Two assumptions of Market
Perfect Competititive: all participants of market should beprice-takersNo Externalities- corrective tax : directive approach to solve externality
- market function : indirective approach to solve externality
1. Modeling the Consumers
1. Indiviudal Demand
While farmers sell different types of fruit and vegetables on this market, today you are looking at the apples.
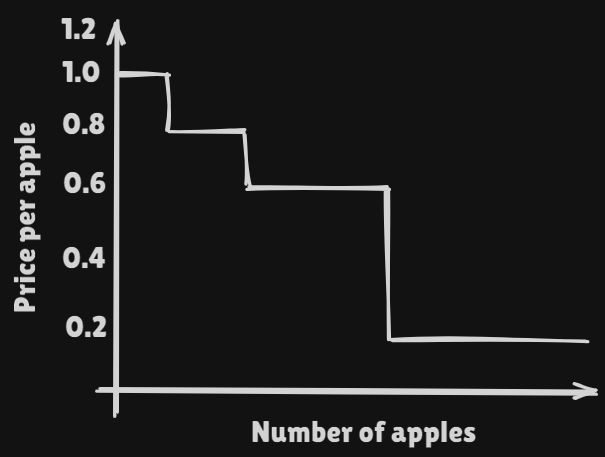
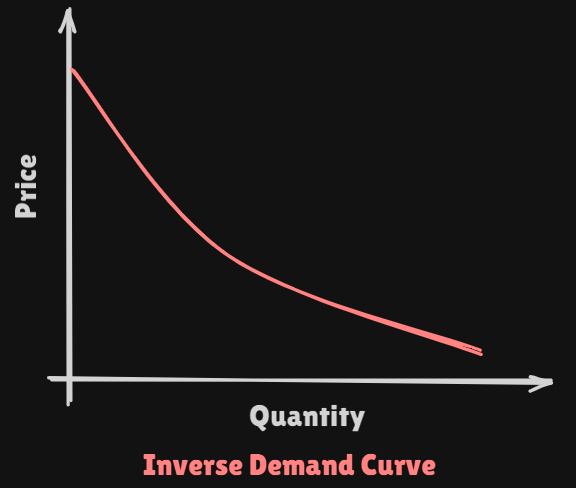
The number of apples you purchase depends on their current price. Such curves show what the price should be for a consumer to purchase a certain amount of a particular or .
2. Surplus
Let us suppse that when you get to the market, the prices is $0.40 per apple. At this price, you decide to buy six apples.
| Value | Quantity | Price | Surplus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fisrt apple | 1 | $1.00 | $1.00 |
| Second apple | 1 | $0.80 | $0.80 |
| Next four apples | 4 | $0.60 | $2.40 |
| Gross Surplus | $4.20 |
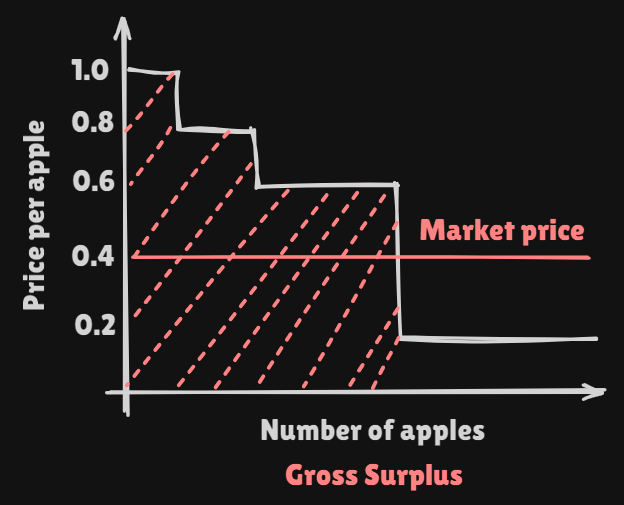
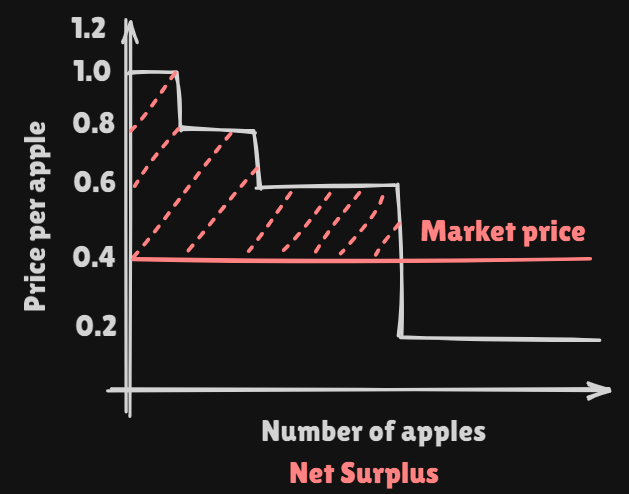
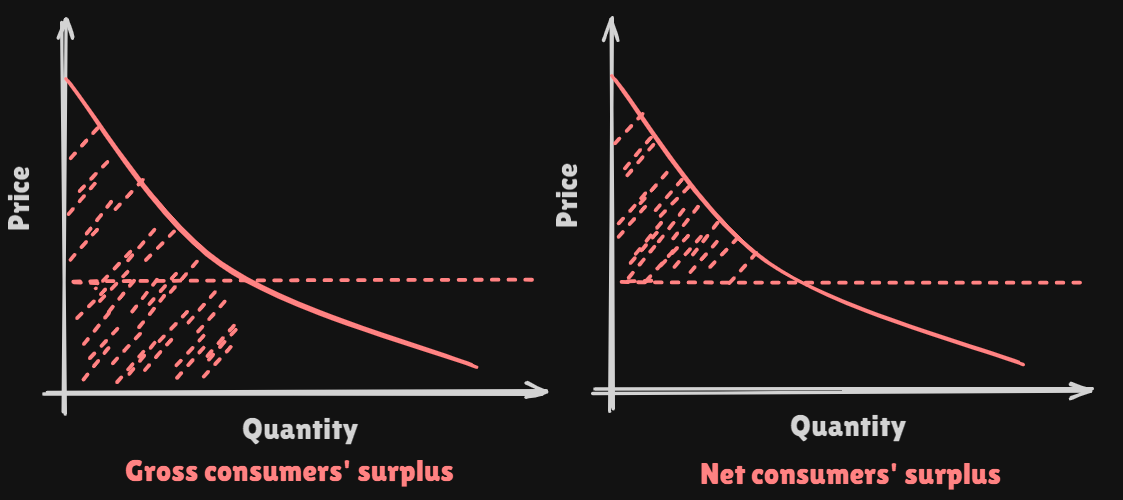
We can define the red colored area as gross surplus of consumer. It can be decomposed into two differnet parts net consumer's surplus, expense of purchasing the goods.
Net consumer's surplusmeans Extra Value that you get from being able to buy all the apples at the same market price, even though the value you attach to some of them is higher than the market price.
3. Demand and Inverse Demand Functions
Some consumers would pay much more for the same number of apples whie others buy apples only when they are cheap.
If we aggregate the
demand characteristicsof asufficiently large number of consumers, the discontinuities introduced by the individual decisions are smoothed away
- If denotes the quantity purchased and the price of the commodity, we can write:
- If we look at the same curve from the other direction, we have the
demand functionfor the commodity - For most, if not all, practical commodities, the
demand functionisdownward slopingThe amount consumed decreases as the price increases.
Demand curvegives themarginal valuethat consumers attach to the commodity.- Their
marginal willingness to paydecreases as their consumption increases.
- The concept of
net surplusis much more important than the calculation of an absolute value for this quantity.Calculating the absolute value of the
net surplusis quite difficult because theinverse demand functionis not known accurately.
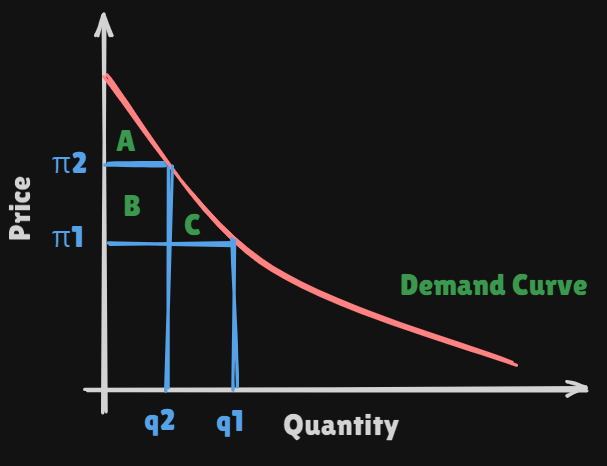
- If the market price is , the consumer purchase a quantity and the
net surplusis equal to the shaded area. - If the market price increases to , the consumption level decreases to and the consumers'
net surplusis reduced to the roughly triangular area labeled A.Two effects contribute to this reduction in
net surplus.- First, because the price is higher, consumption decreases from to . This loss of the
net surplusorwelfareis equal to the area labeled C. - Second, because consumers have to pay a higher price for the quantity that they still purchase, they losd an additional amount of
welfarerepresented by the area labeled B.
- First, because the price is higher, consumption decreases from to . This loss of the
4. Elasticity of Demand
- Increasing the price of a commodity even by a small amount will clearly decrease the demand.
- But by how much?
elasticity: the concept of same products between the demand for commodity and the price of commodity .cross-elasticity: the concept of substitute products between the demand for commodity and the price of commodity .- While the
elasticityof a commodity to its own price is alwaysnegative Cross-elasticitiesbetween substitute products arepositivebecause an increase in the price of one will spur the demand for the other.If two commodities are
complementsa change in the demand for one will be accompanied by a similar change in the demand for the other.Electiricyandelectric heatersare clearlycomplements.- The
cross-elasticitiesofcomplementary commoditiesare negative.
2. Modeling the Producers
1. Opportunity cost
- We also argued that the consumption level is such that the
marginal benefitthat consumers get from this commodity is equal to the price that they have to pay to obtain it. A similar argument can be used to develop our model of the producers. - Generally
opportunity costcould be summurized as biggest cost by making choice when you decide
2. Supply and Inverse Supply Functions
- If the market price for apples is higher, our producer may decide that if is worthwhile to increase the quantity of apples that she brings to the market.
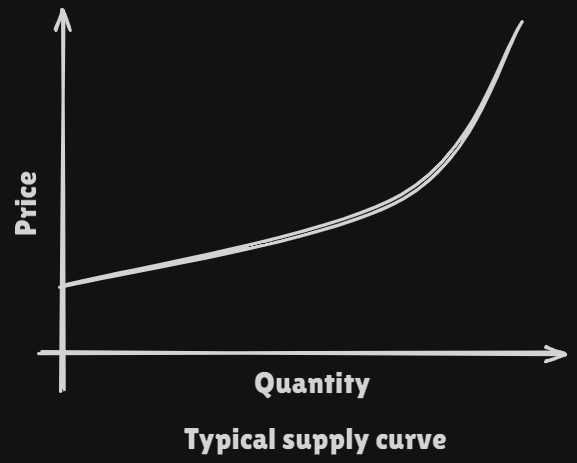
Inverse supply function:Supply function:
- The
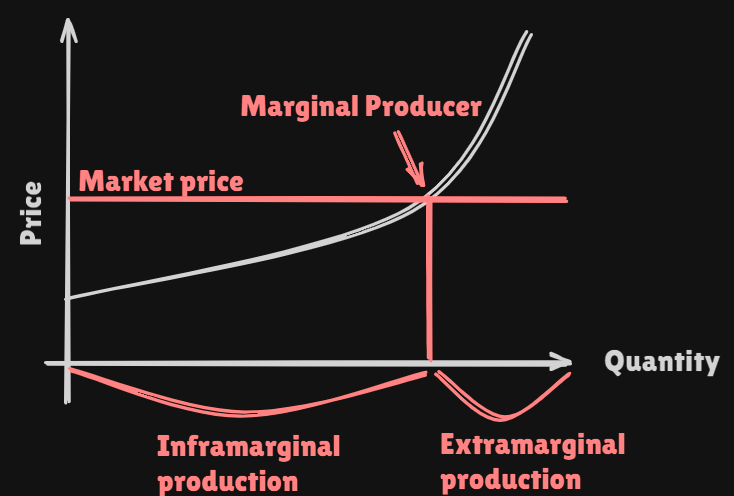
marginal produceris the producer whoseopportunity costis equal to themarket price. Extramarginal production: production that could become worthwhile if the market price were to increase.Inframarginal production: theopportunity costof the production exist below themarket price
3. Producer's Revenue
Producer's Revenue: The red colored area at point
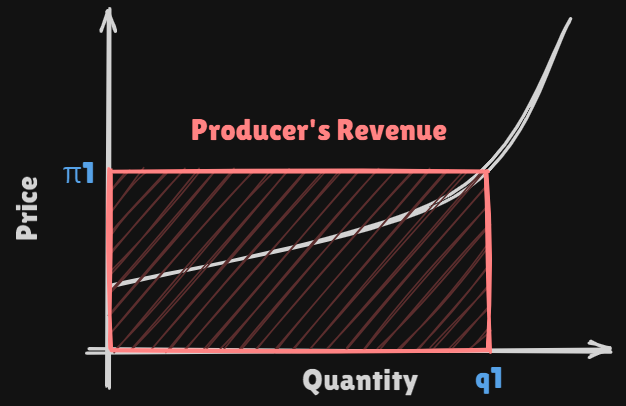
Producer's Net Surplus: Upper area of thesupply curveand lower area of the
4. Elasticity of Supply
price elasticity: change of amount of thesupplyby change ofprice- The
elasticity of supplyisalways positive. - It will usually be higher in the
long runthan in theshort runbecause suppliers have more opportunities to increase the means of production.
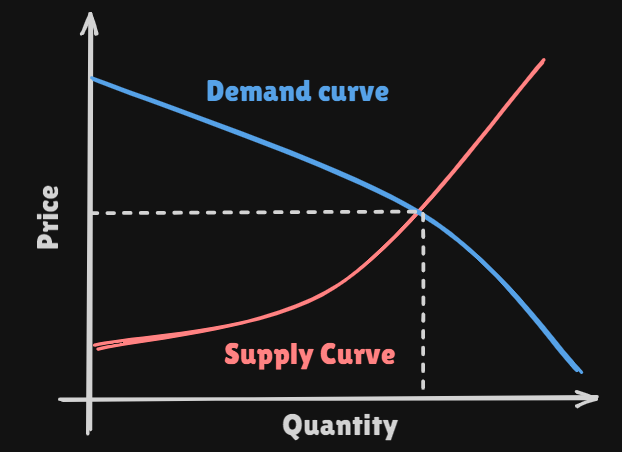
3. Market Equilibrium
- We will make the assumption that each
supplierorconsumercannot affect the price by its individual actions.All market participants take the price as given
- Then, the market is said to be
perfectly competitive market Equilibrium priceormarket clearing price:- The quantity would be decided by following fomula :
Equilibrimalso can befined in terms of theinverse demand functionandinverse supply function.
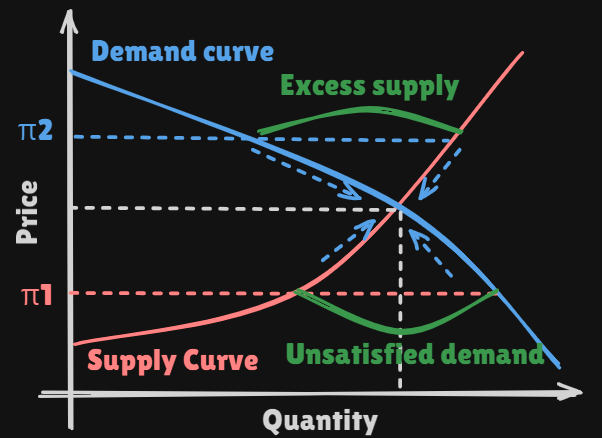
- If the market price is where the
demandis greater than thesupply- Some suppliers will inevitably realize that there are some unsatisfied customers
- The traded
quantity will increasesand so will thepriceuntil theequilibrium conditionsare reached.
- If the market price is where the
supplyis greater than thedemand.- Some suppliers are left with goods for which they cannot find buyers.
- They will
reduce their productionuntil the amount that producers are willing to sell is equal to the amount that consumers are willing to buy.
4. Pareto Efficiency
Pareto efficient: if thebenefitderived by any of the parties can be increased only by reducing thebenefitenjoyed by one of the other parties.- The
equilibrium situationin a competitive market isPareto efficientin terms of both thequantity of goodsexchanged and theallocation of these goods.
- There is someone willing to sell extra units of the good considered at ta price that is less than the price
- Thus, if the total amount traded is less thant the
equilibrium, the situation is notPareto efficient - Also, any amount in
excess of the equilibriumvalue is notPareto efficientIn a
competitive market, all units of a given commodity are traded at the same price and this price represents themarginal rate of substitutionbetween this good and all other goods.
5. Global Welfare and Deadweight Loss
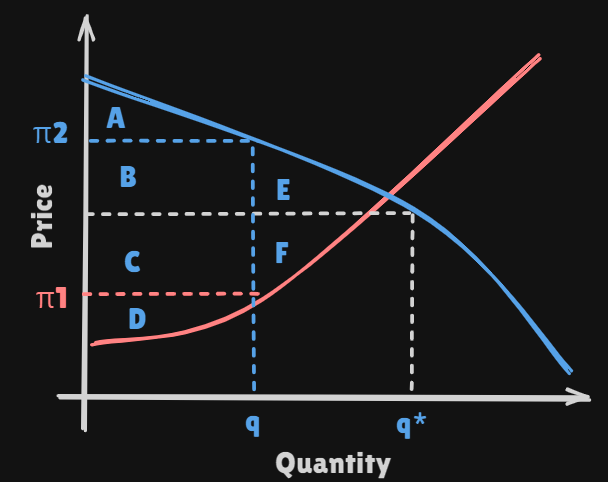
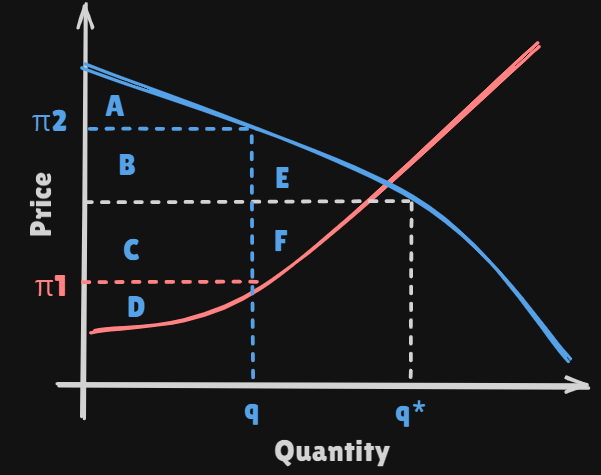
-
Consumer's surplus: A + B + E -
Producer's surplus: C + D + FExternal intervention sometives prevents the price of good from settling at the
equilibrium valuethat would result from a free and competitive market -
If this price is set at a value that is higher than the
competitive market clearing price -
consumers reduce their consumption from to .
Consumers' surplusshrinks : A +B + EProducers' surplus: B + C + D
-
If the government could enforce a maximum price for a good. Price set at a value
Consumers' surplusshrinks : A + B + CProducers' surplus: D
-
Deadweight Loss: E + F