SQL Tuning
- SQL 튜닝은 SQL문을 최적화하여 빠른 시간내에 원하는 결과값을 얻기 위한 작업이다.
데이터 처리 결정
full table scan
- 많은 양의 데이터 검색시 유용하다.
- 첫번째 블록 부터 마지막 블록(High Water Mark)까지 읽어 오는 방식
- Multi Block I/O (EXTENT 안의 BLOCK의 개수 만큼 I/O 종속)
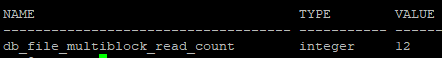
- 한번의 I/O CALL 발생할때 db_file_multiblock_read_count 파라미터가 설정되어 있는 블록 수를 최대값으로 설정. extent 안에 db_file_multiblock_read_count 설정되어 있는 갯수 만큼 있을 경우에 나름 Multi Block I/O 성능을 좋게 할 수 있다.
db file scattered read이벤트가 발생한다.- full table scan으로 인해 과도한 multiblock I/O 시에 발생하는 wait event
- SQL문을 실제 수행하지 않고 실행계획 출력
set autot traceonly exp
- 실행계획 출력 끄기
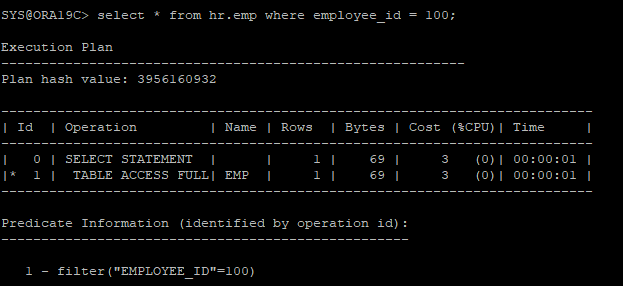
set autot offselect * from hr.emp where employee_id = 100;
- filter 검색을 하는건 해당 row를 찾기 위해 full table scan을 하는거다
- full table scan 속도를 개선
1.db_file_multiblock_read_count 파라미터의 값을 조정
alter session set db_file_multiblock_read_count=128;
2.병렬작업(parallel 힌트 사용)
select /*+ full(e) parallel(e,2) */ * from hr.emp e;- 프로세스 2개(deree 값)를 띄어서 병렬처리 하는데 사용한다.
rowid scan
-
by user rowid,by index rowid를 이용하여 소량의 데이터 검색시 유용하다. -
single block I/O 발생
-
db file sequential read이벤트가 발생한다. -
rowid에서 값 추출
select
employee_id,
rowid,
dbms_rowid.rowid_object(rowid) as data_object_id,
dbms_rowid.rowid_relative_fno(rowid) as file_no,
dbms_rowid.rowid_block_number(rowid) as block_no,
dbms_rowid.rowid_row_number(rowid) as row_clot_no
from hr.emp
where employee_id = 100;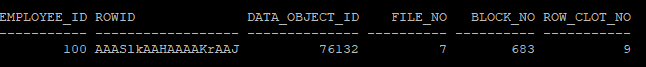
- by user rowid scan
select * from hr.emp where rowid = 'AAASlkAAHAAAAKrAAJ';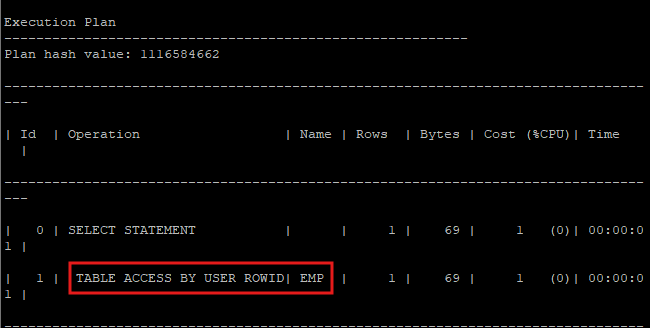
INDEX
- 인덱스는 대용량 테이블에서 필요한 데이터만 빠르고 효율적으로 액세스할 목적으로 사용하는 오브젝트이다.
1. index range scan
- 인덱스 root block -> brach block -> leaf block 까지 수직으로 탐색한 후 leaf block에서 필요한 범위만 스캔하는 방식(one plus on scan)
- 데이터블록 i/o 이후에도 unique scan이 아니기 때문에 최소 1번은 더 leaf block을 I/O 해야한다.
- 인덱스 생성
create index hr.emp_idx on hr.emp(employee_id);- 인덱스 정보 확인
select ix.index_name, ix.uniqueness, ic.column_name
from dba_indexes ix, dba_ind_columns ic
where ix.index_name = ic.index_name
and ix.table_name = 'EMP'
and ix.owner='HR';
- 실행계획 확인
set autot traceonly exp
select * from hr.emp where employee_id =100;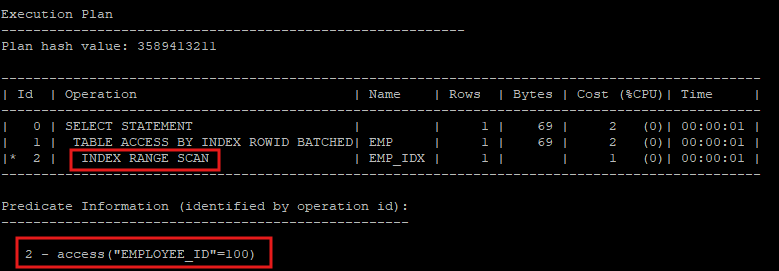
- access : 찾으려는 row가 어느 block에 있는지 알고 찾아가는 방식
- index range scan : row를 찾아 active set 결과를 만들었어도 다시 leaf block을 스캔해야 한다.
nonunique이기 때문이다.
- hint를 사용해서 의도적으로 full table scan을 유도
select /*+ full(e) */ * from hr.emp e where employee_id=100;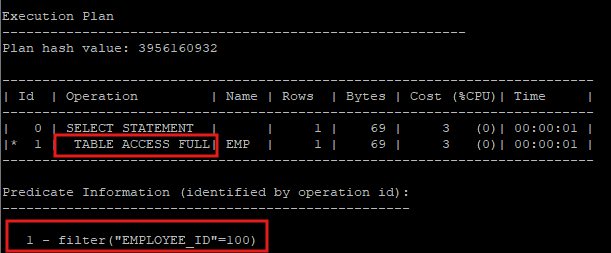
- 컬럼의 형변환을 해도 full table scan을 하게 된다.
select * from hr.emp where to_number(employee_id)=100;
- hint로 index scan 유도
- 해당 인덱스가 unique index 이면 index unique scan을 하게 된다.
- 해당 인덱스가 nonunique index 이면 index range scan을 하게 된다.
select /*+ index(e emp_idx) */ * from hr.emp e where employee_id = 100;
- hint를 사용하여 의도적으로 index range scan을 유도
select /*+ index_rs(e emp_idx) */ * from hr.emp e where employee_id = 100;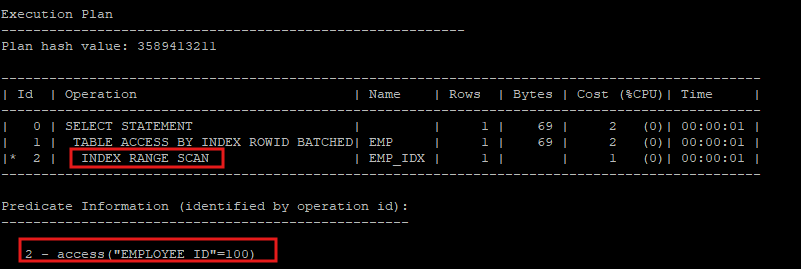
2. index unique scan
- 컬럼에 유일한 값으로 인덱스가 생성된 경우 사용된다.
- 비교연산자는 = 사용할때만 사용된다.
- unique index가 생성되어 있더라도 범위스캔을 수행할 경우 index range scan으로 수행된다.
- unique index 먼저 생성
create unique index hr.emp_idx on hr.emp(employee_id);- 인덱스 이름과 제약조건을 이름을 다르게 해야할 경우 인덱스를 먼저 생성 후 제약조건을 후에 생성한다. using index 절 이용
alter table hr.emp add constraint emp_id_pk primary key(employee_id) using index hr.emp_idx;- 인덱스 정보 확인
select ix.index_name, ix.uniqueness, ic.column_name
from dba_indexes ix, dba_ind_columns ic
where ix.index_name = ic.index_name
and ix.table_name = 'EMP'
and ix.owner='HR';
- 제약조건 확인
select c.column_name, u.constraint_name, u.constraint_type, u.search_condition, u.index_name
from dba_constraints u, dba_cons_columns c
where u.constraint_name = c.constraint_name
and u.table_name='EMP';
- 실행계획 확인
select * from hr.emp where employee_id = 100;'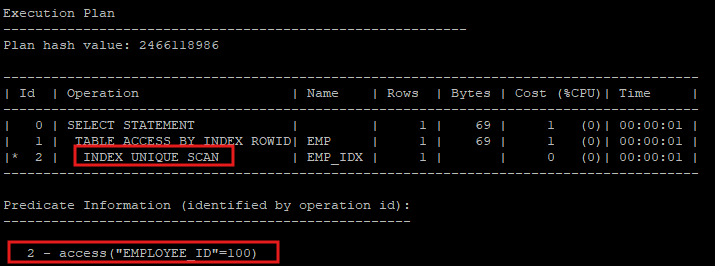
- unique index로 생성되었기 때문에 index unique scan 하고있다.
- 범위스캔 할 경우 실행계획 확인
select * from hr.emp where employee_id between 100 and 101;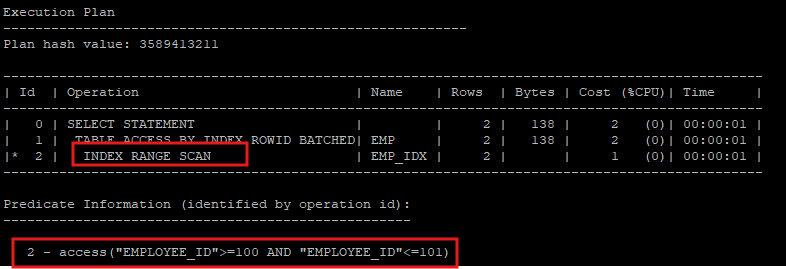
- 컬럼이 unique index로 설정되어 있어도 범위 스캔을할 경우 index range scan으로 실행계획이 만들어 진다.
- hint로 index scan 유도
- 해당 인덱스가 unique index이기 때문에 index unique scan을 하게 된다.
select /*+ index(e emp_idx) */ * from hr.emp e where employee_id = 100;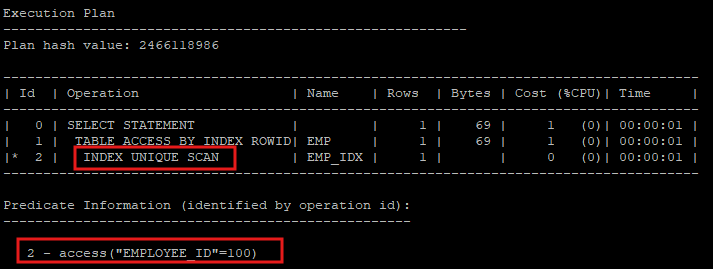
- hint를 사용하여 의도적으로 index range scan을 유도하려고 하였지만 오라클은 unique index 설정이 되어있는데 굳이 range scan을 하려고 하지 않는다.
select /*+ index_rs(e emp_idx) */ * from hr.emp e where employee_id = 100;
3. inlist iterator
- 실행계획을 보게되면 INLIST ITERATOR으로 실행계획이 만들어진다.
select * from hr.emp where employee_id in (100,200);
select * from hr.emp where employee_id = 100 or employee_id = 200;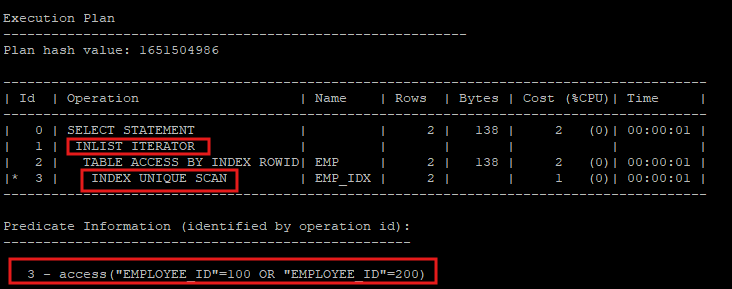
- index range scan으로 풀게 되면 100이 있는 leaf block에서 200이 있는 leaf block까지 전부 scan을 해야하지만 inlist iterator 방식은 필요한 row가 있는 leaf block으로 root - branch - leaf 로 찾아가게 된다.
- inlist iterator 방식은 내부적으로는 union all을 사용한 해당 쿼리문으로 실행된다.
select * from hr.emp where employee_id = 100
union all
select * from hr.emp where employee_id = 200;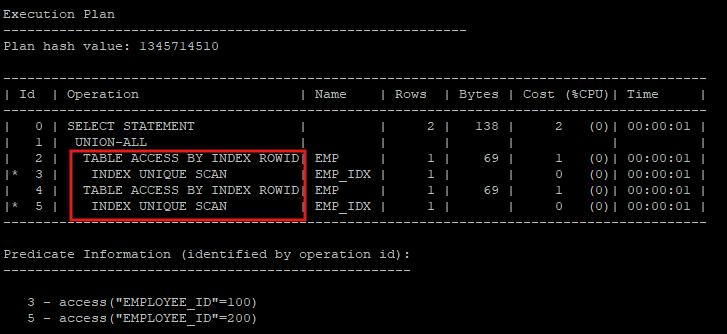
4. 조합 인덱스
- where 조건절에 자주 사용되는 컬럼들을 하나의 인덱스로 생성
- 선행컬럼을 잘 만들어야 한다.
- 선행컬럼 기준
1) 혼자서도 자주 사용되는 컬럼을 선행컬럼으로 설정
2) 검색 범위를 줄일수 있는 컬럼을 선행컬럼으로 설정
3) = 비교연산자를 사용하는 컬럼을 선행컬럼으로 설정
- 선행컬럼 기준
- 조합 인덱스를 사용하지 않고 각 컬럼별 인덱스를 만들게 될 경우 후에 같은 rowid 가지고 merge 해야하는 과정을 거쳐야 하기 때문에 성능상 좋지 않다.
조합 인덱스를 사용하지 않았을때 문제
- 새로운 nonunique index 생성
create index hr.emp_name_idx on hr.emp(last_name);select ix.index_name, ix.uniqueness, ic.column_name
from dba_indexes ix, dba_ind_columns ic
where ix.index_name = ic.index_name
and ix.table_name = 'EMP'
and ix.owner='HR';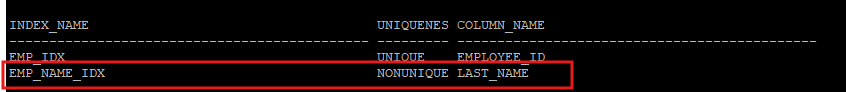
- 실행계획 확인
select * from hr.emp where last_name='King';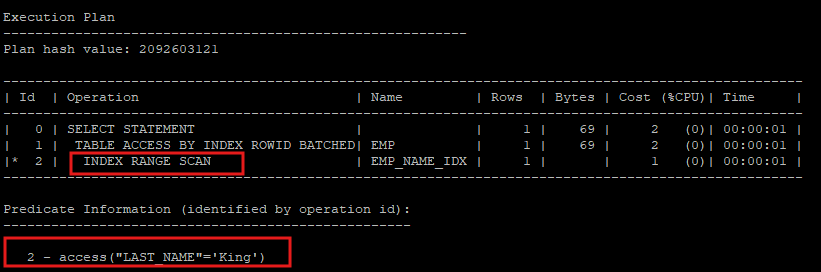
- last_name은 nonunique index가 설정되어 있고, first_name은 인덱스가 설정되어 있지 않다.
- access 술어랑 filter 술어가 같이 있으면 성능상 문제가 있을 수도 있다.
- access 술어로 찾은 row가 filter 술어로 찾는 값인지 확인해야 하는데 이 과정에서 불필요한 I/O가 발생할 수도 있다.
select * from hr.emp where last_name='King' and first_name = 'Steven';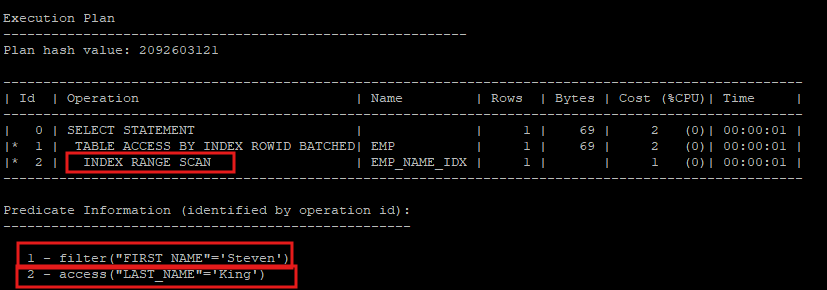
조합 인덱스를 이용한 문제해결
- 이전 인덱스 삭제
drop index hr.emp_name_idx;- 조합 인덱스 생성
create index hr.emp_name_idx on hr.emp(last_name, first_name);- 인덱스 정보 확인
select ix.index_name, ix.uniqueness, ic.column_name
from dba_indexes ix, dba_ind_columns ic
where ix.index_name = ic.index_name
and ix.table_name = 'EMP'
and ix.owner='HR';
- 조합 인덱스를 이용하기 때문에 access 술어만 이용한다.
select * from hr.emp where last_name='King' and first_name = 'Steven';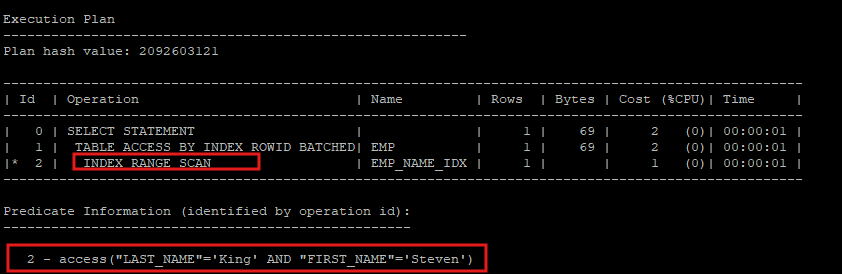
- 선행 컬럼인 last_name 만 가지고 검색할때는 문제 없이 index range scan을 한다.
select * from hr.emp where last_name='King';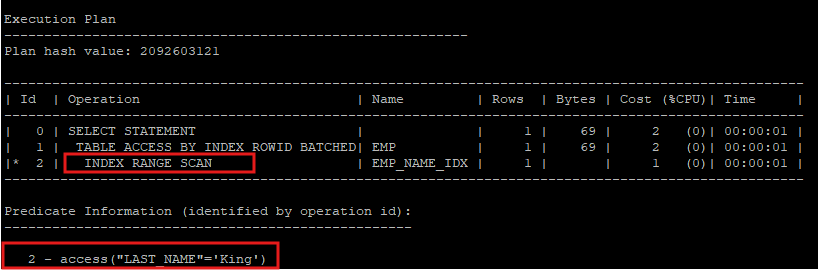
- 후행 컬럼인 first_name 만 가지고 검색 할때는 index skip scan을 하게 되는데 이 scan은 선행 컬럼을 다 확인하면서 후행컬럼을 검색 하기 때문에 I/O가 좋지 않다.
select * from hr.emp where first_name = 'Steven';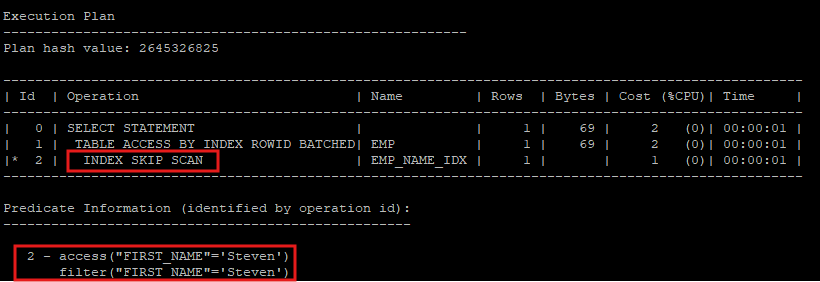
5. index skip scan
- 8i 버전까지는 조합인덱스의 후행컬럼만 사용할 경우 인덱스 스캔이 아닌 full table scan으로 실행계획이 만들어진다.
- 9i 버전에 새로나온 인덱스 스캔 기법
- skip scan 기법이 수행되려면 선행컬럼의 값이 distinct value 개수가 적고 후행컬럼의 distinct value 개수가 많을때 유용하다.
| 선행컬럼 | 후행컬럼 |
|---|---|
| A | steven |
| A | lisa |
| B | nana |
| B | oracle |
| C | koko |
| C | biba |
- hint를 사용해 의도적으로 index skip scan을 유도
select /*+ index_ss(e emp_name_idx) */ * from hr.emp e where first_name='Steven';
- hint를 사용해 index skip scan으로 실행계획을 만들지 말고 index full scan을 유도
select /*+ no_index_ss(e emp_name_idx) */ * from hr.emp e where first_name='Steven';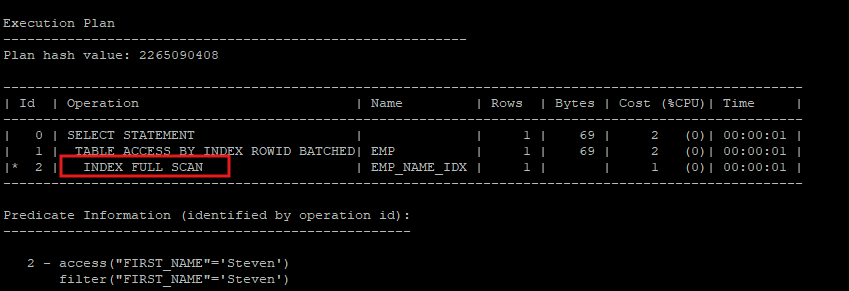
6. index full scan
- 첫번째 leaf block 부터 마지막 leaf block 까지 전부 탐색
- 실제 테이블을 access 하지는 않는다.
- 하지만 index scan이기 때문에 결국에는 single block i/o를 수행하는데 정렬이 필요 없이 한번에 많은 leaf block을 메모리에 올려야 하는경우에는 부적절 하다.
select last_name, first_name from hr.emp;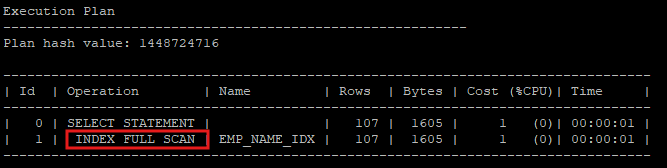
- 건수를 셀대도 index full scan을 이용하는데 이때 index는 2가지중 한개를 사용하게 된다. not null제약조건이 있는 index 또는 primary key 제약조건이 있는 index를 사용한다.
- 하지만 건수를 세는데 굳이 leaf block 들을 정렬하면서 single block i/o를 하는건 불필요 하다.
select count(*) from hr.emp;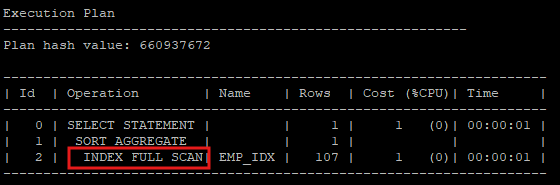
7. index fast full scan
- hint를 사용해 index fast full scan 을 유도
- 건수를 세는데 정렬은 굳이 필요 없고 single block i/o보다 multi block i/o 가 성능상 유리하기 때문에 index fast full scan이 좋다.
select /*+ index_ffs(e emp_idx) */ count(*) from hr.emp e;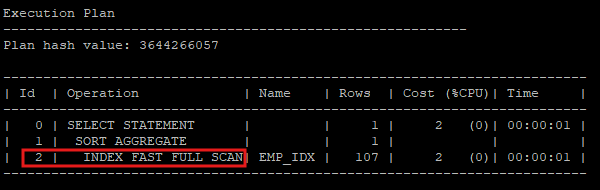
index full scan 과 index fast full scan의 차이
index full scan
- single block i/o 발생
- 속도 느리다.
- db file sequential read
- 정렬보장
index fast full scan
- multi block i/o 발생
- 속도 빠르다.
- db file scatterd read
- 정렬이 보장되지 않는다.
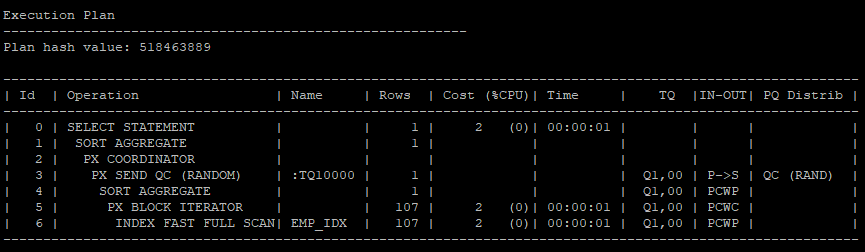
index fast full scan을 더 빠른 결과집합을 만들기 위해서
- multi block i/o의 수를 많이 설정
alter session set db_file_multiblock_read_count = 128; - 병렬 처리를 수행하면 속도가 빠르다.
- 병렬처리는 multi block i/o 하고만 같이 사용할 수 있다.
select /*+ index_ffs(e emp_idx) parallel_index(e,emp_idx,2) */ count(*) from hr.emp e;
OPTIMIZER
- 사용자가 요청한 SQL을 가장 효율적이고 빠르게 수행할 수 있는 최저 비용의 처리경로를 선택해주는 엔진
explain plan
- optimizer 가 SQL문 실행에 사용하는 실행계획을 생성
- plan_table 저장
- 실제 SQL문은 실행하지 않는다.
- plan_table은 synonym 객체이다.
- 10g 부터는 DB생성시 기본적으로 SYS.PLAN_TABLE$ 테이블이 만들어진다.
select * from all_synonyms where synonym_name = 'PLAN_TABLE';
- 실행계획을 plan_table 딕셔너리에 저장
explain plan for
select * from hr.emp where employee_id = 100;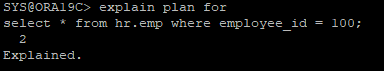
- plan_table 딕셔너리에 있는 실행계획을 basic 모드로 보게 되면 심플하게 보여줌
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display(null,null,'basic'));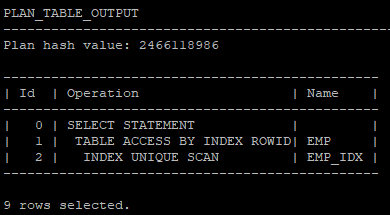
- typical모드로 보게 되면 더 자세한 실행계획을 보여줌
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display(null,null,'typical'));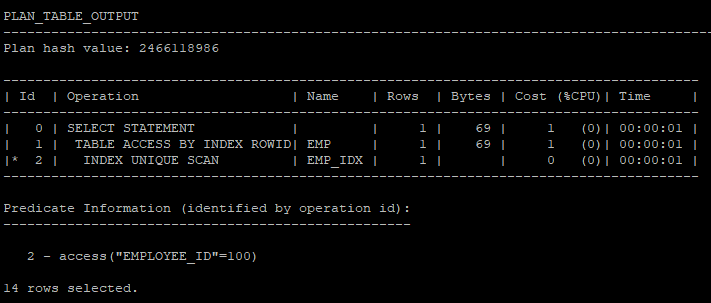
실행계획 컬럼 정보
Id : 각 Operation 번호, id에 * 있는경우 Predicate Information에 access, filter에 관한 정보
Operation : 실행되는 job
Name : Operation이 액세스하는 테이블, 인덱스
Rows : 각 Operation이 끝났을때 return되는 행수(예상치)
Bytes : 각 Operation이 수행했을때 byte값(예상치)
Cost (%CPU) : 각 Operation의 cost, 누적치(예상치)
Time : 각 Operation의 수행시간, 누적치(예상치)
access predicate : 실제 블록을 읽기전에 어떤 방법으로 블록을 읽을 것인가를 결정(찾고자 하는 행이 있는 블록의 위치를 알고 있을때, 보편적으로 rowid scan을 수행할 경우)
filter predicate : 실제 블록을 읽은 후에 데이터를 걸러내기 위해 사용된다. (찾고자 하는 행이 어느 블록에 있는지 위치를 모를때)- 내가 임의로 문장아이디를 설정해서 실행계획을 만들 수 있다.
explain plan set statement_id = 'demo1' for
select * from hr.emp where employee_id = 100;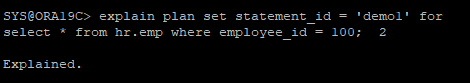
- 실행계획 확인
dbms_xplan.dislay(plan table,문장아이디,조회모드)
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display('plan_table','demo1','typical'));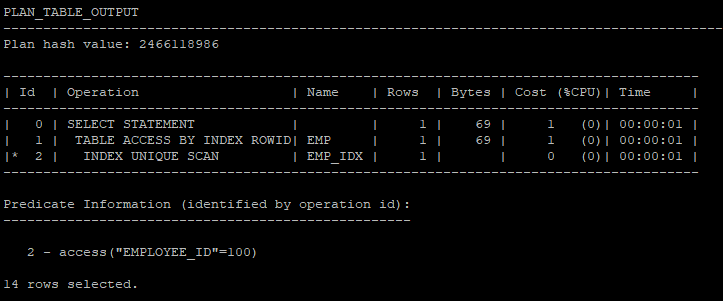
- query block(가상집합)을 만들어서 실행계획을 만든다.
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display('plan_table','demo1','all'));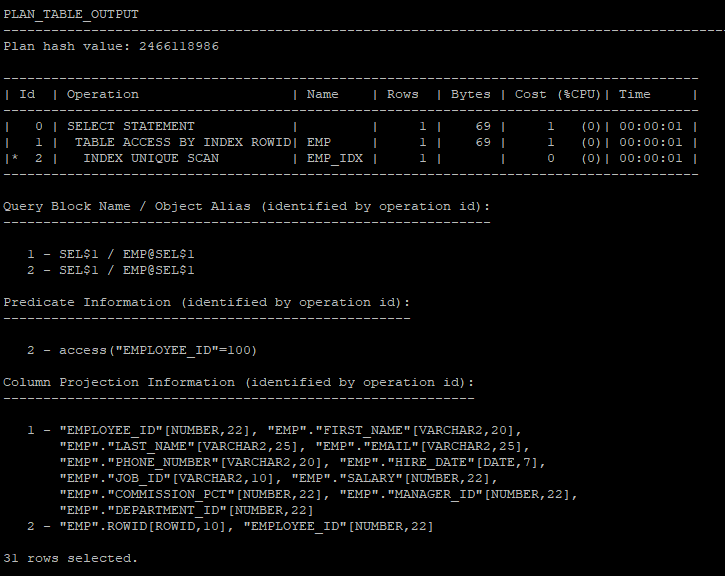
- 옵티마이저가 실행계획을 만들때 사용한 hint 확인할수 있는 실행계획 조회
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display('plan_table','demo1','outline'));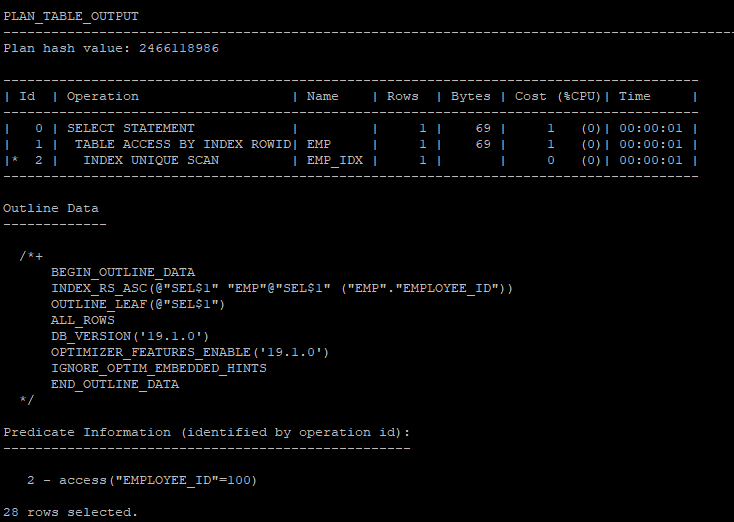
- outline하고 all하고 합쳐진 실행계획을 조회
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display('plan_table','demo1','advanced'));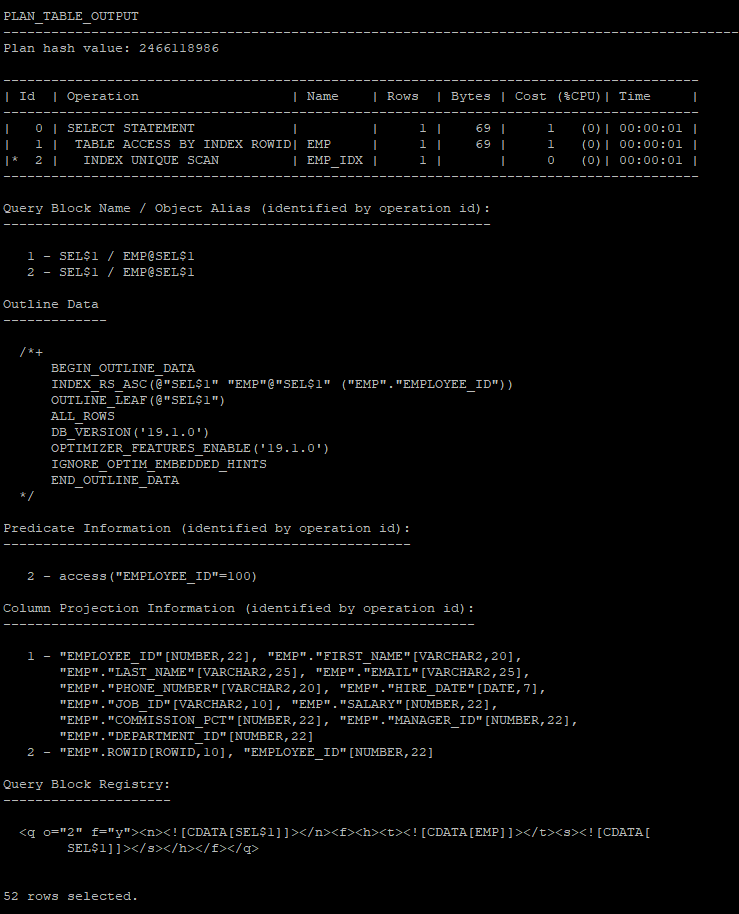
- advanced 에서 outline은 빼고 실행계획 하고 싶을때
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display('plan_table','demo1','advanced -outline'));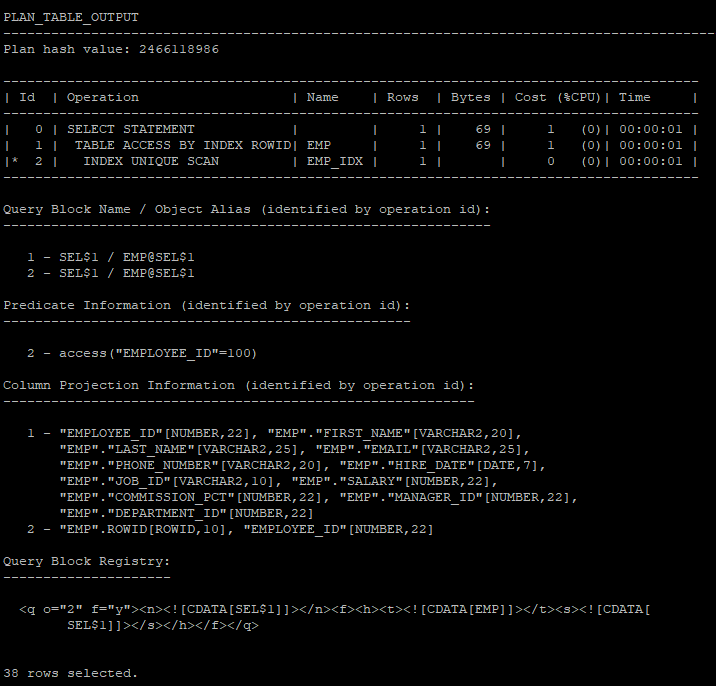
autotrace
- SQL*PLUS, SQL DEVELOPER 기능
- PLAN_TABLE, PLUSTRACE ROLE 필요(통계정보를 액세스)
- SQL문 실행 후 실행계획 및 실행결과, 실행 통계정보를 출력
- PLUSTRACE ROLE 생성
스크립트 실행
@$ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/plustrce.sql
- 딕셔너리 뷰에 select 할 수있는 권한을 role에 부여하고 있다.
<<sys session>>
grant plustrace to hr;<<hr session>>
select * from session_roles;
- SQL문 실제 수행하고 결과와 함께 실행계획, 실행통계 정보 출력
set autotrace on
select * from hr.emp where employee_id = 100;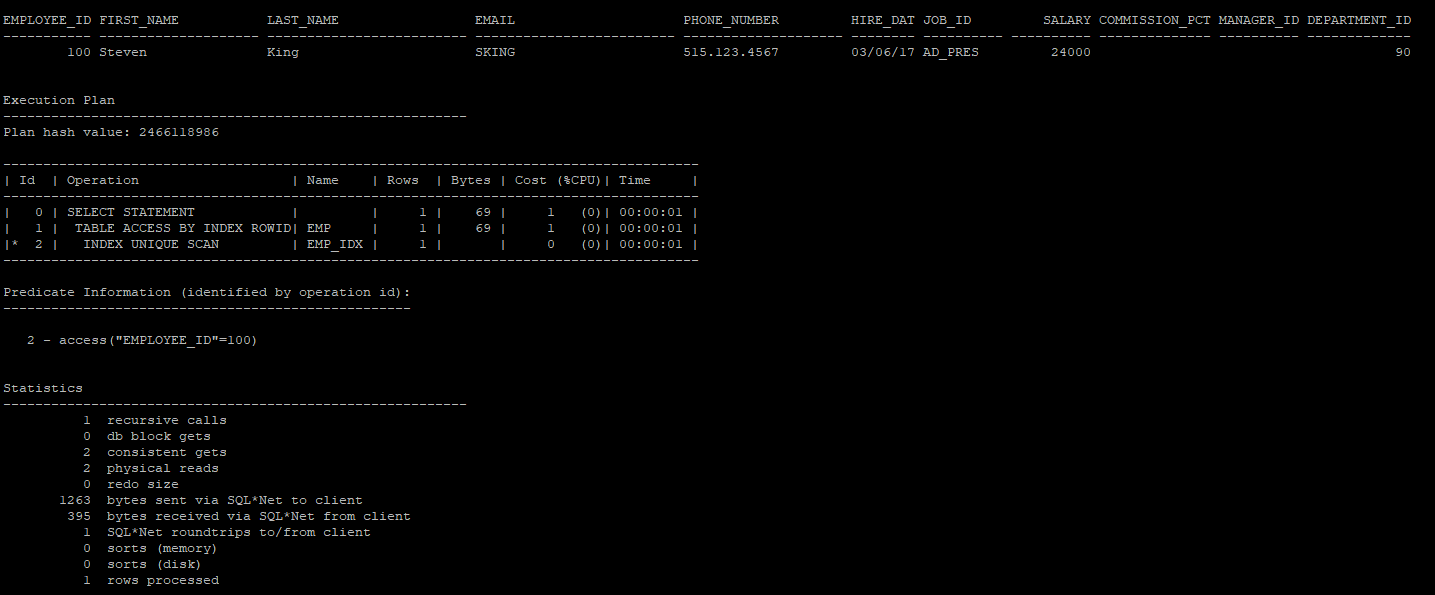
실행통계 정보
recursive calls : 유저레벨과 시스템 레벨에서 생성되는 재귀호출의 수
db block gets : DML 작업시에 체크, current한 블록이 요청된 회수를 나타낸다. 메모리에서 access한 블록의 수
consistent gets : SELECT 작업시에 체크, 블록에 대해 일관성 읽기가 요청된 횟수를 나타낸다. 메모리에서 access한 블록의 수, physical reads 수를 포함한다.
physical reads : 디스크에서 읽은 데이터 블록의 수
redo size : DML작업시 사용한 리두 사이즈(byte)
bytes sent via SQL*Net to client : 클라이언트로 보낸 총 바이트값
bytes received via SQL*Net from client : 클라이언트로 받은 바이트값
SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client : 클라이언트와 주고 받은 오라클 NET 메시지 수
sorts (memory) : 메모리에서 수행되어 디스크 쓰기가 필요하지 않은 정렬작업의 수
sorts (disk) : 최소한 하나의 디스크 쓰기가 필요한 정렬 작업의 수
rows processed : 처리된 행의 수