REDO LOG BUFFER
- 데이터베이스 데이터 블록의 모든 변경 사항을 기록한다.
- 목적은 복구(recovery) 이다.
- 내부의 기록된 변경사항을 리두항목(redo entry)라고한다.
- change vector(#1, #2, #3) -> redo entry
- redo entry에는 변경사항을 재구성하거나 재실행할 정보가 포함되어 있다.
- 리두 항목이 생성되는 SQL문 : DML, CREATE, ALTER, DROP, SELECT..FROM..FOR UPDATE
- 리두 로그 버퍼는 LOG_BUFFER 파라미터로 설정
- OS 블록의 배수단위로 설정
alter system set log_buffer = ... scope=spfile;(static parameter)
OS블록 사이즈 확인
SELECT max(lebsz) FROM x$kccle;
LGWR
- redo log buffer에 있는 redo entry를 redo log file에 기록하는 프로세스
- 3초 마다
- redo log buffer가 1/3 차면
- redo entry 크기가 1mb 이상 입력이 되면
- commit, rollback이 발생되면(Log Force a Commit)
- DBWR가 작동하기 전에(Write Ahead Logging)
Log Force a Commit
- transaction과 관련된 모든 redo entry를 redo log file에 저장한 후 commit(rollback) 완료 수행한다.
Write Ahead Logging
- database buffer cache에 있는 변경된 블록을 기록하기 전에 log buufer에 있는 redo entry를 먼저 기록한다.
- 데이터파일에 기록하기 전에 리두 로그 파일에 먼저 기록
redo copy latch
-
PGA내의 change vector를 redo log buffer로 복사하려면 redo copy latch를 획득해야 한다.
-
CPU개수의 2배
-
redo copy latch를 획득하지 못하면
latch : redo copywait event가 발생한다. -
redo copy latch의 수 확인
- 현재 cpu의 개수는 2개 이기 때문에 2배인 4개가 만들어졌다.
select a.ksppinm as parameter,b.ksppstvl as session_value, c.ksppstvl as instance_value
from x$ksppi a, x$ksppcv b, x$ksppsv c
where a.indx = b.indx
and a.indx = c.indx
and a.ksppinm = '_log_simultaneous_copies';
- 다른 방법으로 latch의 수 확인
select name, gets from v$latch_children where name = 'redo copy';
redo allocation latch
- change vector를 redo log buffer에 복사하기 위해서는 redo log buffer내에 공간을 확보하고 하는 과정에서 redo allocation latch를 획득해야 한다.
- redo allocation latch를 획득 못하면
latch : redo allocationwait event가 발생한다. - 8i 버전까지는 redo allocation latch는 1개였다.
- 9i 버전에는
shared read strands라는 개념으로 redo log buffer의 영역을 일정 개수로 분할해서 사용함으로써 분할된 영역에 각각으로 redo allocation latch가 생성되었다.- 오라클의 권장사항은 (cpu수/8) redo strand의 개수로 지정
- 10g 버전에는 shared read strands 개수를 오라클이 동적으로 관리한다.
- "zero copy redo"
private redo strands기능을 사용함으로써 PGA영역에서 change vector를 생성하는 것이 아니라 shared pool에 private redo strands영역에 저장하며 이 영역에 저장된 redo entry는 redo log buffer를 거치지 않고 바로 redo log file에 저장된다. - 이 기능으로 인해 redo copy latch에 대한 경합이 줄어들게 되었다.
- private redo strands 영역의 redo entry는 server process가 write 하게 된다.
- shared pool의 5% 정도를 사용한다.
- "zero copy redo"
- 오라클이 동적으로 관리하는 shared read strands 사용 여부
_log_parallelism_dynamic: 사용하면 true_log_private_mul: shared pool에서 private redo strands에 사용하는 비율
select a.ksppinm as parameter,b.ksppstvl as session_value, c.ksppstvl as instance_value
from x$ksppi a, x$ksppcv b, x$ksppsv c
where a.indx = b.indx
and a.indx = c.indx
and a.ksppinm in ('_log_parallelism_dynamic','_log_private_mul');
- 다른 방법으로 redo allocation latch 개수 확인
select count(*) from v$latch_children where name = 'redo allocation';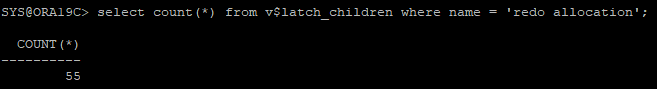
- shared pool의 private strands 공간 확인
select * from v$sgastat where name='private strands';
redo writing latch
-
redo log buffer의 프리공간을 확보하기 위해 LGWR에게 쓰기 요청을 하려면 redo writing latch를 획득해야 한다.
-
1개만 존재한다.
-
redo writing latch를 획득못하면
latch : redo writingwait event가 발생한다. -
1개만 있는 독립적인 latch는 v$latch_parent 뷰로 확인해야 한다.
- gets는 해당 latch를 잡은 횟수
select name,gets from v$latch_parent where name = 'redo allocation';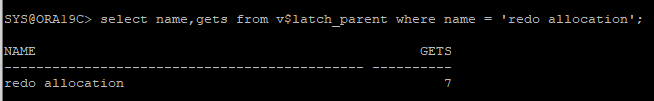
redo monitoring
- 현재 세션에 대한 해당 구간의 redo 통계 정보 확인
- redo entries : redo entry가 redo log buffer에 기록된 횟수
- redo size : redo size(byte)
- redo synch writes : commit, rollback에 의해 수행된 redo write 수
- redo writes : LGWR가 수행된 수(redo synch writes가 있어서 commit, rollback 제외)
- redo blocks written : redo log file에 write된 redo log block 수
- redo log space requests : redo log buffer에 redo entry들을 redo log file에 쓰려는데 redo log file이 꽉차서 log switch가 발생한 횟수
- redo log space wait time : redo log space requests에 소요된 시간(1/100초)
- hr로 다른 세션에서 접속후 sys 세션에서 해당 쿼리 던졌을때
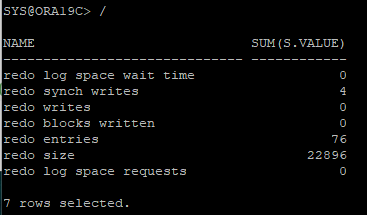
select n.name, sum(s.value)
from v$sesstat s, v$statname n
where n.name in ('redo entries', 'redo size', 'redo synch writes', 'redo writes', 'redo blocks written', 'redo log space requests', 'redo log space wait time')
and s.statistic# = n.statistic#
and s.sid = (select sid from v$session where username = 'HR')
group by n.name;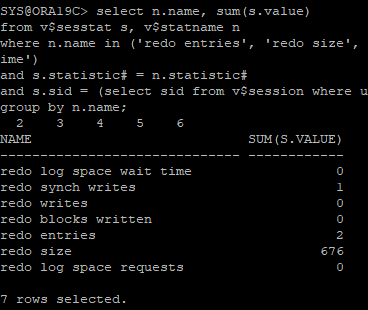
- hr session
create table hr.redo_test(id number, name char(100));: create 문장으로 인해 redo entry 생성insert into hr.redo_test(id, name) select object_id, object_name from user_objects;: DML 작업으로 인해 redo entry 생성
- sys session
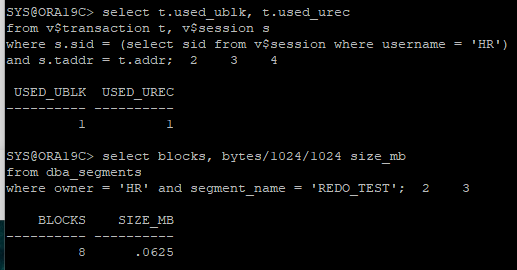
select blocks, bytes/1024/1024 size_mb
from dba_segments
where owner = 'HR' and segment_name = 'REDO_TEST';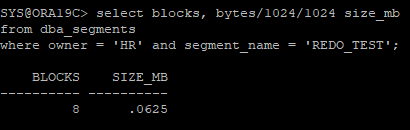
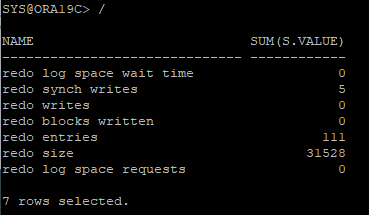
- hr session
rollback;
- sys session
- hr session
drop table hr.redo_test purge; : drop으로 인해 redo entry 생성
- sys session
- hr로 다른 세션에서 접속후 sys 세션에서 해당 쿼리 던졌을때
select n.name, sum(s.value)
from v$sesstat s, v$statname n
where n.name in ('redo entries', 'redo size', 'redo synch writes', 'redo writes', 'redo blocks written', 'redo log space requests', 'redo log space wait time')
and s.statistic# = n.statistic#
and s.sid = (select sid from v$session where username = 'HR')
group by n.name;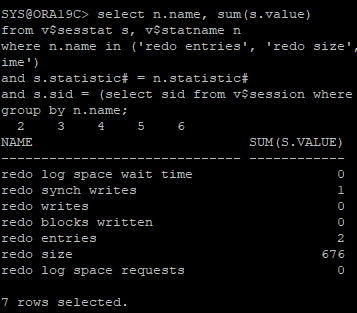
- hr session
create table hr.redo_test(id number, name char(100));: create 문장으로 인해 redo entry 생성insert into hr.redo_test(id, name) select object_id, object_name from user_objects;: DML 작업으로 인해 redo entry 생성
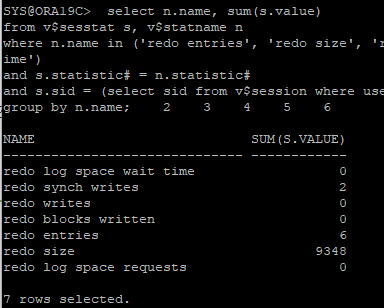
- hr session에서 exit했다가 재접속 후 진행
insert /*+ append */ into hr.redo_test(id, name) select object_id, object_name from user_objects;: hint를 사용한 DML 작업으로 인해 redo entry 생성(direct path write)
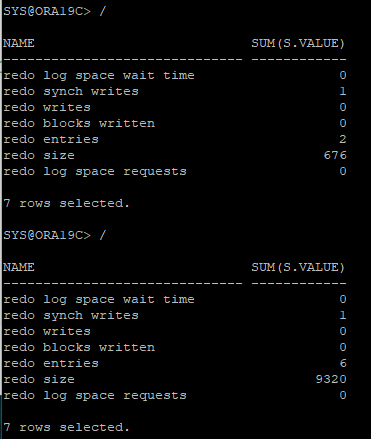
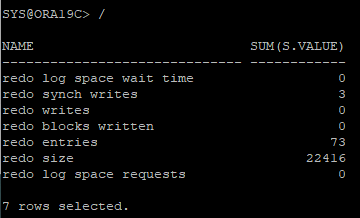
# redo size delta = 9320 - 676
- 블럭 수 확인
2배로 늘어난 거 확인
select blocks, bytes/1024/1024 size_mb
from dba_segments
where owner = 'HR' and segment_name = 'REDO_TEST';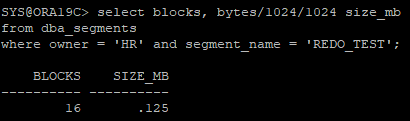
- undo 발생량 확인
- used_ublk: 사용한 undo block의 수
- used_urec: 사용한 undo record의 수(행의 수)
select t.used_ublk, t.used_urec
from v$transaction t, v$session s
where s.sid = (select sid from v$session where username = 'HR')
and s.taddr = t.addr;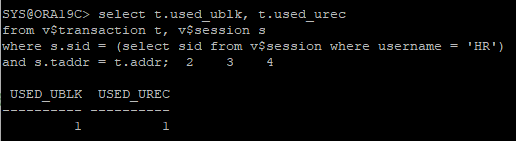
- hr session
rollback;truncate table hr.redo_test;
- sys session
select blocks, bytes/1024/1024 size_mb
from dba_segments
where owner = 'HR' and segment_name = 'REDO_TEST';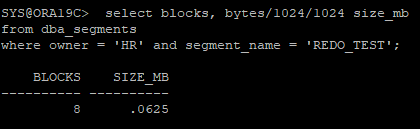
- sys session redo 통계정보 확인
select n.name, sum(s.value)
from v$sesstat s, v$statname n
where n.name in ('redo entries', 'redo size', 'redo synch writes', 'redo writes', 'redo blocks written', 'redo log space requests', 'redo log space wait time')
and s.statistic# = n.statistic#
and s.sid = (select sid from v$session where username = 'HR')
group by n.name;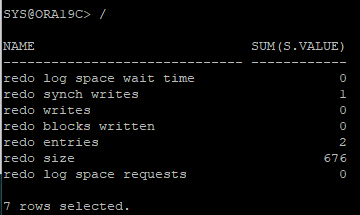
대량의 데이터를 insert * select 할때
- 운영중인 테이블은 logging모드로 해야 나중에 복구가능하므로 nologging 모드인 테이블을 데일리 체크해야함
- nologging 옵션 설정
- 현재 logging 모드 확인
select logging from dba_tables where owner = 'HR' and table_name = 'REDO_TEST'; - no logging 모드로 변환
alter table hr.redo_test nologging; - logging 모드로 변환
alter table hr.redo_test logging;
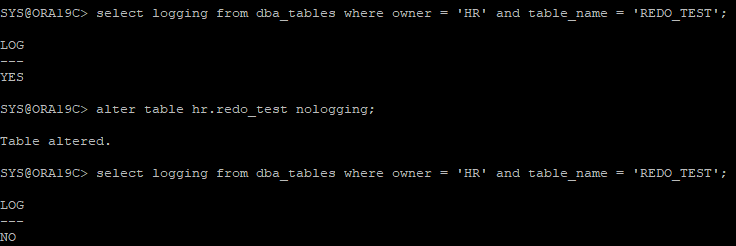
- direct path write 수행
insert /*+ append */ into hr.redo_test(id, name) select object_id, object_name from user_objects;
- redo 발생량 확인
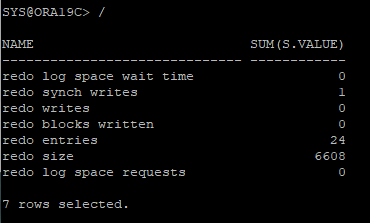
- undo 발생량 및 블럭 수와 사이즈확인
# redo size delta : 6608 - 676
=> redo 발생량을 줄이기위해 direct path를 사용할거면 해당 테이블을 nologging으로 설정해 최소화하면 좋음
Direct path write
- 오라클 SGA를 거치지 않고 데이터 파일에 직접 쓰기 작업 수행
- DBWR에 의해 쓰기 작업이 이뤄지는 것이 아니라 서버 프로세스에 의해 직접 쓰기 작업이 수행됨
- HWM(High Water Mark)이후에 블럭을 추가(append방식)
- 테이블의 nologging 옵션이 설정된 경우 redo 발생량을 줄일 수 있음
- 테이블의 TM LOCK을 exclusive하게 획득하기 때문에 다른 세션에서 DML이 허용되지 않음(따라서 밤에 주로 수행)
- 테이블 생성
create table hr.emp as select * from hr.employees;
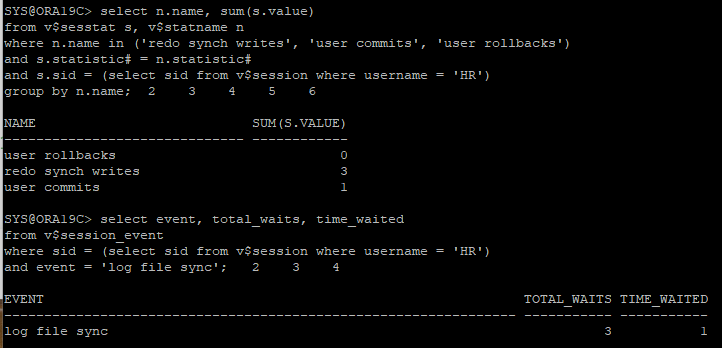
- 새로운 redo 통계정보 확인
redo synch writes: commit, rollback에 수행된 redo write 수user commits: commit 수user rollbacks: rollback 수
select n.name, sum(s.value)
from v$sesstat s, v$statname n
where n.name in ('redo synch writes', 'user commits', 'user rollbacks')
and s.statistic# = n.statistic#
and s.sid = (select sid from v$session where username = 'HR')
group by n.name;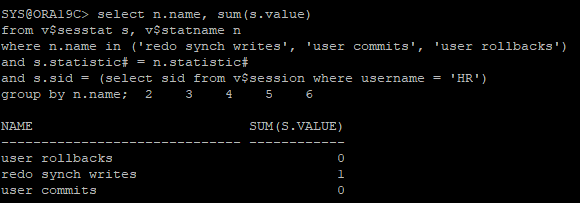
- log file sync 이벤트에 대한 대기 정보를 조회
select event, total_waits, time_waited
from v$session_event
where sid = (select sid from v$session where username = 'HR')
and event = 'log file sync';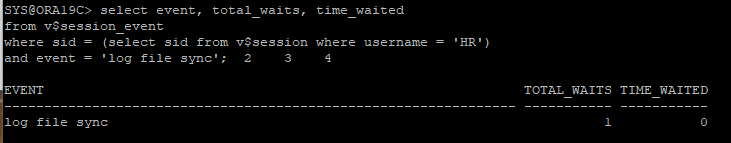
- hr session
update hr.emp set salary = salary * 1.1 where employee_id = 100;
commit;
- sys session
- hr session
update hr.emp set salary = salary * 1.1 where employee_id = 200;
rollback;
- sys session
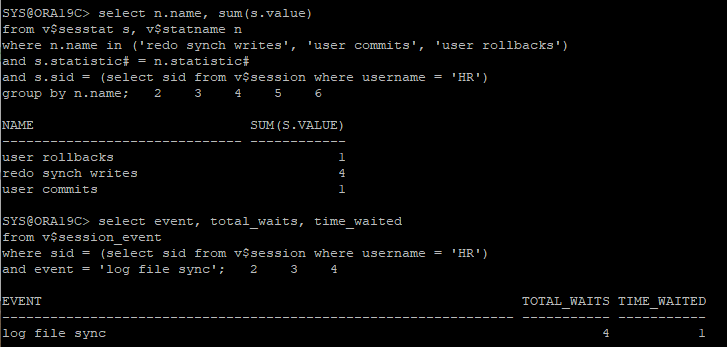
- hr에서 새로 접속한 상태에서 초기 상태 확인 sys session
select n.name, sum(s.value)
from v$sesstat s, v$statname n
where n.name in ('redo synch writes', 'user commits', 'user rollbacks')
and s.statistic# = n.statistic#
and s.sid = (select sid from v$session where username = 'HR')
group by n.name;
select event, total_waits, time_waited
from v$session_event
where sid = (select sid from v$session where username = 'HR')
and event = 'log file sync';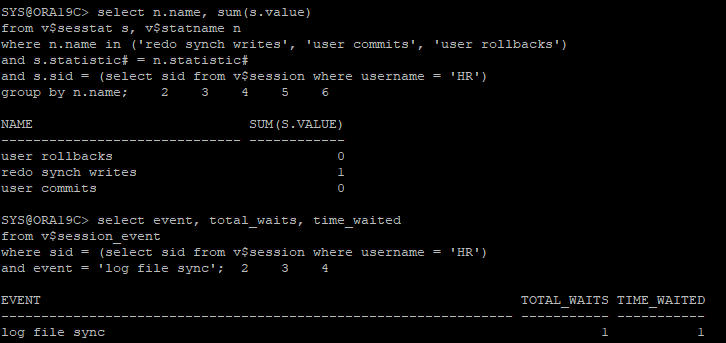
- hr session
/*
커밋이 반복문 안에 있으면 돌아갈때마다 commit되는데
이는 성능에 좋지않으므로 오라클이 알아서 group commit을 진행
*/
declare
type numlist is table of number;
v_num numlist := numlist(100, 101, 200);
begin
for i in v_num.first..v_num.last loop
update hr.emp
set salary = salary * 1.1
where employee_id = v_num(i);
commit;
end loop;
end;
/- sys session
- user commits은 3으로 증가됐지만 redo synch writes가 1로 증가한 것을 보고 LGWR는 1번으로 끝낸 것, 즉 group commit이 진행된 것을 확인할 수 있음
redo synch writes: GROUP COMMIT으로 LGWR 작동횟수user commits: COMMIT문 횟수
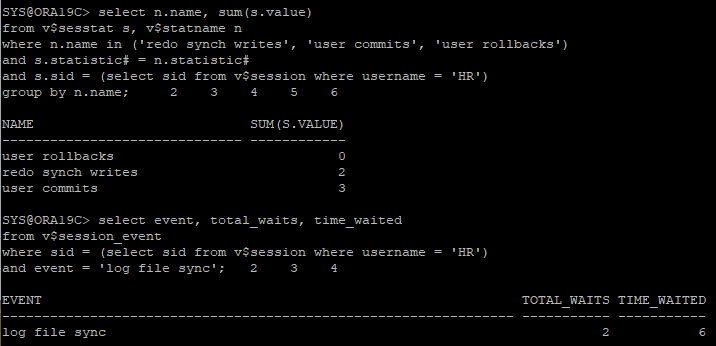
PL/SQL 반복문 안에 있는 COMMIT문은 내부적으로 GROUP COMMIT으로 수행됨
즉 COMMIT이 3번 수행했지만 GROUP COMMIT의 개념으로 1번만 수행함 -> LGWR도 한번만 수행
log file sync
- commit, rollback을 수행하면 LGWR는 redo log buffer에 있는 redo entry를 redo log file에 기록하는데 이때 sync write라 하며 redo sync write 통계값이 증가됨
- 빈번한 commit은 log file sync 대기 원인이 될 수 있음
log buffer space
- transaction에 의해 생성되는 redo의 양에 비해 redo log buffer의 크기가 작은경우 발생
log file switch completion
- LGWR가 redo buffer에 redo record(레코드)를 redo log file에 쓰려는데 현재 redo log file이 꽉차서 더이상 write할 수 없을 경우 다음 그룹으로 log switch가 발생하는데 이때
log file switch completion이라는 이벤트 발생하며 대기 - redo log file의 크기가 크면 log switch가 발생하는 주기는 줄지만 archive 모드일때 문제가 생길 수 있음
log file switch (checkpoint incompletion)
- 새로 사용할 redo log file에 대한 체크포인트 작업이 아직 끝나지 않았다면 DBWR에 의해 체크포인트 대상에 해당하는 dirty buffer가 아직 데이터 파일에 쓰지 않았으므로 log switch가 대기해야 하는 현상 발생. 이런 대기 이벤트가 발생하면 새로운 트랜잭션이 기다릴 수 있음
- 위 문제는 즉 log switch가 발생하는 주기가 짧다는 것으로 redo log group을 추가해 해결할 수 있음
log file switch (archiving needed)
- 새로 사용할 redo log file에 대해 archive 작업이 아직 끝나지 않았다면 log switch가 대기해야하는데 이때 발생하는 이벤트
log file parallel write
- 리두 로그 파일이 위치한 I/O 시스템 성능이 느린 경우에는 LGWR의 sync write를 수행하는 시간이 늘어 나고 이로 인해 log file sync 대기 시간이 증가할 수 있다.
- 해결 방법으로는 리두 로그 파일을 가장 빠른 디바이스에 위치 시켜야 한다.
- 리두 로그 그룹의 멤버를 디스크 경합을 피하기 위해서는 서로 다른 디스크에 분산 시켜야 한다.
block parameter
initrans: Block header에 있는 transaction layer에 transaction slot의 수, 미리 생성한 transaction slot 수, 만약에 initrans 값이 5로 되어 있다면 미리 5개가 생성된다.(1개당 23byte)maxtrans: 데이터가 저장되어 있는 공간에 free 공간이 있으면 데이터저장공간에 transaction slot을 생성할 수 있는 최대수, 10g 부터는 고정되는 값으로 변경 255개pctfree: 처음 이 블록에 데이터가 저장될때 pctfree값을 제외시키고 입력한다.- 블록의 free공간을 미리 만들어 놓는 파라미터
- 첫번째 이유
- 기존 행의 값들의 증가분 때문에 free 공간을 미리 남겨놓은 영역
만약 free 공간이 없으면 기존 행이 다른 블록으로 이전을 한 후 증가하는데, 이때가 row migration이 발생할때 이다.row migration의 문제점은 블록 I/O가 많이 발생한다. 행이 새로운 블록으로 이전이 되었지만 rowid는 이전 블록으로 가리키기 때문에 이전 블락을 i/o 후 새로운 블록을 i/o하기 때문에 이중 i/o가 발생한다. - 사후적으로 해결방법은 table의 reorg 를 해주면 된다.
- 기존 행의 값들의 증가분 때문에 free 공간을 미리 남겨놓은 영역
- 두번째 이유
- maxtrans 값을 보장하기 위해서, 만약에 transaction slot을 생성하지 못하면 트랜잭션을 수행하는 세션에서는 대기해야한다.
enq : TX - allocate ITL entry
- maxtrans 값을 보장하기 위해서, 만약에 transaction slot을 생성하지 못하면 트랜잭션을 수행하는 세션에서는 대기해야한다.
- 파라미터를 설정하여 테이블 생성
create table hr.itl_table(id number, l_name varchar2(1000), f_name varchar2(1000)) initrans 1 maxtrans 2 pctfree 0;
select ini_trans, max_trans, pct_free from dba_tables where owner = 'HR' and table_name = 'ITL_TABLE';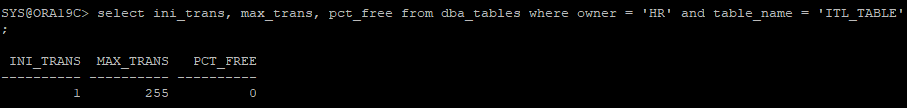
- 1000byte로 컬럼의 데이터값을 꽉 채워서 입력하였다.
insert into hr.itl_table(id,l_name,f_name)
select level, rpad('x',1000,'x'), rpad('z',1000,'z')
from dual
connect by level <= 10;
commit- 통계정보 확인
- 아직 통계 수집을 하지 않아 BLOCKS 와 AVG_ROW_LEN이 비어있다.
select blocks, avg_row_len, ini_trans, max_trans, pct_free from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name='ITL_TABLE';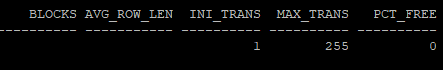
- 통계수집
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','itl_table')- 통계수집 확인
select blocks, avg_row_len, ini_trans, max_trans, pct_free from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name='ITL_TABLE';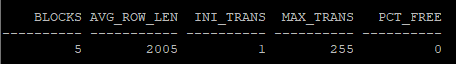
- 같은 block 안에 들어있는 row수 확인
select id, rowid, dbms_rowid.rowid_block_number(rowid) block_no
from hr.itl_table
order by 3;
<<session 1>>
update hr.itl_table
set l_name = rpad('y',1000,'y'), f_name = rpad('a',1000,'a')
where id = 1;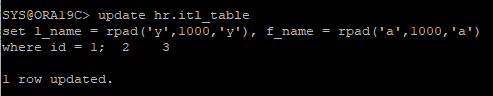
- transaction layer의 initrans를 잡고 transaction 작업을 하기 때문에 dml작업이 가능하다.
<<session 2>>
update hr.itl_table
set l_name = rpad('y',1000,'y'), f_name = rpad('a',1000,'a')
where id = 2;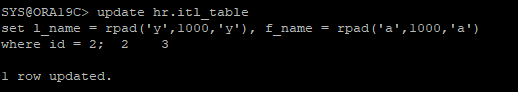
- 데이터저장공간의 free 공간에서 maxtrans를 잡았기 때문에 transaction 작업이 가능했다.
<<session 3>>
update hr.itl_table
set l_name = rpad('y',1000,'y'), f_name = rpad('a',1000,'a')
where id = 3;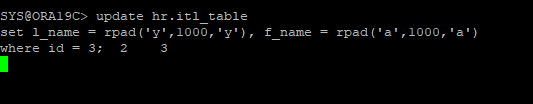
- transaction slot을 잡지 못해서 대기하고 있다.
<<sys session>>
- enq : TX - allocate ITL entry wait event 확인
select sid, serial#, username, blocking_session, event, sql_id, prev_sql_id
from v$session
where event like '%TX%';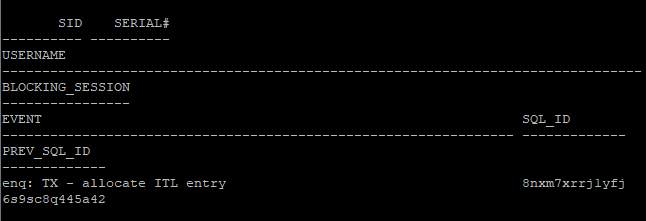
- prev_sql_id를 이용해서 lock이 걸려있는 쿼리문 확인
select sql_text from v$sql where sql_id = '8nxm7xrrj1yfj'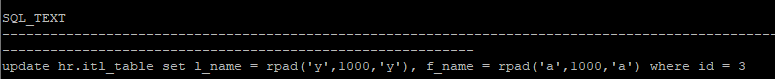
- lock을 일으키고 있는 prev_sql_id 값 확인
select sid, serial#, username, sql_id, prev_sql_id
from v\$session
where sid in (select blocking_session from v$session);
- 어떤 문장이 lock을 발생하고 있는지 확인
select sql_text from v$sql where sql_id = '3r949qb90g5pn'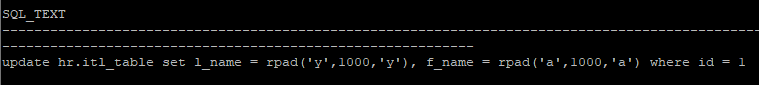
- ITL 부족에 의한 경합이 발생한 정보 확인
select * from v$segment_statistics where owner='HR' and statistic_name='ITL waits';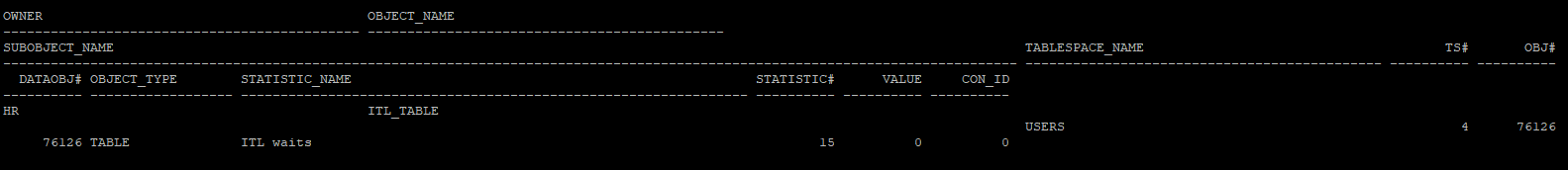
- 해결방법
- 3번째 세션이 lock이 걸린 이유는 1번째 세션이 ini trans를 가지고 있기 때문에 생긴 lock이기 때문에 1번째 세션에서 transaction 작업을 마무리 해야 lock이 해제된다.
enq: TX - allocate ITL entry 해결방안 ?
- block parameter 확인
select blocks, avg_row_len, ini_trans, max_trans, pct_free from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name='ITL_TABLE';
- initrans, pctfree 값 수정
- block parameter를 변경하였어도 이미 만들어진 block은 이전 값을 가지고 있다.
- 새로 만들어지는 block부터 적용된다.
- 기존 block도 새로운 block parameter 값으로 사용하려면 테이블을 재구성해야한다.
alter table hr.itl_table initrans 2 pctfree 10;- 수정된 값 확인
select blocks, avg_row_len, ini_trans, max_trans, pct_free from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name='ITL_TABLE';
- 재배치 시작
- 테이블을 move 하게 되면 그 테이블과 연관있는 index도 재구성해야한다.
alter index 인덱스이름 rebuild online;
alter table hr.itl_table move;- 통계수집
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','itl_table')- pct free 값 때문에 기존의 block 보다 더 많은 block를 사용하고 있다.
select blocks, avg_row_len, ini_trans, max_trans, pct_free from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name='ITL_TABLE';
- 같은 block 안에 들어있는 row수 확인
- 테이블을 재구성 하면 row id는 변경된다.
select id, rowid, dbms_rowid.rowid_block_number(rowid) block_no
from hr.itl_table
order by 3;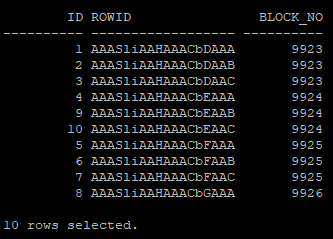
- 결과적으로 늘어난 ini trans 값과 pct free 공간으로 enq: TX - allocate ITL entry 이벤트는 발생되지 않는다.
