF - If a truly efficient estimator exists, then the
MLprocedure finds it! - Use
If then achieve
CRLB - Theorem :
Asymptoticproperties of theMLE- If the PDF of the data satisfies some
regularityconditions, then theMLEof the unknown parameter isasymptoticallydistributed (for large data records) according towhere is theFisher informationevaluated at the true value of , the unknown parameter Regularity condition: existence of the derivatives of thelog-likelihoodfunction and nonzeroFisher information- Related to
Central limit theorem
- If the PDF of the data satisfies some
Monte Carlo Simulations(Appendix 7A)
- A methodology for doing computer simulations to evaluate performance of any estimation method illustrate for deterministic signal in
AWGN - Monte Carlo Simulation :
- Select a particular true parameter value,
Often interested in doing this for a variety of values of , so you would run oneMCsimulation for each value of interest - Generate signal having true
- Generate
WGNhaving unit variance, - Form measured data :
- Choose to get the desired
SNR - Usually want to run at many
SNRvalues → do oneMCsimulation for eachSNRvalue
- Choose to get the desired
- Compute estimate from data
- Repeat steps 3-5 times
- Store all estimates in a vector EST (assumes scalar )
- Select a particular true parameter value,
- Statistical Evaluation :
- Compute bias
- Compute error RMS
- Compute the error Variance
- Plot Histogram or Scatter Plot (if desired)
- Explore (via plots) how : Bias, RMS, and VAR vary with : value, SNR value, value, etc.
- DC Level in WGN(
Asymptoticproperties of theMLE)
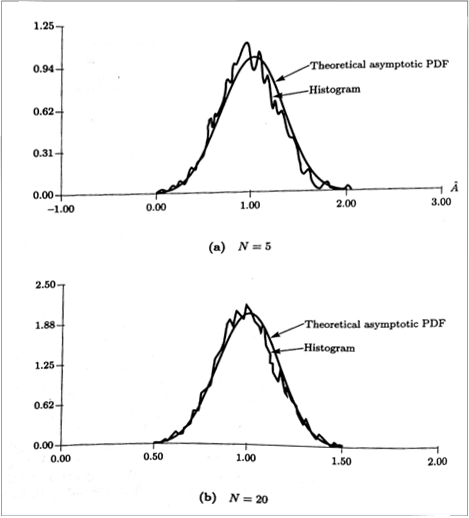 If get bigger 4 times,
If get bigger 4 times,std→ 1/2,var→ 1/4
Example : Phase Estimation in WGN
MLEof the sinusoidal phase in WGN- All methods for finding the
MVUEwill fail! → So... TryMLE - Jointly
sufficient statistics MLE: thatmaximizes- or
minimize - Then
- Where for not near or
- Therefore
MLEis function of thesufficient statisticssince,AsymptoticPDF of the estimatorwhere- Variance
MLE for Transformed Parameters
-
Given PDF but want an estimate of
-
What is the
MLEfor ?-
Two cases :
-
is a one-to-one function
-
is not a one-to-one function
Need to define
modified likelihood function
-
-
Example 1
- Example) Transformed DC Level in WGN
- Wish to find the
MLEof Maximizingresults in- The
MLEof thetransformed parameteris the transform of theMLEof the original parameterInvariance property
Example 2
- Transformed DC Level in WGN, : not one-to-one
- The
MLEof is the value thatmaximizesthe maximum between and
Invariance Property of MLE
- Theorem :
Invariance propertyof theMLE- If parameter is mapped according to then the
MLEof is given bywhere is theMLEof , found by maximizingIf is not a one-to-one function, then maximizes the
modified likelihoodfunction , defined as
- If parameter is mapped according to then the
Numerical Determination of the MLE
- In all previous examples we ended up with a closed-form expression for the
MLE Numerical determinationof theMLE
A distint advantage of theMLEis that we can find it for a given data setnumerically- For a finite interval -
grid search - But... For the parameters that span
infiniteinterval- Newton-Raphson method
- Scoring approach
- Expectation-Maximization(EM) algorithm
Iterative methods ▷ will result in local maximum ▷ good initial guess is important
-
For the parameters that can span
infiniteinterval - iterative method
- Step 1 : Pick some
initial estimate - Step 2 : Iteratively improve it using
- Step 1 : Pick some
-
Convergence Issues : May
not converge, or may converge, but tolocal maximumGood initial guess is needed
(Use rough grid search to initialize or multiple initialization)
Exponential in WGN Example
- Estimate
- To find
MLE - Iterative method :
Newton-Raphsonmethod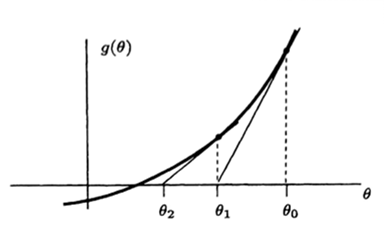
- The iteration
may not converge - Even if the iteration converges, the point found may not be the
globalmaximum but possibly only alocalmaximum or even alocalminimumGood initial guess is important
- Iterative method : the method of
scoring - Motivation :
- For IID samples, by the law of large numbers
- The method of
scoringThe expectation provides more
stableiteration
MLE for a Vector Parameter
- is the vector that satifies
- Example : DC Level in AWGN with unknown noise variance
Asymptotic Properties of Vector MLE
- Theorem :
Asymptoticproperties of theMLE(vector parameter)- If the PDF of the data satisfies some
regularityconditions, - Then the
MLEof the unknown parameter isasymptoticallydistributed(for large data records) according towhere is theFisher informationmatrix evaluated at the true value of the unknown parameter
- If the PDF of the data satisfies some
- So the vector
MLisasymptoticallyunbiased and efficient Invariance PropertyHolds for Vector Case- Example : DC Level in AWGN with unknown noise varianceand mutually independent
- For large , by
central limit theoremor
- For large , by
Expectation-Maximization Algorithm
Newton-Raphson methodScoring approach- Expectation-Maximization(EM) algorithm
- Increase the likelihood at each step
- Guaranteed to converge under mild conditions(to at least a local maximum)
- Uses
completeandincompletedata concepts - Good for complicated multi-parameter cases
- Example : Multiple frequencies in WGn
- : WGN
- Variance
- : parameter to estimate
- Objective function to
minimize: - If the original data could be replaced by the independent data setswhere is WGN with variance , then the problem would be decoupled
Decoupledobjective function tominimize:minimization reduced to seperate 1-D minimization- The new data set :
completedata - : original or
incomplete data - The decomposition is
not unique:
Expectation-Maximization Algorithm - General
- Suppose that there is a
completetoincompletedata transformation
, where is a many-to-one transformation MLE: that maximizesEM algorithm: maximize , but is not available, so maximize- Expectation (E) Step : Determine the average log-likelihood the complete data
- Maximization (M) Step : Maximize the average log-likelihood function of the complete data
- Expectation (E) Step : Determine the average log-likelihood the complete data
- Example : Multiple frequencies in WGN
- Expectation (E) Step : For
- Maximization (M) Step : For where 's can be arbitrarily chosen as long as
- Expectation (E) Step : For
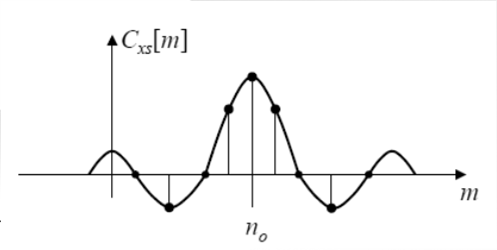
MLE Example - Range Estimation
- Transmit pulse , nonzero over
- Receive reflection
- Estimation of time delay , since the round trip delay
- Continuous time signal model
- Discrete time signal model
- Sample every sec,
- has non-zero samples starting at
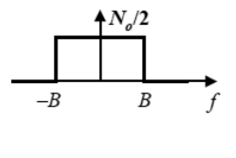
PSD of ACF of
- Range Estimation
Likelihood Function: - Minimize
- Or, maximize
So,
MLEimplementation is based onCross-correlation:
"Correlate" received signal with trasmitted signal - Therefore
- Think of this as an inner product for each
- Compare data to all possible delays of signal
Pick to make them most alike